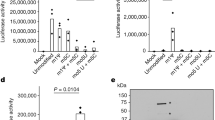
Abstract
The internal ribosome entry site (IRES), a highly conserved structured element of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomic RNA, is an attractive target for antiviral drugs. Here we show that benzimidazole inhibitors of the HCV replicon act by conformational induction of a widened interhelical angle in the IRES subdomain IIa, which facilitates the undocking of subdomain IIb from the ribosome and ultimately leads to inhibition of IRES-driven translation in HCV-infected cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maheshwari, A., Ray, S. & Thuluvath, P.J. Lancet 372, 321–332 (2008).
Ji, H., Fraser, C.S., Yu, Y., Leary, J. & Doudna, J.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16990–16995 (2004).
Pestova, T.V. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7029–7036 (2001).
Otto, G.A. & Puglisi, J.D. Cell 119, 369–380 (2004).
Brown, E.A., Zhang, H., Ping, L.H. & Lemon, S.M. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 5041–5045 (1992).
Kieft, J.S. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 292, 513–529 (1999).
Lukavsky, P.J. Virus Res. 139, 166–171 (2009).
Seth, P.P. et al. J. Med. Chem. 48, 7099–7102 (2005).
Dibrov, S.M., Johnston-Cox, H., Weng, Y.H. & Hermann, T. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 46, 226–229 (2007).
Lukavsky, P.J., Kim, I., Otto, G.A. & Puglisi, J.D. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 1033–1038 (2003).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Science 291, 1959–1962 (2001).
Boehringer, D., Thermann, R., Ostareck-Lederer, A., Lewis, J.D. & Stark, H. Structure 13, 1695–1706 (2005).
Wyles, D.L., Kaihara, K.A., Vaida, F. & Schooley, R.T. J. Virol. 81, 3005–3008 (2007).
Blight, K.J., McKeating, J.A., Marcotrigiano, J. & Rice, C.M. J. Virol. 77, 3181–3190 (2003).
Song, Y. et al. J. Virol. 80, 11579–11588 (2006).
Hermann, T. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 39, 1890–1904 (2000).
Hermann, T. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 15, 355–366 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Ho and C. Higginson for help with compound synthesis. We acknowledge the kind gift of NS5B protein by Gilead Sciences. This work was supported in part by the US National Institutes of Health, grants R01 AI72012 (T.H.) and K08 AI069989 (D.L.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.P.C. synthesized the IRES-binding benzimidazole inhibitors. S.D. synthesized NS5B inhibitors. S.M.D. participated in the design of the RNA FRET construct. J.P. performed biochemical experiments and was involved in concept development of the FRET assay. D.L.W. conceived and performed cell-based assays. T.H. conceived and supervised the project and wrote the manuscript. J.P., D.L.W. and T.H. were involved in the discussion and interpretation of the experimental data.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Results (PDF 373 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parsons, J., Castaldi, M., Dutta, S. et al. Conformational inhibition of the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site RNA. Nat Chem Biol 5, 823–825 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.217
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.217
This article is cited by
-
Targeting RNA structures with small molecules
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2022)
-
Unconventional viral gene expression mechanisms as therapeutic targets
Nature (2021)
-
IRES-targeting small molecule inhibits enterovirus 71 replication via allosteric stabilization of a ternary complex
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Versatile kit of robust nanoshapes self-assembling from RNA and DNA modules
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Rapid RNA–ligand interaction analysis through high-information content conformational and stability landscapes
Nature Communications (2015)