Abstract
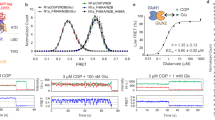
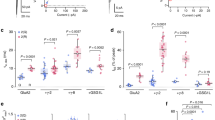
Cell signaling is often mediated by the binding of multiple ligands to multisubunit receptors. The probabilistic nature and sometimes slow rate of binding encountered with diffusible ligands can impede attempts to determine how the ligand occupancy controls signaling in such protein complexes. We describe a solution to this problem that uses a photoswitched tethered ligand as a 'ligand clamp' to induce rapid and stable binding and unbinding at defined subsets of subunits. We applied the approach to study gating in ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs), ligand-gated ion channels that mediate excitatory neurotransmission and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses in the brain. We probed gating in two kainate-type iGluRs, GluK2 homotetramers and GluK2–GluK5 heterotetramers. Ultrafast (submillisecond) photoswitching of an azobenzene-based ligand on specific subunits provided a real-time measure of gating and revealed that partially occupied receptors can activate without desensitizing. The findings have implications for signaling by locally released and spillover glutamate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Traynelis, S.F. et al. Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 62, 405–496 (2010).
Contractor, A., Mulle, C. & Swanson, G.T. Kainate receptors coming of age: milestones of two decades of research. Trends Neurosci. 34, 154–163 (2011).
Lerma, J. & Marques, J.M. Kainate receptors in health and disease. Neuron 80, 292–311 (2013).
Mosbacher, J. et al. A molecular determinant for submillisecond desensitization in glutamate receptors. Science 266, 1059–1062 (1994).
Straub, C. & Tomita, S. The regulation of glutamate receptor trafficking and function by TARPs and other transmembrane auxiliary subunits. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 22, 488–495 (2012).
Christie, L.A. et al. AMPA receptor desensitization mutation results in severe developmental phenotypes and early postnatal lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 9412–9417 (2010).
Rosenmund, C., Stern-Bach, Y. & Stevens, C.F. The tetrameric structure of a glutamate receptor channel. Science 280, 1596–1599 (1998).
Sobolevsky, A.I., Rosconi, M.P. & Gouaux, E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature 462, 745–756 (2009).
Jin, R., Banke, T.G., Mayer, M.L., Traynelis, S.F. & Gouaux, E. Structural basis for partial agonist action at ionotropic glutamate receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 803–810 (2003).
Mayer, M.L. Crystal structures of the GluR5 and GluR6 ligand binding cores: molecular mechanisms underlying kainate receptor selectivity. Neuron 45, 539–552 (2005).
Stern-Bach, Y., Russo, S., Neuman, M. & Rosenmund, C. A point mutation in the glutamate binding site blocks desensitization of AMPA receptors. Neuron 21, 907–918 (1998).
Sun, Y. et al. Mechanism of glutamate receptor desensitization. Nature 417, 245–253 (2002).
Armstrong, N., Jasti, J., Beich-Frandsen, M. & Gouaux, E. Measurement of conformational changes accompanying desensitization in an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Cell 127, 85–97 (2006).
Weston, M.C., Schuck, P., Ghosal, A., Rosenmund, C. & Mayer, M.L. Conformational restriction blocks glutamate receptor desensitization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 1120–1127 (2006).
Paternain, A.V., Cohen, A., Stern-Bach, Y. & Lerma, J. A role for extracellular Na+ in the channel gating of native and recombinant kainate receptors. J. Neurosci. 23, 8641–8648 (2003).
Plested, A.J. & Mayer, M.L. Structure and mechanism of kainate receptor modulation by anions. Neuron 53, 829–841 (2007).
Chaudhry, C., Weston, M.C., Schuck, P., Rosenmund, C. & Mayer, M.L. Stability of ligand-binding domain dimer assembly controls kainate receptor desensitization. EMBO J. 28, 1518–1530 (2009).
Zhang, Y., Nayeem, N., Nanao, M.H. & Green, T. Interface interactions modulating desensitization of the kainate-selective ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit GluR6. J. Neurosci. 26, 10033–10042 (2006).
Dawe, G.B. et al. Defining the structural relationship between kainate-receptor deactivation and desensitization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 1054–1061 (2013).
Smith, T.C. & Howe, J.R. Concentration-dependent substate behavior of native AMPA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 992–997 (2000).
Robert, A. & Howe, J.R. How AMPA receptor desensitization depends on receptor occupancy. J. Neurosci. 23, 847–858 (2003).
Robert, A., Irizarry, S.N., Hughes, T.E. & Howe, J.R. Subunit interactions and AMPA receptor desensitization. J. Neurosci. 21, 5574–5586 (2001).
Bowie, D. & Lange, G.D. Functional stoichiometry of glutamate receptor desensitization. J. Neurosci. 22, 3392–3403 (2002).
Swanson, G.T. et al. Differential activation of individual subunits in heteromeric kainate receptors. Neuron 34, 589–598 (2002).
Mott, D.D., Rojas, A., Fisher, J.L., Dingledine, R.J. & Benveniste, M. Subunit-specific desensitization of heteromeric kainate receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 588, 683–700 (2010).
Fisher, J.L. & Mott, D.D. Distinct functional roles of subunits within the heteromeric kainate receptor. J. Neurosci. 31, 17113–17122 (2011).
Barberis, A., Sachidhanandam, S. & Mulle, C. GluR6/KA2 kainate receptors mediate slow-deactivating currents. J. Neurosci. 28, 6402–6406 (2008).
Heckmann, M., Bufler, J., Franke, C. & Dudel, J. Kinetics of homomeric GluR6 glutamate receptor channels. Biophys. J. 71, 1743–1750 (1996).
Jayaraman, V. Channel-opening mechanism of a kainate-activated glutamate receptor: kinetic investigations using a laser-pulse photolysis technique. Biochemistry 37, 16735–16740 (1998).
Li, G., Oswald, R.E. & Niu, L. Channel-opening kinetics of GluR6 kainate receptor. Biochemistry 42, 12367–12375 (2003).
Bartels, E., Wassermann, N.H. & Erlanger, B.F. Photochromic activators of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 1820–1823 (1971).
Lester, H.A., Krouse, M.E., Nass, M.M., Wassermann, N.H. & Erlanger, B.F. A covalently bound photoisomerizable agonist: comparison with reversibly bound agonists at Electrophorus electroplaques. J. Gen. Physiol. 75, 207–232 (1980).
Volgraf, M. et al. Allosteric control of an ionotropic glutamate receptor with an optical switch. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 47–52 (2006).
Gorostiza, P. et al. Mechanisms of photoswitch conjugation and light activation of an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 10865–10870 (2007).
Fehrentz, T., Schönberger, M. & Trauner, D. Optochemical genetics. Angew. Chem. 50, 12156–12182 (2011).
Levitz, J. et al. Optical control of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 507–516 (2013).
Tochitsky, I. et al. Optochemical control of genetically engineered neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nat. Chem. 4, 105–111 (2012).
Kienzler, M.A. & Reiner, A. et al. A red-shifted, fast-relaxing azobenzene photoswitch for visible light control of an ionotropic glutamate receptor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 17683–17686 (2013).
Herb, A. et al. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron 8, 775–785 (1992).
Wisden, W. & Seeburg, P.H. A complex mosaic of high-affinity kainate receptors in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 13, 3582–3598 (1993).
Contractor, A. et al. Loss of kainate receptor-mediated heterosynaptic facilitation of mossy-fiber synapses in KA2−/− mice. J. Neurosci. 23, 422–429 (2003).
Gallyas, F. Jr., Ball, S.M. & Molnar, E. Assembly and cell surface expression of KA-2 subunit-containing kainate receptors. J. Neurochem. 86, 1414–1427 (2003).
Ren, Z. et al. Multiple trafficking signals regulate kainate receptor KA2 subunit surface expression. J. Neurosci. 23, 6608–6616 (2003).
Nasu-Nishimura, Y. et al. Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum-retention motif in an intracellular loop of the kainate receptor subunit KA2. J. Neurosci. 26, 7014–7021 (2006).
Reiner, A., Arant, R.J. & Isacoff, E.Y. Assembly stoichiometry of the GluK2/GluK5 kainate receptor complex. Cell Rep. 1, 234–240 (2012).
Kumar, J., Schuck, P. & Mayer, M.L. Structure and assembly mechanism for heteromeric kainate receptors. Neuron 71, 319–331 (2011).
Swanson, G.T., Green, T. & Heinemann, S.F. Kainate receptors exhibit differential sensitivities to (S)-5-iodowillardiine. Mol. Pharmacol. 53, 942–949 (1998).
Cui, C. & Mayer, M.L. Heteromeric kainate receptors formed by the coassembly of GluR5, GluR6, and GluR7. J. Neurosci. 19, 8281–8291 (1999).
Pinheiro, P.S. et al. Selective block of postsynaptic kainate receptors reveals their function at hippocampal mossy fiber aynapses. Cereb. Cortex 23, 323–331 (2013).
Ma-Högemeier, Z.L. et al. Oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum and intracellular trafficking of kainate receptors are subunit-dependent but not editing-dependent. J. Neurochem. 113, 1403–1415 (2010).
Zhou, L.M. et al. (2S,4R)-4-methylglutamic acid (SYM 2081): a selective, high-affinity ligand for kainate receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 280, 422–427 (1997).
Numano, R. et al. Nanosculpting reversed wavelength sensitivity into a photoswitchable iGluR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 6814–6819 (2009).
Everts, I., Villmann, C. & Hollmann, M. N-Glycosylation is not a prerequisite for glutamate receptor function but is essential for lectin modulation. Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 861–873 (1997).
Patneau, D.K., Mayer, M.L., Jane, D.E. & Watkins, J.C. Activation and desensitization of AMPA/kainate receptors by novel derivatives of willardiine. J. Neurosci. 12, 595–606 (1992).
Jane, D.E. et al. Synthesis of willardiine and 6-azawillardiine analogs: pharmacological characterization on cloned homomeric human AMPA and kainate receptor subtypes. J. Med. Chem. 40, 3645–3650 (1997).
Jonas, P. Fast application of agonists to isolated membrane patches. In Single-Channel Recording (eds. Sakmann, B. & Neher, E.) 231–242 (Plemum Press, 1995).
Schwarz, G. Kinetic analysis by chemical relaxation methods. Rev. Mod. Phys. 40, 206–218 (1968).
Colquhoun, D. & Hawkes, A.G. A Q-matrix cookbook. In Single-Channel Recording (eds. Sakmann, B. & Neher, E.) 589–633 (Plenum Press, 1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Levitz for discussion, and we are grateful to K.M. Partin (Colorado State University) and P.H. Seeburg (Max Planck Institute Heidelberg) for the gift of clones as well as to D. Trauner (Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) for the gift of L-MAG-0 and many stimulating discussions. This work was supported by grants to E.Y.I. from the US National Institutes of Health (2PN2EY018241 and U24NS057631) as well as a postdoctoral fellowship to A.R. from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG RE 3101/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.R. and E.Y.I. designed experiments, A.R. performed and analyzed experiments, and A.R. and E.Y.I. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Figures 1–11, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Notes 1 and 2. (PDF 4849 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiner, A., Isacoff, E. Tethered ligands reveal glutamate receptor desensitization depends on subunit occupancy. Nat Chem Biol 10, 273–280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1458
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1458
This article is cited by
-
Optical control of neuronal ion channels and receptors
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2019)
-
Holographic two-photon activation for synthetic optogenetics
Nature Protocols (2019)
-
How to control proteins with light in living systems
Nature Chemical Biology (2014)
-
The light fantastic
Nature Chemical Biology (2014)