Abstract
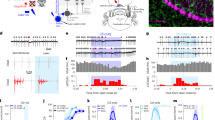
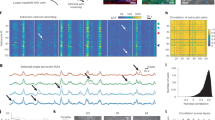
The amygdala is important in emotion, but it remains unknown whether it is specialized for certain stimulus categories. We analyzed responses recorded from 489 single neurons in the amygdalae of 41 neurosurgical patients and found a categorical selectivity for pictures of animals in the right amygdala. This selectivity appeared to be independent of emotional valence or arousal and may reflect the importance that animals held throughout our evolutionary past.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phelps, E.A. & LeDoux, J.E. Neuron 48, 175–187 (2005).
Murray, E.A. Trends Cogn. Sci. 11, 489–497 (2007).
Herry, C. et al. J. Neurosci. 27, 5958–5966 (2007).
Leonard, C.M., Rolls, E.T., Wilson, F.A. & Baylis, G.C. Behav. Brain Res. 15, 159–176 (1985).
Gothard, K.M., Battaglia, F.P., Erickson, C.A., Spitler, K.M. & Amaral, D.G. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 1671–1683 (2007).
Nishijo, H., Ono, T. & Nishino, H. J. Neurosci. 8, 3570–3583 (1988).
Paton, J.J., Belova, M.A., Morrison, S.E. & Salzman, C.D. Nature 439, 865–870 (2006).
Kreiman, G., Koch, C. & Fried, I. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 946–953 (2000).
Whalen, P. & Phelps, E.A. The Human Amygdala (Oxford University Press, New York, 2009).
Mormann, F. et al. J. Neurosci. 28, 8865–8872 (2008).
Kriegeskorte, N. et al. Neuron 60, 1126–1141 (2008).
Pessoa, L. & Adolphs, R. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 773–783 (2010).
Bar, M. & Neta, M. Neuropsychologia 45, 2191–2200 (2007).
New, J., Cosmides, L. & Tooby, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16598–16603 (2007).
Vallortigara, G. & Rogers, L.J. Behav. Brain Sci. 28, 575–589 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank all of our subjects for their participation, E. Behnke, T. Fields, E. Ho, V. Isiaka, E. Isham, K. Laird, N. Parikshak and A. Postolova for technical assistance with the electrophysiological recordings, and D. Tsao, I. Riedel-Kruse, U. Rutishauser and K. Fliessbach for useful discussion and comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by grants from the European Commission (Marie Curie OIF 040445, to F.M.), World Class University program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R31-10008, to C.K.), the US National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the G. Harold and Leila Y. Mathers Foundation, the Gimbel Discovery Fund, and the Dana Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.M., S.K., R.Q.Q., I.F. and C.K. designed the electrophysiology study. I.F. carried out all of the neurosurgical procedures. F.M., M.C., M.I., R.Q.Q., A.K. and I.F. collected the electrophysiological data, and S.K. and F.M. analyzed the electrophysiological data. F.M., N.T., M.M., C.K. and R.A. designed the fMRI control experiment, F.M., M.M., J.D. and N.T. collected the fMRI data, and J.D. and F.M. analyzed the fMRI data. F.M., R.A. and C.K. wrote the paper. All of the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–12, Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Results, Supplementary Control Analyses and SupSupplementary Discussion (PDF 2944 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mormann, F., Dubois, J., Kornblith, S. et al. A category-specific response to animals in the right human amygdala. Nat Neurosci 14, 1247–1249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2899
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2899
This article is cited by
-
Single-neuron mechanisms of neural adaptation in the human temporal lobe
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Consciousness: a neurosurgical perspective
Acta Neurochirurgica (2023)
-
Codifying Wildness: Wild Behaviour for Improving Human-Robot Interaction
International Journal of Social Robotics (2023)
-
Neurons as will and representation
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2022)
-
The Consciousness of Embodied Cognition, Affordances, and the Brain
Topoi (2020)