Advertisement
-
-
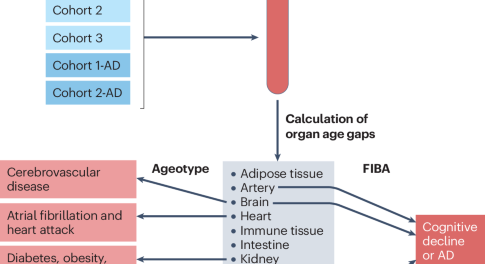
Not every organ ticks the same
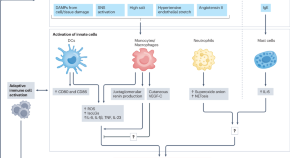
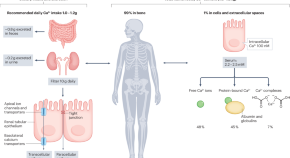
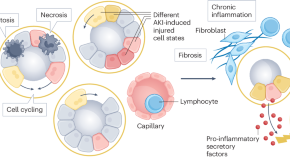
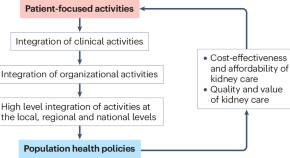
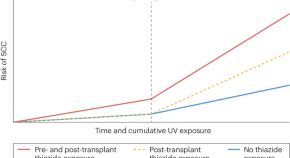
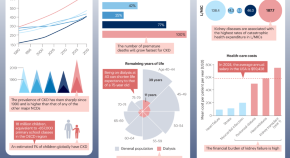
A new study describes the development of proteomics-based ageing clocks that calculate the biological age of specific organs and define features of extreme ageing associated with age-related diseases. Their findings support the notion that plasma proteins can be used to monitor the ageing rates of specific organs and disease progression.
-
-