Abstract
The removal of dying neurons by microglia has a key role during both development and in several diseases. To date, little is known about the cellular and molecular processes underlying neuronal engulfment in the brain. Here we took a live imaging approach to quantify neuronal cell death progression in embryonic zebrafish brains and studied the response of microglia. We show that microglia engulf dying neurons by extending cellular branches that form phagosomes at their tips. At the molecular level we found that microglia lacking the phosphatidylserine receptors BAI1 and TIM-4, are able to recognize the apoptotic targets but display distinct clearance defects. Indeed, BAI1 controls the formation of phagosomes around dying neurons and cargo transport, whereas TIM-4 is required for phagosome stabilization. Using this single-cell resolution approach we established that it is the combined activity of BAI1 and TIM-4 that allows microglia to remove dying neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The vertebrate brain is equipped with specialized phagocytes, called microglia (for review see refs 1, 2). In recent years these cells have been suggested to play important roles both during development and disease. For example, Derecki et al.3 have shown that compromised microglial phagocytosis is responsible for Rett syndrome pathophysiology. Transplantation of wild-type microglia can arrest the disease, unless, microglial phagocytosis is pharmacologically impaired3. Thus, it is of great importance to understand how these cells engulf sick and dying neurons. While there are perhaps differences in the signals that attracted these cells towards the different targets, the molecular and cellular machineries underlying engulfment are likely to be shared. To date, however, nothing is known about factors that allow neuronal engulfment by microglia. Clearance of dying cells is fast and efficient and, for this reason, several studies have proposed an active role for phagocytes in promoting cell death progression. For example, microglia have been suggested to mediate the release of apoptotic checkpoints to couple neuronal cell death and engulfment4. As these studies were conducted in brain slices they might not fully represent the activity of these cells under physiological conditions. Moreover, it can be assumed that also ‘eat-me’ signals are in place to ensure that only dying cells get engulfed. The best studied is phosphatidylserine (PS), a plasma membrane lipid that is ‘flipped-out’ and exposed on the surface of apoptotic cells5,6. Remarkably, many molecules have been shown to act as PS receptors and among these, there are Scavenger Receptors (CD36, SRA-1, etc), αvβ3 integrins, MerTK, TIM-1 and 4, BAI1, and Stabilin1 and 2 (for review see ref. 7). Giving the large number of candidate molecules, it is likely that these may act at different levels, however, to date, distinct roles for these molecules have not been demonstrated in vivo. Indeed, studies in which non-phagocytic cells were transfected with TIM-4 and BAI1 point towards the fact that both receptors might be involved in recognition and target binding8,9.
The zebrafish developing brain is a powerful model system to study microglia and mechanisms of neuronal engulfment, as in the transparent embryonic brain microglia form an easy-to-image cellular network that is composed of only 20–25 large cells10,11,12.
Here by taking a quantitative live imaging approach we have established an in vivo assay to investigate neuronal–microglial interactions at single-cell resolution. In this way we have uncovered the temporal pattern of neuronal apoptosis and the response of microglia to it. We show that these cells engulf apoptotic neurons by extending branches with large phagosomes at their tips. We extended this approach to show that TIM-4 and BAI1, PS receptors expressed on microglia, mediate the removal of dying neurons. In particular, we show that they are dispensable for recognition and that while, BAI1 is involved in the formation and transport of the phagosomes, TIM-4 stabilizes these structures by allowing actin polymerization around them. Thus, it is the combined activity of TIM-4 and BAI1, that allows for the removal of dying neurons by microglia.
Results
Temporal dissection of apoptotic cell clearance by microglia
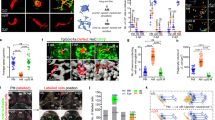
A long-standing question in the field is how microglial cells find and engulf dying neurons. To address this we took a live imaging approach and labelled dying neurons in vivo using Annexin-V, a protein that binds to PS lipids exposed on apoptotic cells13. Generation of stable transgenic lines (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-BFP) in which Annexin-V is fused to a fluorescent marker and secreted within the brain extracellular space allows to follow the process of neuronal cell death in vivo. Single-cell resolution analysis reveals that fluorescent neurons die by fragmenting into a large cell body (Fig. 1n, yellow arrowhead and Supplementary Movie 1) and several small axonal parts (Fig. 1n, white arrowhead and Supplementary Movie 1). We combined this and other apoptotic markers, such as an antibody against activated Caspase-3, and Acridine Orange (AO) that stains condensed chromatin, with a transgenic line in which microglia are fluorescently labelled. This reveals clear differences in the number of Caspase-3 (Fig. 1a–d), PS (Fig. 1e–h) and also AO (Fig. 1i–l) labelled neurons that are not yet engulfed and are found outside microglia in 4-days-old embryos (Fig. 1m). Pair-wise comparisons allowed us to determine the sequence of events that characterizes neuronal cell death. The earliest and most widespread marker is Caspase-3 activation (Fig. 1a–d) and only a subset of Caspase-3-positive neurons is also PS-positive (Supplementary Fig. 1e–g). In the same way, only some PS-positive neurons have condensed chromatin as shown by AO labelling (Fig. 2a). This indicates that the sequence of events that characterizes neuronal apoptosis starts with Caspase-3 activation, followed by PS exposure and finally DNA condensation (AO). By examining earlier time points we found that at day 3 there are significantly more Caspase-3, PS and AO labelled neurons (Supplementary Fig. 1a–d) than at day 4 (Fig. 1a–m). Interestingly however, the ratio between the PS and the AO markers remains constant, indicating that the sequence of events that characterizes apoptosis is conserved throughout development (Supplementary Fig. 1a).
(a–d) Dorsal views of a 4 dpf larval brain; 30 μm stack. (a) Microglia in red (pU1::Gal4-UAS::GFP). (b) Antibody staining against activated Caspase-3 (Act-Casp3, green). (c) Overlay. (e–h) Dorsal views of a 4 dpf larval brain; 80 μm stack. (e) Microglia in red (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP). (f) Phosphatidylserine-positive neurons in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). (g) Overlay. (i–l) Dorsal views of a 4 dpf larval brain; 80 μm stack. (i) Microglia in red (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP). (j) Condensed chromatin visible using Acridine Orange in green. (k) Overlay. (d,h,l) Schematic representations of microglial in red and un-engulfed neurons in white. (m) Number of un-engulfed apoptotic cells that are positive for Activated Caspase-3, phosphatidylserine and Acridine Orange in 4 dpf brain. N, number of embryos tested; bars show mean and the range, with s.d. boxed, ***P<0.0001. P-value determined with one-way analysis of variance. (n) Time course of a wild-type neuron undergoing apoptosis in a NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-BFP transgenic animal. Yellow arrowheads point to the apoptotic cell body and white arrowhead points to the fragmenting axon. Time is indicated in minutes. Scale bars for all images, 40 μm. Images were generated using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
(a) Double staining of PS exposure and chromatin condensation. Neurons exposing PS in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) and condensed chromatin in green (Acridine Orange). White arrowheads point to apoptotic neurons that are positive for PS but negative for AO. The yellow arrowhead points to a neuron that is positive for both markers. Top panel-overlay; middle panel—PS-positive neurons; bottom panel—AO-positive neurons. (b) Number of uncollected apoptotic neurons that are positive for PS (blue bar) and for AO (green bar) in 3.5 dpf brains with (+ microglia) and without microglia (− microglia). Quantification has been achieved by examining a ROI (120 × 120 × 80 μm) as shown in d and e. (c–e) Dorsal views of 3.5 dpf larval brains injected with pU1 morpholino to remove microglia. (c) 30 μm confocal stack showing activated Caspase-3 antibody in red. (d) PS-positive neurons in red (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). 30 μm stack. (e) Acridine Orange-positive neurons in green. 30 μm stack. The dotted line in d and e represents the ROI used for quantification (120 × 120 × 80 μm). Experiments performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective. Scale bar for a, 5 μm; scale bar for c−e, 25 μm. ROI, region of interest.
By using brain organotypic cell cultures it has been proposed that phagocytosis promotes apoptosis, thus providing a mechanism for pairing these two processes4,14. To test for this hypothesis we compared apoptotic markers in brains with and without microglia. If microglia were important for pushing cells through apoptosis we would expect in brains without microglia an increase in one marker without a concomitant conversion to the next in the pathway. To this aim we have injected an antisense morpholino against pU1, a transcription factor that is essential for generating all myeloid cells, including microglia15. In brains without microglia all three markers showed increased occurrence (compare Fig. 1a–l with Fig. 2c–e). In particular, in brains with and without microglia, quantification of PS- and AO-positive neurons showed a 13.5 and 18.78 fold increase, respectively (Fig. 2b). Thus, these in vivo data do not support the idea that microglia influence apoptosis progression during brain development.
Dynamics of apoptotic cell clearance by microglia
In vivo labelling of apoptotic cells by the PS reporter allowed a quantitative analysis of microglial behaviour specifically in response to neuronal cell death. NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-BFP embryos have the same number of Caspase-3 and AO-positive un-engulfed neurons as non-transgenic animals, indicating that engulfment occurs at a normal rate in these embryos (Supplementary Fig. 1h–k). This analysis revealed that phagocytic events take ~20 min (Fig. 3d) and phagocytosis is characterized by the formation of large phagosomes at the tip of long cellular branches that travel towards dying neurons at a speed of 2 μm min−1 (Fig. 3a,b, Supplementary Movies 2 and 3 , and Supplementary Fig. 2f). The process of phagosome formation is rapid (~8 min) and characterized by a zippering-like mechanism with the phagocytic cup closing over the apoptotic cell (Fig. 3a,b and Supplementary Movies 2 and 3). This observation is in line with scanning electron microscopy data showing that indeed phagosomes form a tight fitting around apoptotic particles16,17. Upon phagosome closure, ingestion is the result of microglial cell rear movement (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Movie 3; average speed of 2.5–3.5 μm min−1) or phagocytic branch retraction (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Movie 2; average speed of 1.7 μm min−1). In this study we have focused mostly on events that are characterized by branch withdraw, as these are more frequent. Our approach revealed also that in one-third of all examined cases initial phagosome formation is aborted and these apoptotic targets are collected during a later attempt (Fig. 3c, Supplementary Movie 4). This aborted phagocytosis does not correlate with obvious apoptotic features, such as, time from PS exposure or distance from phagocytes. Also, this is not a feature of the PS reporter we use, as it is also observed in an independent system in which we induce neuronal apoptosis in labelled neurons using the bacterial enzyme Nitroreductase (Fig. 3e; refs 18, 19). This live approach provides a quantitative framework of how microglia engulf neuronal dying cells during brain development.
(a–c) Time course of wild-type microglia in red (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) engulfing apoptotic neurons in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). (a) Ingestion characterized by phagocytic branch retraction. (b) Ingestion characterized by cell rear movement. (c) Two-step engulfment, with one transient interaction before engulfment. (d) Phagocytosis duration in a wild-type brain. (e) Time-lapse imaging of a microglia in green (pU1::Gal4-UAS::GFP) engulfing a red neuron in which apoptosis has been induced using the NTR system (NBT:: ΔLexPR::NTR-mCherry). Scale bars, 10 μm. Experiments were performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
BAI1 and TIM-4 mediate neuronal engulfment by microglia
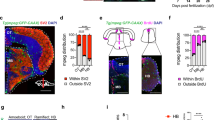
We applied the in vivo approach described above to address the functional role of PS receptors in this process. We investigated the role of TIM-4 and BAI1, two PS binding receptors that are expressed in macrophages and microglia (Supplementary Fig. 1l–n and refs 9, 20, 21). To this aim, TIM-4 and BAI1 were knocked down by using multiple morpholinos that block translation and splicing of these molecules (see online Methods and Fig. 4g,h). The outcome is a significant increase in the number of uncollected PS-positive neurons present in the trunk (Supplementary Fig. 2a–e) and in the brain (Fig. 4a–e), a phenotype that can be rescued by expressing spliced-RNA of these two receptors in microglia (Fig. 4i,j). To establish if the increase is owing to the defects in engulfment rather than elevated neuronal apoptosis, we have injected TIM-4 and BAI1 morpholinos in combination with the pU1 morpholino that removes microglia. This approach allows simple quantification of apoptotic neurons in the absence of engulfment. As the number of apoptotic neurons in either TIM-4/pU1 or BAI1/pU1 morphant embryos is comparable to that of the pU1 morpholino alone, we conclude that the accumulation of PS-positive neurons is owing to the defects in phagocytosis and that these two receptors mediate apoptotic cell clearance during brain development (Fig. 4f).
(a–d) Dorsal views of 3.5 dpf embryonic brain; 80 μm stacks. (a–d left panels) Microglia are in red (pU1::GAL4-UAS::Tag-RFP) and PS exposing cells in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). (a–d right panels) Schematic representations of un-engulfed neurons (white) and microglia (red). (a) wild type; (b) TIM-4 knockdown; (c) BAI1 knockdown; (d) TIM-4/BAI1 double knockdown. (e) Number of uncollected PS-positive apoptotic neurons in 80-μm-thick confocal stacks of 3.5 dpf wild type, TIM-4, BAI1 and TIM-4/BAI1 knockdown brains. Plot represents the mean values±s.e.m., *** represents P<0.0001. P-value was determined with one-way analysis of variance test. (f) Quantification of AO-positive cells in 3.5 dpf pU1, pU1/TIM-4 and pU1/BAI1 knockdown brains. Plot shows medians with 25–75 percentiles boxed, bars indicate the range. (g) Reverse transcription–PCR analysis showing the band shift caused by BAI1 morpholino injection (h) RT–PCR analysis showing the band shift caused by TIM-4 morpholino injection (i) Rescue of TIM-4 knockdown. This was obtained by expressing TIM-4 cDNA (UAS::TIM-4) in pU1::Gal4-UAS::GFP embryos injected with the TIM-4 morpholino (j) Rescue of BAI1 knockdown. This was obtained by expressing BAI1 cDNA (UAS::BAI1) in pU1::Gal4::UAS::GFP embryos injected with the BAI1 morpholino. Plot shows medians with 25–75 percentiles boxed, bars show ranges. Indicated P-values were obtained using one-way analysis of variance multiple comparison test; ***P<0.0001. N=number of embryos and n=number of cells tested. Scale bars, 35 μm. All experiments were performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
BAI1 promotes phagosome formation and transport during engulfment
To establish the role of BAI1 in neuronal engulfment by microglia we applied the same quantitative parameters that we used to characterize the wild-type process. Accumulation of uncollected apoptotic neurons in BAI1 morphants is owing to a significant drop in microglial engulfment efficiency when compared with wild type (Supplementary Fig. 2h). Indeed, while on an average a wild-type microglia engulfs an apoptotic neuron per hour, BAI1 morphant cells take double this time (Supplementary Fig. 2h). Interestingly, while length and speed at which phagocytic branches travel to contact apoptotic cells is comparable to that of wild-type cells (Supplementary Fig. 2f), phagosome formation, defined by the initial touch until closure of the phagocytic cup, is slow (Fig. 5g; compare Fig. 5a,b with Fig. 5c,d and compare Supplementary Movie 2 with Supplementary Movie 5). However, even though slowly, these structures form as in wild type by closing tightly over the apoptotic cell (compare Fig. 5a,b with Fig. 5c,d). During this time the two cells remain in contact, arguing against a role for BAI1 in recognition and adhesion to apoptotic cells21,22. BAI1 morphant microglia showed normal projection velocity (1.8 μm min−1; Supplementary Fig. 2f) but reduced branch retraction speed (0.5 μm min−1; Fig. 6e; compare Fig. 6a with Fig. 6b and Supplementary Movie 6 with Supplementary Movie 7). BAI1 has also been implicated in bacterial engulfment23 and indeed there is a decrease in clearance efficiency when we inject fluorescently labelled bacteria in BAI1 morphant brains (Supplementary Fig. 2g). Taken together these data indicate that in apoptotic cell clearance BAI1 is dispensable for target recognition but it is involved in phagosome formation and ingestion.
(a–f) Time lapses representing phagosome formation. Time is indicated in minutes. (a,c,e) Microglia in red (pU1::GAL4-UAS::Tag-RFP) and PS exposing cells in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). (b,d,f) Microglia in red (pU1::GAL4-UAS::Tag-RFP). (a,b) wild type, (c,d) BAI1 knockdown, (e,f) TIM-4 knockdown (g) Phagosome formation duration. Plot represents the medians with 25–75 percentiles boxed, bars indicate the range. The data were tested with one-way analysis of variance Kruskal–Wallis test. N=number of embryos and n=number of cells tested, *** represents P<0.0001. (h) Mode of engulfment in wild type (n=113), TIM-4 (n=33) and BAI1 (n=30) knockdown embryos. Percentage of direct engulfment is in light blue and percentage of multiple interactions before engulfment is in light red (i) Duration of contacts between microglia and apoptotic neurons in wild type and TIM-4 knockdowns. Data was analyzed with one-way analysis of variance multiple comparison test; lines and bars show median with the range, 25–75 percentiles boxed; ***P<0,0001. Scale bars, 5 μm. All experiments were performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
(a–d,f) Time lapses representing branch retraction. Time is indicated in minutes. Microglia in red (pU1::GAL4-UAS::Tag-RFP) and PS exposing cells in grey (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP). (a) wild type, (b) BAI1 knockdown, (c) TIM-4 knockdown, (d) BAI1/TIM-4 double knockdowns. In a,b,c,d the upper panel shows snapshots taken from time lapses of wild type, BAI1, TIM-4 and BAI1/TIM-4 knockdowns, respectively (red dot, microglia; green dot, neuron; blue dot, piece of a neuron). The middle panel shows the relative distance between the microglia and its neuronal target (green line, neuron; blue line, piece of neuron). Lower panel shows the relative velocity of neuron and neuron part to microglia (velocity is positive as distance between them decreases). (e) Branch retraction velocity extracted from time-lapse images of wild type, BAI1, TIM-4 and BAI1/TIM-4 knockdowns. The data were tested with one-way analysis of variance Kruskal–Wallis test. N=number of embryos and n=number of cells tested, *** represents P<0.0001. (f) Representative example to a TIM-4 phagosome loosing part of its content. Scale bars, 5 μm. Time indicated in minutes. All experiments were performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
TIM-4 is required downstream of phagosome formation
We next analyzed the role of TIM-4 in this process and found that in TIM-4 morphant embryos there is a significant drop in apoptotic cell clearance efficiency when compared with wild type (Supplementary Fig. 2h), while, bacterial clearance is unaffected (Supplementary Fig. 2g). Live imaging demonstrates that in TIM-4 morphant microglia length and speed at which branches travel towards their targets is normal (Supplementary Fig. 2f), however, the proportion of neurons that are contacted multiple times before engulfment increases significantly (Fig. 5h). Interestingly, each microglia–neuronal interaction on an average lasts significantly longer (40 min; Fig. 5i) than phagosome formation (8 min Fig. 5g), aborted engulfment (10 min; Fig. 5i and Fig. 3c) and phagocytosis in wild type (20 min; Fig. 3d). This indicates that TIM-4 plays no role in target recognition, as in this case we would expect a reduction in contact duration. Microglia–neuronal interactions in TIM-4 morphants are characterized by the formation of unstable phagosomes that close and open repeatedly (compare Fig. 5a with Fig. 5e and Supplementary Movies 2 and 5 with Supplementary Movie 8). Remarkably, these phagosomes often lose their apoptotic cargo or part of it during the transport phase, even though, branches move at a normal speed (Fig. 6c,e and f and Supplementary Movies 9 and 10). To further characterize the TIM-4 phenotype we analyzed actin dynamics during phagocytosis by using LifeAct24. Previous work has shown that during foreign particle ingestion actin polymerization is lost as soon as the phagosome closes25,26,27. This is in contrast with what we find in apoptotic cell clearance. Indeed, here, soon after closure there are bursts of actin polymerization around the phagosome (Fig. 7a,b and Supplementary Fig. 2i), leading to the formation of a prominent actin layer that surrounds this vesicle during the transport phase (Fig. 7a,b). In TIM-4 morphants, this actin layer does not form, even though the two cells remain in contact for extended time periods (Fig. 7c,d and Supplementary Fig. 2i). Interestingly, we find that BAI1 plays no role in the formation of this actin layer as actin polymerization takes place in BAI1 morphant microglia (Fig. 7e,f and Supplementary Fig. 2i).
(a–c) Representative time course of F-actin dynamics in WT (a), TIM-4 Kd (c) and BAI1 (e). Normalized LifeAct intensity over time in WT (b), TIM-4 (d) and BAI1 (f). Red dots represent the time points shown in the figures. Time indicated in minutes. The scale bar, 5 μm. All experiments were performed using an Olympus FV 1000 with a × 40/NA 1.15 objective.
TIM-4 and BAI1 work together to engulf neurons
This analysis shows that BAI1 and TIM-4 play distinct roles in apoptotic cell clearance. Next we asked if these molecules are part of the same process by generating double knockdowns. In double knockdowns, microglia are able to find and stick to their apoptotic targets indicating that in these cells other factors are responsible for target recognition (Fig. 6d and Supplementary Movie 11). Live imaging shows that BAI1 is epistatic to TIM-4 as double morphants are slow in forming phagosomes (Fig. 5g) and in retracting their branches (Fig. 6d,e and Supplementary Movie 11). Furthermore, double morphant phagosomes often lose their cargo during the slow branch retraction phase (Fig. 6d,f and Supplementary Movie 11). In pU1 knockdown embryos lacking microglia, a large number of neurons (approximately 250; Fig. 2b) die during the first 3.5 days of development, however, in BAI1 and TIM-4 double morpholino injections the number of uncollected apoptotic neurons increases but is comparable to that of single knockdowns (~60; Fig. 4d,e). Thus, while other pathways might also contribute to clearance in this context, lack of genetic enhancement indicates that these two receptors are part of the same phagocytic machinery and that they work in concert to allow microglia to properly engage and engulf dying neurons.
Discussion
Here we have established that clearance in the brain is a three-step process characterized by recognition, phagosome formation and ingestion. This single-cell resolution analysis has uncovered the in vivo function of two engulfment receptors, BAI1 and TIM-4. We found that for both the end-point phenotype is the same, namely a drop in clearance efficiency and an increase in the number of un-engulfed apoptotic neurons within the brain. However, this live imaging approach revealed that in BAI1 morphants this is caused by slow phagosome formation and ingestion while in TIM-4 this is owing to the repeated disengagement of phagosomes from their targets.
Previous work on TIM-4 has shown that expression of this receptor on ‘poor phagocytes’ such as Ba/F2 cells promotes adhesion to apoptotic PS expressing cells28. By looking in vivo we found that TIM-4 is not required for recognition, as previously suggested22 and that in microglia other factors are likely to mediate short-range target identification. Furthermore, this analysis does not support a role for TIM-4 in the classical ‘tether-and-tickle’ model28,29 in which TIM-4-mediated adhesion is responsible for recruiting another molecule for engulfment, as in this case TIM-4 knockdown would lead to short cell–cell interactions and failure in forming phagosomes. On the contrary, in TIM-4 morphant microglia, phagosomes form but they are unstable. This leads us to propose an alternative scenario in which both BAI1 and TIM-4 contribute directly to engulfment and, in particular, to the formation of phagosomes. Binding of PS to BAI1 is known to promote ELMO1/DOCK180/Rac-dependent membrane remodelling21. Our data indicate a role for BAI1 in stretching of the phagocytic cup over the apoptotic cell. TIM-4, on the other hand, might play a role in stabilizing these structures and/or in sealing them. We found that a feature of wild-type phagosomes is the formation of a prominent F-actin layer that surrounds these vesicles soon after closure and during transport. Interestingly, it has been shown that TIM-4 engulfment relies on the actin cytoskeleton and myosin-II motor proteins for function22. While our approach does not establish if the role of TIM-4 on actin polymerization is direct we find that this layer fails to form in TIM-4 and we speculate that this might be the reason for phagosomal instability in these morphants. Indeed, a role of TIM-4 in allowing actin layer formation would explain why TIM-4 phagosomes are unstable, opening repeatedly and often losing their cargo during the ingestion phase.
The perfect correlation between phagocytosis and apoptosis in many tissues led to the proposal that phagocytes might be able to influence cell death. In particular, it was suggested that microglia might indeed promote apoptosis in Purkinje neurons by releasing apoptotic checkpoints4. Here we focused in particular on apoptosis progression and by genetically ablating microglia we observed that sequential molecular events that characterize apoptosis, such as exposure of PS and chromatin condensation, undergo a comparable increase in the absence of these cells. This indicates that in the zebrafish brain, microglia are not required to push neurons through the apoptotic programme. It remains to be determined if the total number of neurons that die in the brain is dependant on microglia. However, considering the speed at which microglia engulf neurons, this will require new imaging approaches that combine low photo-toxicity with fast-long-term acquisition to establish how many neurons undergo apoptosis in the presence of these cells.
Many disorders affecting the brain are characterized by microglial neuronal removal and recent work points to the fact that microglial phagocytosis might not just be directed towards neurons but also clearance of Aβ42 with consequences in Alzheimer’s disease progression30. Thus, microglial phagocytosis is central in many brain pathologies and diminishing or intensifying this activity might reduce the devastating impact that these diseases have on the brain. To this aim, understanding how these cells engulf neurons is central for the development of new therapeutic targets.
Methods
Fish maintenance
Zebrafish were kept at 26–27 °C in a 14 h light and 10 h dark cycle. Embryos were collected by natural spawning and raised at 28.5 °C in E3 solution. To avoid pigmentation, 0.003% 1-phenyl-2-thiourea was added at 1 day post-fertilization (dpf). Staging of embryos was done according to ref. 31.
Transgenic fish lines
To image microglia we used pu1::Gal4-UAS::green fluroscent protein (GFP)10 and pu1::Gal4-UAS::Tag red fluorescent protein (RFP)11, transgenic lines in which the expression of GFP and RFP is under the control of a Gal4::UAS cassette and of the pU1 promoter. To study actin dynamics in microglia we generated a transgenic line in which the F-actin reporter is under the control of a Gal4::UAS cassette and the pU1 promoter to drive expression in macrophages and microglia.
Generation of the NBT::DLexPR::secA5-TagBFP transgenic line
We have cloned tagBFP downstream of secreted Annexin-V13 using XhoI and XbaI restriction sites. This construct was placed under the control of the NBT promoter (Neuronal Beta Tubulin promoter) (5′ Entry vector) and ΔLexPR (Mid Entry vector; Gateway Invitrogen). ΔLexPR is a constitutively active form of inducible LexPR system32. The construct was injected together with transposase mRNA (50 ng μl−1). For this study we have used F0, F1 and F2 transgenic embryos.
Generation of NBT::DLexPR::NTR-mCherry transgenic line
This line was generated by using the Tol2kit33. The NTR-mCherry18,19 was cloned under the control of the NBT promoter (5′ Entry vector, Gateway Invitrogen) and ΔLexPR (Mid Entry vector; Gateway Invitrogen).
Tim-4 cloning
The zebrafish Tim-4 (NM_001002434.1) was amplified by PCR starting from complementary DNA (cDNA) obtained by 3 dpf zebrafish heads using the following primers:
Forward:5′GGGGACAGCTTTCTTGTACAAAGTGGGGCACCATGACTGATCTTCACAGCTGGTTCCTCTCATC3′ Reverse:5′GGGGACAACTTTGTATAATAAAGTTGGATATTAATGCCACTGTTCGTATTCGCTTTCAGC3′.
The PCR product was cloned into a p3′ Entry clone (Gateway, Invitrogen). For the rescue experiment we cloned zf-TIM-4 downstream of the UAS sequence and injected this together with the splice morpholino (see below) into the pu1::Gal4-UAS::GFP transgenic line.
BAI1 cloning
The zebrafish BAI1 (XM_003200498.1) was amplified by PCR starting from cDNA obtained by 3 dpf zebrafish using the following primers:
Forward:5′CACCATGTTCAGCCCAAGTCTCTG3′
Reverse:5′TCACACCTCTGTCTGGAGGTC3′
The PCR product was subsequently cloned into a p3′ Entry clone (Gateway, Invitrogen). For the recue experiment we cloned zf-BAI1 downstream of the UAS sequence and injected this together with the splice morpholino (see below) into the pu1::Gal4-UAS::GFP transgenic line.
Morpholinos knockdowns
For this study we have used the following morpholinos obtained from Gene Tools:
CATAGTTTATCAACACTTACCATCA for Tim-4 (Recommended; it blocks splicing between exon-2 and intron-2; when used at a concentration of 1–0.9 mM. Based on TUNEL it gives a penetrance of ~41%).
CATCTGCAAACTGAGAGACAGTAAT for Tim-4 (It blocks splicing between intron-1 and exon-2, however, it also gives a slight developmental delay).
CTAGAACTCTAACACACTTACTCAT for Bai1 (Recommended; it blocks splicing between 1 and 2 exons; when used at a concentration of 1-0.7 mM. Based on TUNEL it gives a penentrance of about 55%).
GAGTGCAGAGACTTGGGCTGAACAT for BAI1 (It blocks translation at concentration of 0.2–0.3 mM. However, this also leads to developmental delay and mortality among injected embryos).
GATATACTGATACTCCATTGGTGGT for pU1 (ref. 15); used at a concentration of 0.5 mM.
To validate the efficiency of Tim-4 and Bai1 splice site blocking morpholinos, we have used the following primers for reverse transcription–PCRs in injected and control embryos:
Tim-4 forward:5′ATGACTGATCTTCACAG CTGGTTCCTCTCATCATGG3′
Tim-4 reverse: 5′TTAATGCCACTGTTCGTATTCGCTTTCAGCC3′
BAI1 forward:5′CCAGCACCCACGGAAACCCC3′
BAI1 reverse:5′GGCTGAGGGTTGCAGGCTCG3′
Bacterial infections
E. coli (DH5α) strain carrying the dsRED-expressing pGEMDs3 plasmid10 were grown in standard Luria Bertani medium containing Ampicillin (50 μg ml−1). For infections, 200 μM overnight cultures were centrifuged for 3 min at 4,000 g and pellets washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). After washing, these were re-suspended in 200 μM of PBS. Bacteria were injected directly into the optic tectum of anesthetized larvae using a micromanipulator attached to an Andor Spinning Disk. Ninety minutes after injection we imaged the brain using the Andor Spinning Disk with 20 × /NA 0.7 objective. Images were analyzed using Imaris software to quantity how many microglia cells had engulfed bacteria in WT, BAI1 and TIM-4 morphants.
Immunohistochemistry
For whole brain immunohistochemistry on 3 and 4 dpf embryos we used an antibody against activated Caspase-3 (1:1,000 Abcam). Embryos were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature. After fixation samples were washed with PBS Tween 20 (PBST) (0.1% Triton-x) for 15 min, and blocked with PBST and 5% normal goat serum and 0.1 mg ml−1 bovine serum albumin. Anti activated Caspase-3 was added over night at 4 °C. Samples were washed with PBST and incubated with Alexa 568 fluorophore (1:1,000 dilution). To preserve the endogenous GFP fluorescent of pU1::Gal4-UAS::GFP embryos, we kept samples in dark throughout the procedure.
Acridine Orange staining and TUNEL staining
To visualize DNA condensation we incubated 3 and 4 dpf zebrafish embryos with 10 μg ml−1 AO in E3 for 50–60 min in the dark. Embryos were washed with an E3 solution extensively and mounted in low-melting point Agarose for microscopy. To visualize DNA fragmentation we have used TUNEL (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling) staining according to the maker protocol (Roche). Embryos were fixed in 4% formaldehyde overnight and treated with 100 μl Proteinase K Solution.
In situ hybridization
In situ hybridization was carried out using a TIM-4 and BAI1 probe following the protocol described by Ober and Schulte-Merker34.
Microscopy and imaging
For live imaging, zebrafish embryos were anesthetized in 0.01% tricaine and embedded in 1.3% low-melting point agarose prepared using an E3 solution. Imaging was performed using an Olympus Fluoview 1000 or an Andor Spinning Disk Confocal microscope with 40 × NA1.15 or 20 × /NA 0.7 objectives. We used the Imaris (Bitplane) and Fiji softwares for image analysis and for obtaining maximum projections. For whole brain recordings we imaged stacks of typically 80–90 μm in depth.
In Fig. 6, kymographs are generated along microglia–neuron interaction paths giving intensity profiles over time. Central position of glia and neuron body was defined using ‘spectrum Search’ in R package ‘Peaks’. Distance and velocity functions were calculated from position information using ‘locpoly’ in R package ‘KernSmooth’.
Actin dynamics analysis during phagocytosis was done by generating fish with the following genotype pU1::Gal4::UAS::Tag-RFP/UAS::LifeActGFP. These were crossed with NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP fish to also mark the apoptotic corpses. The three channels were acquired, consecutively. The analysis presented in Fig. 7a was performed on raw images by using the Image J and Imaris 7.6.4 software. For each time point we quantified mean fluorescent intensity by segmenting the phagosome and part of the cytoplasm for both the EGFP and RFP channel. These values were used to calculate the intensity ratio between the phagosome and the cell body of each cell. Ratio values were plotted and analyzed. Data comparison have been done with two-tailed t-test.
Analysis of BAI1 and TIM-4 expression by macrophages and microglia in 3–4 dpf zebrafish embryos
To estimate whether Bai1 (XM_003200498.1) and Tim-4 (NM_001002434.1) are expressed in macrophages and microglia in 3 and 4 dpf zebrafish embryos we have performed semi-quantitative reverse transcription–PCR analysis comparing expression in heads of wild type and pU1-MO injected embryos lacking macrophages and microglia. These samples were anesthetized with 0.01% tricaine, and RNA was obtained by standard TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) based procedure. Equal amount of RNA from each sample (0.2–0.5 μg) was used for cDNA synthesis using SuperScript 2 Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen). The genes of interest were amplified with the following primers:
TIM-4 forward: 5′TGCCGCTGCTTTCATGTGGAAGC3′
TIM-4 reverse: 5′GGCCCACACTGCTGCCAGAATT3′
BAI1 forward: 5′CCGCTCCGGTGGAGATCGAGT3′
BAI1 reverse: 5′TCTCGCGATCAGGGCGAAGGT3′
The expression of Elongation factor α gene was used as a reference.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Quantification of PS-positive neurons was achieved by counting round cell bodies that are characterized by the presence of a black 5-μm-large nucleus in the center (see Fig. 2a). Quantification of AO-positive neurons was achieved by counting 5μm-large green dots representing the nuclei of apoptotic cells (see Fig. 2a).
Statistical analysis was performed with the GraphPad Prism 6 software. Data sets were checked for normality with d’Agostino and Pearson’s test. The alpha level for all tests was set as 0.05. The data distributed normally were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance with the Dunnett's multiple comparison post-test. Data that did not follow normal distribution were analyzed with non-parametric one-way analysis of variance and Dunn’s multiple comparisons post-test or Mann–Whitney’s test. Graphs show median with 25–75 percentiles boxed and bars indicating the range or mean values±s.e.m. or s.d. Numbers of embryos used for analysis were designated as N and number of cells as n.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Mazaheri, F. et al. Distinct roles for BAI1 and TIM-4 in the engulfment of dying neurons by microglia. Nat. Commun. 5:4046 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5046 (2014).
References
Aguzzi, A., Barres, B. A. & Bennett, M. L. Microglia: scapegoat, saboteur, or something else? Science 339, 156–161.
Schlegelmilch, T., Henke, K. & Peri, F. Microglia in the developing brain: from immunity to behaviour. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 21, 5–10 (2011).
Derecki, N. C. et al. Wild-type microglia arrest pathology in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Nature 484, 105–109 (2012).
Marín-Teva, J. L. et al. Microglia promote the death of developing Purkinje cells. Neuron 41, 535–547 (2004).
Fadok, V. A. et al. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol. 148, 2207–2216 (1992).
Martin, B. S. J. et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J. Exp. Med. 182, 1545–1556 (1995).
Ravichandran, K. S. Beginnings of a good apoptotic meal: the find-me and eat-me signaling pathways. Immunity 35, 445–455 (2011).
Kobayashi, N. et al. TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells. Immunity 27, 927–940 (2007).
Sokolowski, J. D. et al. Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor-1 expression in astrocytes and neurons: implications for its dual function as an apoptotic engulfment receptor. Brain. Behav. Immun. 25, 915–921 (2011).
Peri, F. & Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Live imaging of neuronal degradation by microglia reveals a role for v0-ATPase a1 in phagosomal fusion in vivo. Cell 133, 916–927 (2008).
Sieger, D., Moritz, C., Ziegenhals, T., Prykhozhij, S. & Peri, F. Long-range Ca2+ waves transmit brain-damage signals to microglia. Dev. Cell 22, 1138–1148 (2012).
Sieger, D. & Peri, F. Animal models for studying microglia: the first, the popular, and the new. Glia 61, 3–9 (2013).
van Ham, T. J. et al. Apoptotic cells are cleared by directional migration and elmo1- dependent macrophage engulfment. Curr. Biol. 22, 830–836 (2012).
Hoeppner, D. J., Hengartner, M. O. & Schnabel, R. Engulfment genes cooperate with ced-3 to promote cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 412, 202–206 (2001).
Rhodes, J. et al. Interplay of Pu.1 and gata1 determines myelo-erythroid progenitor cell fate in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 8, 97–108 (2005).
Krysko, D. V., Brouckaert, G., Kalai, M., Vandenabeele, P. & D’Herde, K. Mechanisms of internalization of apoptotic and necrotic L929 cells by a macrophage cell line studied by electron microscopy. J. Morphol. 258, 336–345 (2003).
Krysko, D. V. et al. Macrophages use different internalization mechanisms to clear apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cell. Death. Differ. 13, 2011–2022 (2006).
Curado, S. et al. Nitroreductase-mediated cell/tissue ablation in zebrafish: a spatially and temporally controlled ablation method with applications in developmental and regeneration studies. Nat. Protoc. 3, 948–954 (2008).
Curado, S. et al. Conditional targeted cell ablation in zebrafish: a new tool for regeneration studies. Dev. Dyn. 236, 1025–1035 (2007).
Thisse, B. et al. Spatial and temporal expression of the zebrafish genome by large-scale in situ hybridization screening. Meth. Cell. Biol. 77, 1–1 (2004).
Park, D. et al. BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module. Nature 450, 430–434 (2007).
Park, D. et al. The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-4 does not mediate direct signaling. Curr. Biol. 19, 346–351 (2009).
Das, S. et al. Brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1) is a pattern recognition receptor that mediates macrophage binding and engulfment of Gram-negative bacteria. PNAS 108, 2136–2141 (2011).
Riedl, J. et al. Lifeact: a versatile marker to visualize F-actin. Nat. Methods 5, 605–607 (2008).
Swanson, J. A. & Swanson, J. A. Shaping cups into phagosomes and macropinosomes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 639–649 (2008).
Swanson, J. A. et al. A contractile activity that closes phagosomes in macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 112, 307–316 (1999).
Hoppe, A. D. Cdc42, Rac1, and Rac2 display distinct patterns of activation during phagocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 3509–3519 (2004).
Toda, S. et al. Two-step engulfment of apoptotic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32, 118–125 (2011).
Hoffmann, P. R. et al. Phosphatidylserine (PS) induces PS receptor-mediated macropinocytosis and promotes clearance of apoptotic cells. J. Cell Biol. 155, 649–660 (2001).
Griciuc, A. et al. Alzheimer’s disease risk gene cd33 inhibits microglial uptake of amyloid beta. Neuron 78, 631–643 (2013).
Kimmel, C. B., Ballard, W. W., Kimmel, S. R., Ullmann, B. & Schilling, T. F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 203, 253–310 (2005).
Scott, E. K. et al. Targeting neural circuitry in zebrafish using GAL4 enhancer trapping. Nat. Methods 4, 323–326 (2007).
Kwan, K. M. et al. The Tol2kit: A multisite gateway-based construction kit forTol2 transposon transgenesis constructs. Dev. Dyn. 236, 3088–3099 (2007).
Ober, E. A. & Schulte-Merker, S. Signals from the yolk cell induce mesoderm, neuroectoderm, the trunk organizer, and the notochord in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 215, 167–181 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Celine Revenu for sharing with us the UAS::LifeAct transgenic line, Michael Parsons for the NTR-mcherry construct and Sergey Prykhozhij for generating the NBT::ΔLexPR::NTR-mCherry line. We would like to thank Antonella Lauri for helping with the schematic. We are grateful to the Advanced Light Microscopy Facility (EMBL, Heidelberg) for assistance with microscope imaging. We would like to thank Olympus Europe for continuous support of the Advanced Light Microscopy Facility. Many thanks to Darren Gilmour, Christian Moritz, Timm Schlegelmilch, Shinya Komoto, Federico Maria Rossi, Marie Daclin and Sanjita Banerjee for critical reading of this manuscript. This project was supported by an ERC starting grant to F.P. Oksana Breus was supported by an EIPOD postdoctoral fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.M., O.B. and F.P. designed the experiments and analyzed the data. F.M. and O.B. contributed equally to this work. S.D. and D.G. analyzed cargo transport data. P.H. and J.W. generated the ΔLexPR construct. F.M., O.B. and F.P. prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Figures 1-2 (PDF 1047 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
Death of a neuron. Time-lapse movie showing one neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP; grey) undergoing apoptosis in a 3.5 dpf embryo. Pictures were taken every 4 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 400 kb)
Supplementary Movie 2
Ingestion by branch retraction. Time-lapse movie showing a microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP; red) ingesting one apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR-secA5-TagBFP; gray). The process of engulfment takes around 24 minutes. Pictures were taken every 4 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 55 kb)
Supplementary Movie 3
Ingestion by cell rear movement. Time-lapse movie showing a microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP; red) ingesting one apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR-secA5-TagBFP; gray). The process of engulfment takes around 28 minutes. Pictures were taken every 4 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 82 kb)
Supplementary Movie 4
Transient interaction between microglia and dying neuron prior (MOV 246 kb)
Supplementary Movie 5
Phagosome formation in BAI1 knockdown. Time-lapse showing phagosome formation in Bai1 knockdown. Microglia (pU1::Gal4UAS-RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) in gray. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 76 kb)
Supplementary Movie 6
Phagosome formation by microglia in TIM-4 knockdown. Time-lapse showing phagosome formation in TIM-4 knockdown. Microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPRsecA5-TagBFP) in grey. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 23 kb)
Supplementary Movie 7
Branch retraction in wild type. Time-lapse movie showing branch retraction in wild type. Microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) in gray. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 142 kb)
Supplementary Movie 8
Branch retraction in BAI1 knockdown. Time-lapse movie showing branch retraction in BAI1. Microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) in gray. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 334 kb)
Supplementary Movie 9
Branch retraction in TIM-4 knockdown. Time-lapse movie showing branch retraction in TIM-4. Microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) in gray. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 135 kb)
Supplementary Movie 10
Branch retraction in TIM-4 knockdown. The microglia loses its apoptotic cargo. Time-lapse movie showing branch retraction and loss of cargo in TIM-4. Microglia (pU1::Gal4-UAS::RFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR-secA5-TagBFP) in gray. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV 1000). (MOV 136 kb)
Supplementary Movie 11
Branch retraction in BAI1/TIM-4 double knockdown. Time-lapse movie showing branch retraction in BAI1/TIM-4. Microglia (pU1::Gal4UASRFP) in red and apoptotic neuron (NBT::ΔLexPR::secA5-TagBFP) in grey. Pictures were taken every 5 minutes with a 40Å~ objective lens (Olympus FV (MOV 204 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazaheri, F., Breus, O., Durdu, S. et al. Distinct roles for BAI1 and TIM-4 in the engulfment of dying neurons by microglia. Nat Commun 5, 4046 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5046
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5046
This article is cited by
-
Noteworthy perspectives on microglia in neuropsychiatric disorders
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Phosphatidylserine in the Nervous System: Cytoplasmic Regulator of the AKT and PKC Signaling Pathways and Extracellular “Eat-Me” Signal in Microglial Phagocytosis
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor gluing action guides tissue development and disease
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Presenilin 1 phosphorylation regulates amyloid-β degradation by microglia
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Diving into the streams and waves of constitutive and regenerative olfactory neurogenesis: insights from zebrafish
Cell and Tissue Research (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.