Abstract
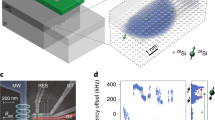
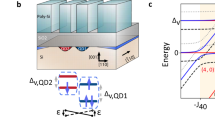
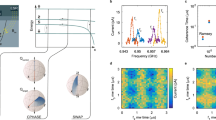
Silicon is more than the dominant material in the conventional microelectronics industry: it also has potential as a host material for emerging quantum information technologies. Standard fabrication techniques already allow the isolation of single electron spins in silicon transistor-like devices. Although this is also possible in other materials, silicon-based systems have the advantage of interacting more weakly with nuclear spins. Reducing such interactions is important for the control of spin quantum bits because nuclear fluctuations limit quantum phase coherence, as seen in recent experiments in GaAs-based quantum dots1,2. Advances in reducing nuclear decoherence effects by means of complex control3,4,5 still result in coherence times much shorter than those seen in experiments on large ensembles of impurity-bound electrons in bulk silicon crystals6,7. Here we report coherent control of electron spins in two coupled quantum dots in an undoped Si/SiGe heterostructure and show that this system has a nuclei-induced dephasing time of 360 nanoseconds, which is an increase by nearly two orders of magnitude over similar measurements in GaAs-based quantum dots. The degree of phase coherence observed, combined with fast, gated electrical initialization, read-out and control, should motivate future development of silicon-based quantum information processors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005)
Koppens, F. H. L., Nowack, K. C. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spin echo of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 236802 (2008)
Reilly, D. J. et al. Suppressing spin qubit dephasing by nuclear state preparation. Science 321, 817–821 (2008)
Barthel, C., Medford, J., Marcus, C. M., Hanson, M. P. & Gossard, A. C. Interlaced dynamical decoupling and coherent operation of a singlet-triplet qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 266808 (2010)
Bluhm, H. et al. Dephasing time of GaAs electron-spin qubits coupled to a nuclear bath exceeding 200 μs. Nature Phys. 7, 109–113 (2011)
Simmons, S. et al. Entanglement in a solid-state spin ensemble. Nature 470, 69–72 (2011)
Tyryshkin, A. M. et al. Electron spin coherence exceeding seconds in high purity silicon. Nature Mater . (in the press); preprint at 〈http://arxiv.org/abs/1105.3772〉 (2011)
Ladd, T. D. et al. Quantum computers. Nature 464, 45–53 (2010)
Kane, B. E. A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer. Nature 393, 133–137 (1998)
Eriksson, M. A. et al. Spin-based quantum dot quantum computing in silicon. Quantum Inf. Process. 3, 133–146 (2004)
Borselli, M. G. et al. Pauli spin blockade in undoped Si/SiGe two-electron double quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 063109 (2011)
Goswami, S. et al. Controllable valley splitting in silicon quantum devices. Nature Phys. 3, 41–45 (2007)
Xiao, M., House, M. G. & Jiang, H. W. Parallel spin filling and energy spectroscopy in few-electron Si metal-on-semiconductor-based quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 032103 (2010)
Borselli, M. G. et al. Measurement of valley splitting in high-symmetry Si/SiGe quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 123118 (2011)
Lai, N. S. et al. Pauli spin blockade in a highly tunable silicon double quantum dot. Sci. Rep. 1, 110 (2011)
Hayes, R. R. et al. Lifetime measurements (T1) of electron spins in Si/SiGe quantum dots. Preprint at 〈http://arxiv.org/abs/0908.0173〉 (2009)
Xiao, M., House, M. G. & Jiang, H. W. Measurement of the spin relaxation time of single electrons in a silicon metal-oxide-semiconductor-based quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 096801 (2010)
Morello, A. et al. Single-shot readout of an electron spin in silicon. Nature 467, 687–691 (2010)
Simmons, C. B. et al. Tunable spin loading and T 1 of a silicon spin qubit measured by single-shot readout. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 156804 (2011)
Johnson, A. C. et al. Triplet–singlet spin relaxation via nuclei in a double quantum dot. Nature 435, 925–928 (2005)
Liu, H. W. et al. Pauli-spin-blockade transport through a silicon double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 77, 073310 (2008)
Shaji, N. et al. Spin blockade and lifetime-enhanced transport in a few-electron Si/SiGe double quantum dot. Nature Phys. 4, 540–544 (2008)
Laird, E. A. et al. Effect of exchange interaction on spin dephasing in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 056801 (2006)
Petta, J. R. et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization with single electron spins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 067601 (2008)
Press, D. et al. Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot. Nature Photon. 4, 367–370 (2010)
Coish, W. A. & Loss, D. Singlet-triplet decoherence due to nuclear spins in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 72, 125337 (2005)
Assali, L. V. C. et al. Hyperfine interactions in silicon quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 83, 165301 (2011)
DiVincenzo, D. P., Bacon, D., Kempe, J., Burkard, G. & Whaley, K. B. Universal quantum computation with the exchange interaction. Nature 408, 339–342 (2000)
Tomita, Y., Merrill, J. T. & Brown, K. R. Multi-qubit compensation sequences. N. J. Phys. 12, 015002 (2010)
West, J. R., Lidar, D. A., Fong, B. H. & Gyure, M. F. High fidelity quantum gates via dynamical decoupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 230503 (2010)
Acknowledgements
We thank C. M. Marcus for discussions, J. R. Petta for assistance with measurement techniques and B. H. Fong for assistance with hyperfine calculations. Sponsored by United States Department of Defense. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressly or implied, of the United States Department of Defense or the US Government. Approved for public release, distribution unlimited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.M.M., M.G.B., C.A.W., K.S.H. and A.T.H. contributed to device measurement and testing. B.H., P.W.D., I.A.-R., A.E.S. and M.S. contributed to material growth and device fabrication. B.M.M., T.D.L., A.A.K., R.S.R. and M.F.G. contributed to modelling and data analysis. B.M.M., T.D.L., A.A.K. and M.F.G prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Methods and Data, Supplementary Figures 1-5 with legends and additional references. (PDF 962 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maune, B., Borselli, M., Huang, B. et al. Coherent singlet-triplet oscillations in a silicon-based double quantum dot. Nature 481, 344–347 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10707
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10707
This article is cited by
-
Single PbS colloidal quantum dot transistors
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Compilation and scaling strategies for a silicon quantum processor with sparse two-dimensional connectivity
npj Quantum Information (2023)
-
Spreading entanglement through pairwise exchange interactions
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Design and integration of single-qubit rotations and two-qubit gates in silicon above one Kelvin
Communications Materials (2022)
-
A shuttling-based two-qubit logic gate for linking distant silicon quantum processors
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.