Abstract
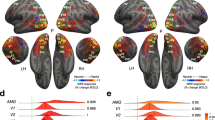
High and low spatial frequency information in visual images is processed by distinct neural channels. Using event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in humans, we show dissociable roles of such visual channels for processing faces and emotional fearful expressions. Neural responses in fusiform cortex, and effects of repeating the same face identity upon fusiform activity, were greater with intact or high-spatial-frequency face stimuli than with low-frequency faces, regardless of emotional expression. In contrast, amygdala responses to fearful expressions were greater for intact or low-frequency faces than for high-frequency faces. An activation of pulvinar and superior colliculus by fearful expressions occurred specifically with low-frequency faces, suggesting that these subcortical pathways may provide coarse fear-related inputs to the amygdala.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeDoux, J.E. The Emotional Brain (Simon & Schuster, New York, 1996).
Morris, J., Öhman, A. & Dolan, R.J. Conscious and unconscious emotional learning in the human amygdala. Nature 393, 467–470 (1998).
Whalen, P.J. et al. Masked presentations of emotional facial expressions modulate amygdala activity without explicit knowledge. J. Neurosci. 18, 411–418 (1998).
Vuilleumier, P., Armony, J.L., Driver, J. & Dolan, R.J. Effects of attention and emotion on face processing in the human brain: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron 30, 829–841 (2001).
Morris, J.S., Öhman, A. & Dolan, R.J. A subcortical pathway to the right amygdala mediating 'unseen' fear. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1680–1685 (1999).
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Pourtois, G. & Weiskrantz, L. Non-conscious recognition of affect in the absence of striate cortex. Neuroreport 10, 3759–3763 (1999).
Weiskrantz, L. Blindsight: a Case Study and Implications (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1986).
Morris, J.S., DeGelder, B., Weiskrantz, L. & Dolan, R.J. Differential extrageniculostriate and amygdala responses to presentation of emotional faces in a cortically blind field. Brain 124, 1241–1252 (2001).
Livingstone, M. & Hubel, D. Segregation of form, color, movement and depth: anatomy, physiology and perception. Science 240, 740–749 (1988).
Merigan, W.H. & Maunsell, J.H. How parallel are the primate visual pathways? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 16, 369–402 (1993).
Schiller, P.H., Malpeli, J.G. & Schein, S.J. Composition of geniculostriate input to superior colliculus of the rhesus monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 42, 1124–1133 (1979).
Leventhal, A.G., Rodieck, R.W. & Dreher, B. Central projections of cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 237, 216–226 (1985).
Berson, D.M. Retinal and cortical inputs to cat superior colliculus: composition, convergence and laminar specificity. Prog. Brain Res. 75, 17–26 (1988).
Sergent, J. Influence of task and input factors on hemispheric involvement in face processing. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 11, 846–861 (1985).
Costen, N.P., Parker, D.M. & Craw, I. Effects of high-pass and low-pass spatial filtering on face identification. Percept. Psychophys. 58, 602–612 (1996).
Schyns, P.G. & Oliva, A. Dr. Angry and Mr. Smile: when categorization flexibly modifies the perception of faces in rapid visual presentations. Cognition 69, 243–265 (1999).
Nasanen, R. Spatial frequency bandwidth used in the recognition of facial images. Vision Res. 39, 3824–3833 (1999).
Liu, C.H., Collin, C.A., Rainville, S.J. & Chaudhuri, A. The effects of spatial frequency overlap on face recognition. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 26, 956–979 (2000).
Calder, A.J., Young, A.W., Keane, J. & Dean, M. Configural information in facial expression perception. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 26, 527–551 (2000).
Tieger, T. & Ganz, L. Recognition of faces in the presence of two-dimensional sinusoidal masks. Percept. Psychophys. 26, 163–167 (1979).
Fiorentini, A., Maffei, L. & Sandini, G. The role of high spatial frequencies in face perception. Perception 12, 195–201 (1983).
Hayes, T., Morrone, M.C. & Burr, D.C. Recognition of positive and negative bandpass-filtered images. Perception 15, 595–602 (1986).
Norman, J. & Ehrlich, S. Spatial frequency filtering and target identification. Vision Res. 27, 87–96 (1987).
Goshen-Gottstein, Y. & Ganel, T. Repetition priming for familiar and unfamiliar faces in a sex-judgment task: evidence for a common route for the processing of sex and identity. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 26, 1198–1214 (2000).
Kanwisher, N., McDermott, J. & Chun, M.M. The fusiform face area: a module in human extrastriate cortex specialized for face perception. J. Neurosci. 17, 4302–4311 (1997).
Naccache, L. & Dehaene, S. The priming method: imaging unconscious repetition priming reveals an abstract representation of number in the parietal lobes. Cereb. Cortex 11, 966–974 (2001).
Henson, R., Shallice, T. & Dolan, R.J. Neuroimaging evidence for dissociable forms of repetition priming. Science 287, 1269–1272 (2000).
Burton, A.M., Miller, P., Bruce, V., Hancock, P.J. & Henderson, Z. Human and automatic face recognition: a comparison across image formats. Vision Res. 41, 3185–3195 (2001).
George, N. et al. Contrast polarity and face recognition in the human fusiform gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 574–580 (1999).
Phan, K.L., Wager, T., Taylor, S.F. & Liberzon, I. Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: a meta-analysis of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage 16, 331–348 (2002).
Robinson, D.L. & Petersen, S.E. The pulvinar and visual salience. Trends Neurosci. 15, 127–132 (1992).
Morris, J.S. et al. A neuromodulatory role for the human amygdala in processing emotional facial expressions. J. Comp. Neurol. 394, 91–105 (1998).
Bruce, V. et al. Recognising facial surfaces. Perception 20, 755–769 (1991).
Hill, H., Schyns, P.G. & Akamatsu, S. Information and viewpoint dependence in face recognition. Cognition 62, 201–222 (1997).
Haxby, J.V., Hoffman, E.A. & Gobbini, M.I. The distributed human neural system for face perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 4, 223–233 (2000).
Adolphs, R. et al. Recognition of facial emotion in nine individuals with bilateral amygdala damage. Neuropsychologia 37, 1111–1117 (1999).
Hamann, S.B. & Adolphs, R. Normal recognition of emotional similarity between facial expressions following bilateral amygdala damage. Neuropsychologia 37, 1135–1141 (1999).
Harting, J.K., Huerta, M.F., Frankfurter, A.J., Strominger, N.L. & Royce, G.J. Ascending pathways from the monkey superior colliculus: an autoradiographic analysis. J. Comp. Neurol. 192, 853–882 (1980).
Benevento, L.A. & Standage, G.P. The organization of projections of the retinorecipient and nonretinorecipient nuclei of the pretectal complex and layers of the superior colliculus to the lateral pulvinar and medial pulvinar in the macaque monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 217, 307–336 (1983).
O'Brien, B.J., Abel, P.L. & Olavarria, J.F. The retinal input to calbindin-D28k-defined subdivisions in macaque inferior pulvinar. Neurosci. Lett. 312, 145–148 (2001).
Cowey, A., Stoerig, P. & Bannister, M. Retinal ganglion cells labeled from the pulvinar nucleus in macaque monkeys. Neuroscience 61, 691–705 (1994).
Jones, E.G. & Burton, H. A projection from the medial pulvinar to the amygdala in primates. Brain Res. 104, 142–147 (1976).
Linke, R., Braune, G. & Schwegler, H. Differential projection of the posterior paralaminar thalamic nuclei to the amygdaloid complex in the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 134, 520–532 (2000).
Bisti, S. & Sireteanu, R.C. Sensitivity to spatial frequency and contrast of visual cells in the cat superior colliculus. Vision Res. 16, 247–251 (1976).
Lomber, S.G. Learning to see the trees before the forest: reversible deactivation of the superior colliculus during learning of local and global visual features. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4049–4054 (2002).
Sahraie, A., Weiskrantz, L., Trevethan, C.T., Cruce, R. & Murray, A.D. Psychophysical and pupillometric study of spatial channels of visual processing in blindsight. Exp. Brain Res. 143, 249–256 (2002).
Kawasaki, H. et al. Single-neuron responses to emotional visual stimuli recorded in human ventral prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 15–16 (2001).
Eimer, M. & Holmes, A. An ERP study on the time course of emotional face processing. Neuroreport 13, 427–431 (2002).
Kline, D.W. & Fuchs, P. The visibility of symbolic highway signs can be increased among drivers of all ages. Hum. Factors 35, 25–34 (1993).
Johnson, M.H. & Vecera, S.P. Cortical Parcellation and the Development of Face Processing (eds. de Boysson-Bardies, B., de Shoenen, S., Jusczyk, P.W., McNeilage, P. & Morton, J.) (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1993).
Acknowledgements
Supported by Wellcome Programme grants (R.J.D. and J.D.), an MRC (UK) cooperative grant at University College London and a Swiss National Science Foundation grant (P.V.). J.D. holds a Royal Society-Wolfson Research Merit Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuilleumier, P., Armony, J., Driver, J. et al. Distinct spatial frequency sensitivities for processing faces and emotional expressions. Nat Neurosci 6, 624–631 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1057
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1057
This article is cited by
-
Frequency disentangled residual network
Multimedia Systems (2024)
-
Non-conscious processing of fear faces: a function of the implicit self-concept of anxiety
BMC Neuroscience (2023)
-
Analysis of convolutional neural networks reveals the computational properties essential for subcortical processing of facial expression
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Potentiated early neural responses to fearful faces are not driven by specific face parts
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Attentional capture in emotion comparison is orientation independent
Psychological Research (2023)