Abstract
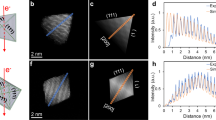
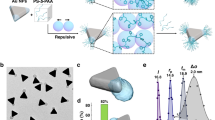
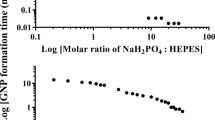
The properties of a nanocrystal are heavily influenced by its shape. Shape control of a colloidal nanocrystal is believed to be a kinetic process, with high-energy facets growing faster then vanishing, leading to nanocrystals enclosed by low-energy facets. Identifying a surfactant that can specifically bind to a particular crystal facet is critical, but has proved challenging to date. Biomolecules have exquisite specific molecular recognition properties that can be explored for the precise engineering of nanostructured materials. Here, we report the use of facet-specific peptide sequences as regulating agents for the predictable synthesis of platinum nanocrystals with selectively exposed crystal surfaces and particular shapes. The formation of platinum nanocubes and nanotetrahedrons are demonstrated with Pt-{100} and Pt-{111} binding peptides, respectively. Our studies unambiguously demonstrate the abilities of facet-selective binding peptides in determining nanocrystal shape, representing a critical step forward in the use of biomolecules for programmable synthesis of nanostructures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anker, J. N. et al. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nature Mater. 7, 442–453 (2008).
Huang, Y. et al. Logic gates and computation from assembled nanowire building blocks. Science 294, 1313–1317 (2001).
Javey, A., Guo, J., Wang, Q., Lundstrom, M. & Dai, H. Ballistic carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nature 424, 654–657 (2003).
Tang, Y. & Ouyang, M. Tailoring properties and functionalities of metal nanoparticles through crystallinity engineering. Nature Mater. 6, 754–759 (2007).
Ahmadi, T. S., Wang, Z. L., Green, T. C., Henglein, A. & El-Sayed, M. A. Shape-controlled synthesis of colloidal platinum nanoparticles. Science 272, 1924–1926 (1996).
Ohkoshi, S-i. et al. Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition. Nature Chem. 2, 539–545 (2010).
Wang, X., Zhuang, J., Peng, Q. & Li, Y. A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature 437, 121–124 (2005).
Tian, N., Zhou, Z. Y., Sun, S. G., Ding, Y. & Wang, Z. L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 316, 732–735 (2007).
Peng, X. et al. Shape control of CdSe nanocrystals. Nature 404, 59–61 (2000).
Herricks, T., Chen, J. & Xia, Y. Polyol synthesis of platinum nanoparticles: control of morphology with sodium nitrate. Nano Lett. 4, 2367–2371 (2004).
Xia, Y., Xiong, Y. J., Lim, B. & Skrabalak, S. E. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 60–103 (2009).
Choi, C. L. & Alivisatos, A. P. From artificial atoms to nanocrystal molecules: preparation and properties of more complex nanostructures. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 61, 369–389 (2010).
Weiner, S. & Addadi, L. Design strategies in mineralized biological materials. J. Mater. Chem. 7, 689–702 (1997).
Ball, P. Life's lessons in design. Nature 409, 413–416 (2001).
Mann, S. Biomineralization: Principles and Concepts in Bioinorganic Materials Chemistry (Oxford Univ. Press, 2001).
De Yoreo, J. J. & Vekilov, P. G. Principles of crystal nucleation and growth. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 54, 57–93 (2003).
Tamerler, C. & Sarikaya, M. Molecular biomimetics: utilizing nature's molecular ways in practical engineering. Acta Biomater. 3, 289–299 (2007).
Yin, Y. & Alivisatos, A. P. Colloidal nanocrystal synthesis and the organic–inorganic interface. Nature 437, 664–670 (2005).
Puntes, V. F., Krishnan, K. M. & Alivisatos, A. P. Colloidal nanocrystal shape and size control: the case of cobalt. Science 291, 2115–2117 (2001).
Sun, Y. & Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 298, 2176–2179 (2002).
Pileni, M-P. The role of soft colloidal templates in controlling the size and shape of inorganic nanocrystals. Nature Mater. 2, 145–150 (2003).
Naik, R. R., Stringer, S. J., Agarwal, G., Jones, S. E. & Stone, M. O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nature Mater. 1, 169–172 (2002).
Sarikaya, M., Tamerler, C., Jen, A. K. Y., Schulten, K. & Baneyx, F. Molecular biomimetics: nanotechnology through biology. Nature Mater. 2, 577–585 (2003).
Uchida, M. et al. Biological containers: protein cages as multifunctional nanoplatforms. Adv. Mater. 19, 1025–1042 (2007).
Whaley, S. R., English, D. S., Hu, E. L., Barbara, P. F. & Belcher, A. M. Selection of peptides with semiconductor binding specificity for directed nanocrystal assembly. Nature 405, 665–668 (2000).
Li, Y., Whyburn, G. P. & Huang, Y. Specific peptide regulated synthesis of ultrasmall platinum nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 15998–15999 (2009).
Gugliotti, L. A., Feldheim, D. L. & Eaton, B. E. RNA-mediated metal–metal bond formation in the synthesis of hexagonal palladium nanoparticles. Science 304, 850–852 (2004).
Brown, S., Sarikaya, M. & Johnson, E. A genetic analysis of crystal growth. J. Mol. Biol. 299, 725–735 (2000).
Li, Y. & Huang, Y. Morphology-controlled synthesis of platinum nanocrystals with specific peptides. Adv. Mater. 22, 1921–1925 (2010).
Park, S. Y. et al. DNA-programmable nanoparticle crystallization. Nature 451, 553–556 (2008).
Somorjai, G. A. Introduction to Surface Chemistry and Catalysis (Wiley, 1994).
Bratlie, K. M., Lee, H., Komvopoulos, K., Yang, P. D. & Somorjai, G. A. Platinum nanoparticle shape effects on benzene hydrogenation selectivity. Nano Lett. 7, 3097–3101 (2007).
Sun, S. & Murray, C. B. Synthesis of monodisperse cobalt nanocrystals and their assembly into magnetic superlattices. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 4325–4330 (1999).
Lee, H. et al. Morphological control of catalytically active platinum nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 118, 7988–7992 (2006).
Seker, U. O. S. et al. Adsorption behavior of linear and cyclic genetically engineered platinum binding peptides. Langmuir 23, 7895–7900 (2007).
Wang, Z. L., Petroski, J. M., Green, T. C. & El-Sayed, M. A. Shape transformation and surface melting of cubic and tetrahedral platinum nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6145–6151 (1998).
So, C. R. et al. Molecular recognition and supramolecular self-assembly of a genetically engineered gold binding peptide on Au{111}. ACS Nano 3, 1525–1531 (2009).
Oren, E. E., Tamerler, C. & Sarikaya, M. Metal recognition of septapeptides via polypod molecular architecture. Nano Lett. 5, 415–419 (2005).
Heinz, H. et al. Nature of molecular interactions of peptides with gold, palladium, and Pd–Au bimetal surfaces in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 9704–9714 (2009).
Karlberg, G. S. Adsorption trends for water, hydroxyl, oxygen, and hydrogen on transition-metal and platinum-skin surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 74, 153414 (2006).
Teng, X. W. & Yang, H. Synthesis of platinum multipods: an induced anisotropic growth. Nano Lett. 5, 885–891 (2005).
Song, H., Kim, F., Connor, S., Somorjai, G. A. & Yang, P. Pt nanocrystals: shape control and Langmuir–Blodgett monolayer formation. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 188–193 (2004).
Acknowledgements
C-Y.C., Y.L., L.R. and Y.H. acknowledge support from the Office of Naval Research (ONR) (award N00014-08-1-0985), the Army Research Office (ARO) (award 54709-MS-PCS and MURI award W911NF-08-1-0364) and from the Sloan Research Fellowship. C-Y.C., Y.L., L.R. and Y.H. also acknowledge the Electron Imaging Center of Nanomachines for TEM support and Y. Tang for LC-MS support. X.Y. and C.B.M. acknowledge the support for metal nanocrystal synthesis from the Department of Energy's Division of Basic Energy Sciences (award DE-SC0002158) and the ARO (MURI award W911NF-08-1-0364).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.H. and C-Y.C. conceived and designed the experiments. C-Y.C. performed the experiments. C-Y.C. and Y.L. collected and analysed the data. L.R., X.Y. and C.B.M. contributed to preparing starting nanoparticle substrates for peptide selection. C-Y.C., Y.L. and Y.H. co-wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2259 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, CY., Li, Y., Ruan, L. et al. Platinum nanocrystals selectively shaped using facet-specific peptide sequences. Nature Chem 3, 393–399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1025
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1025
This article is cited by
-
Adsorption of Lithium on Cell Surface as Nanoparticles through Lithium Binding Peptide Display in Recombinant Escherichia coli
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2023)
-
Morphology-controlled synthesis of MoO3 nanostructures and its effect on heavy metal ion detection
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2023)
-
Atomistic Simulations of the Elastic Compression of Platinum Nanoparticles
Nanoscale Research Letters (2022)
-
Nanoscaled Zinc Oxide Prepared by Mono-amino Acid Templated Assembly and Their Superior Biological Properties
Journal of Cluster Science (2022)
-
Infiltrated thin film structure with hydrogel-mediated precursor ink for durable SOFCs
Scientific Reports (2021)