Abstract
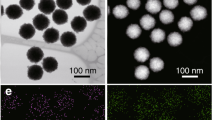
Many important intracellular biochemical reactions are modulated by transition metals, typically in the form of metalloproteins. The ability to carry out selective transformations inside a cell would allow researchers to manipulate or interrogate innumerable biological processes. Here, we show that palladium nanoparticles trapped within polystyrene microspheres can enter cells and mediate a variety of Pd0-catalysed reactions, such as allylcarbamate cleavage and Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling. The work provides the basis for the customization of heterogeneous unnatural catalysts as tools to carry out artificial chemistries within cells. Such in cellulo synthesis has potential for a plethora of applications ranging from cellular labelling to synthesis of modulators or inhibitors of cell function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silverman, R. E. Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions 2nd edn (Academic Press, 2002).
Bugg, T. Introduction to Enzyme and Coenzyme Chemistry 2nd edn (Wiley-Blackwell, 2004).
Lippard, S. J. & Berg, J. M. Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry (University Science Books, 1994).
Andreini, C., Bertini, I., Cavallaro, G., Holliday, G. L. & Thornton, J. M. Metal ions in biological catalysis: from enzyme databases to general principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 13, 1205–1218 (2008).
Waldron, K. J., Rutherford, J. C., Ford, D. & Robinson, N. J. Metalloproteins and metal sensing. Nature 460, 823–830 (2009).
Costas, M., Mehn, M. P., Jensen, M. P. & Que, L Jr. Dioxygen activation at mononuclear nonheme iron active sites: enzymes, models, and intermediates. Chem. Rev. 104, 939–986 (2004).
Tshuva, E. Y. & Lippard, S. J. Synthetic models for non-heme carboxylate-bridged diiron metalloproteins: strategies and tactics. Chem. Rev. 104, 987–1012 (2004).
Lippard, S. J. The inorganic side of chemical biology. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 504–507 (2006).
Tolman, W. B. & Spencer, D. J. E. New advances in ligand design for synthetic modeling of metalloprotein active sites. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 188–195 (2001).
Xing, G. & DeRose, V. J. Designing metal–peptide models for protein structure and function. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 196–200 (2001).
Baltzer, L. & Nilsson, J. Emerging principles of de novo catalyst design. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 12, 355–360 (2001).
Lu, Y. Biosynthetic inorganic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 5588–5601 (2006).
Haas, K. L. & Franz, K. J. Application of metal coordination chemistry to explore and manipulate cell biology. Chem. Rev. 109, 4921–4960 (2009).
Domaille, D. W., Que, E. L. & Chang, C. J. Synthetic fluorescent sensors for studying the cell biology of metals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 4, 168–175 (2008).
McRae, R., Bagchi, P., Sumalekshmy, S. & Fahrni, C. J. In situ imaging of metals in cells and tissues. Chem. Rev. 109, 4780–4827 (2009).
Liang, G., Ren, H. & Rao, J. A biocompatible condensation reaction for controlled assembly of nanostructures in living cells. Nature Chem. 2, 54–60 (2010).
Santra, M., Ko, S.-K., Shin, I. & Ahn, K. H. Fluorescent detection of palladium species with an O-propargylated fluorescein. Chem. Commun. 46, 3964–3966 (2010).
Streu, C. & Meggers, E. Ruthenium-induced allylcarbamate cleavage in living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 5645–5648 (2006).
Bruijnincx, P. C. A. & Sadler, P. J. New trends for metal complexes with anticancer activity. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 12, 197–206 (2008).
Abu-Surrah, A. S. & Kettunen, M. Platinum group antitumor chemistry: design and development of new anticancer drugs complementary to cisplatin. Curr. Med. Chem. 13, 1337–1357 (2006).
Negishi, E. I. Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis (Wiley-Interscience, 2002).
Sanchez-Martin, R. M. et al. Bead-based cellular analysis, sorting and multiplexing. ChemBioChem 6, 1341–1345 (2005).
Sanchez-Martin, R. M., Cuttle, M., Mittoo, S. & Bradley, M. Microsphere-based real-time calcium sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 5472–5474 (2006).
Alexander, L. M., Sanchez-Martin, R. M. & Bradley M. Knocking (anti)-sense into cells: the microsphere approach to gene silencing. Bioconjug. Chem. 20, 422–426 (2009).
Sanchez-Martin, R. M. et al. Microsphere-mediated protein delivery into cells. ChemBioChem 10, 1453–1456 (2009).
Alexander, L. M. et al. Investigation of microsphere-mediated cellular delivery by chemical, microscopic and gene expression analysis. Mol. BioSyst. 6, 399–409 (2010).
Cho, J. K. et al. Captured and cross-linked palladium nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6276–6277 (2006).
Horstmann, M. A. et al. Amsacrine combined with etoposide and high-dose methylprednisolone as salvage therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Haematologica 95, 1701–1703 (2005).
Miyaura, N. & Suzuki, A. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. Chem. Rev. 95, 2457–2483 (1995).
Alonso, F., Beletskaya, I. P. & Yus, M. Non-conventional methodologies for transition-metal catalysed carbonecarbon coupling: a critical overview. Part 2: The Suzuki reaction. Tetrahedron 64, 3047–3101 (2008).
Unciti-Broceta, A., Yusop, M. R., Richardson, P., Walton, J. & Bradley, M. A fluorescein-derived anthocyanidin-inspired pH sensor. Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 3713–3715 (2009).
Smith, R. A., Porteous, C. M., Gane, A. M. & Murphy, M. P. Delivery of bioactive molecules to mitochondria in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5407–5412 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the Government of Malaysia (R.M.Y.), the Swiss National Science Foundation (E.M.V.J.) and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council. R.M.S.M. thanks the Royal Society for a Dorothy Hodgkin Fellowship. The authors thank D. Kelly for his help with the confocal microscopy studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.M.Y. synthesized materials, performed cell-based experiments and analysed the data. A.U.B. designed and supervised the research, analysed the data and co-wrote the paper. E.M.V.J. synthesized materials, performed experiments and analysed the data. R.M.S.M. designed and supervised the experiments and analysed the data. M.B. came up with the concept, designed the research, analysed the data and co-wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 5424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusop, R., Unciti-Broceta, A., Johansson, E. et al. Palladium-mediated intracellular chemistry. Nature Chem 3, 239–243 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.981
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.981
This article is cited by
-
Bioorthogonal chemistry based on-demand drug delivery system in cancer therapy
Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering (2023)
-
Synthetic prodrug design enables biocatalytic activation in mice to elicit tumor growth suppression
Nature Communications (2022)
-
DNA-based platform for efficient and precisely targeted bioorthogonal catalysis in living systems
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Harnessing nanotechnology to expand the toolbox of chemical biology
Nature Chemical Biology (2021)
-
Bioorthogonal chemistry
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2021)