Abstract
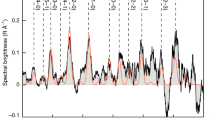
Recent observations, including the discovery1 in typical asteroidal orbits of objects with cometary characteristics (main-belt comets, or MBCs), have blurred the line between comets and asteroids, although so far neither ice nor organic material has been detected on the surface of an asteroid or directly proven to be an asteroidal constituent. Here we report the spectroscopic detection of water ice and organic material on the asteroid 24 Themis, a detection that has been independently confirmed2. 24 Themis belongs to the same dynamical family as three of the five known MBCs, and the presence of ice on 24 Themis is strong evidence that it also is present in the MBCs. We conclude that water ice is more common on asteroids than was previously thought and may be widespread in asteroidal interiors at much smaller heliocentric distances than was previously expected.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsieh, H. H. & Jewitt, D. A population of comets in the main asteroid belt. Science 312, 561–563 (2006)
Campins, H. et al. Water ice and organics on the surface of the asteroid 24 Themis. Nature 10.1038/nature09029 (this issue)
Rayner, J. T. et al. SpeX: a medium-resolution 0.8–5.5 micron spectrograph and imager for the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 115, 362–382 (2003)
Cushing, M. C., Vacca, W. D. & Rayner, J. T. Spextool: a spectral extraction package for SpeX, a 0.8–5.5 micron cross-dispersed spectrograph. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 116, 362–376 (2004)
Lebofsky, L. A. et al. A refined ‘standard’ thermal model for asteroids based on observations of 1 Ceres and 2 Pallas. Icarus 68, 239–251 (1986)
Mastrapa, R. M., Sandford, S. A., Roush, T. L., Cruikshank, D. P. & Dalle Ore, C. M. Optical constants of amorphous and crystalline H2O-ice: 2.5–22 μm (4000–455 cm-1). Astrophys. J. 701, 1347–1356 (2009)
Emery, J. P., Cruikshank, D. P. & van Cleve, J. Thermal emission spectroscopy (5.2–38 μm) of three Trojan asteroids with the Spitzer Space Telescope: detection of fine-grained silicates. Icarus 182, 496–512 (2006)
Shkuratov, Starukhina, L., Hoffmann, H. & Arnold, G. A model of spectral albedo of particulate surfaces: implications for optical properties of the Moon. Icarus 137, 235–246 (1999)
Khare, B. N. et al. Production and optical constraints of ice tholin from charged particle irradiation of (1:6) C2H6/H2O at 77 K. Icarus 103, 290–300 (1993)
Colangeli, L., Mennella, V., Baratt, G. A., Bussoletti, E. & Strazzulla, G. Raman and infrared spectra of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecules of possible astrophysical interest. Astrophys. J. 396, 369–377 (1992)
Jones, T. D. An Infrared Reflectance Study of Water in Outer Belt Asteroids: Clues to Composition and Origin. Ph.D. thesis, Univ. Arizona (1988)
Schorghofer, N. The lifetime of ice on main belt asteroids. Astrophys. J. 682, 697–705 (2008)
Cohen, B. A. & Coker, R. F. Modeling of liquid water on CM meteorite parent bodies and implications for amino acid racemization. Icarus 145, 369–381 (2000)
Dorschner, J., Begemann, B., Henning, T., Jaeger, C. & Mutschke, H. Steps toward interstellar silicate mineralogy. II. Study of Mg-Fe-silicate glasses of variable composition. Astron. Astrophys. 300, 503–520 (1995)
Moroz, L. V., Arnold, G., Korochantsev, A. V. & Wasch, R. Natural solid bitumens as possible analogs for cometary and asteroid organics. Icarus 134, 253–268 (1998)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NASA Planetary Astronomy programme. A.S.R. is a visiting astronomer at the IRTF, which is operated by the University of Hawaii under cooperative agreement no. NNX-08AE38A with NASA, Science Mission Directorate, Planetary Astronomy programme. All the observations used in this publication were obtained at the IRTF. We would like to thank the telescope operators of the IRTF for their efforts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S.R. performed all of the telescopic observations and reduced all of the data, including the thermal flux removal. J.P.E. performed the spectral modelling of the ice and organics and performed spectral library searches. The authors contributed equally to interpretation and analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Information and Data comprising: Consideration of alternate explanations for 3.1-µm absorption, Supplementary References, Supplementary Table S1 and Supplementary Figures S1-S4 with legends. (PDF 2547 kb)
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivkin, A., Emery, J. Detection of ice and organics on an asteroidal surface. Nature 464, 1322–1323 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09028
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09028
This article is cited by
-
Spectroscopic identification of water emission from a main-belt comet
Nature (2023)
-
Late accretion of Ceres-like asteroids and their implantation into the outer main belt
Nature Astronomy (2023)
-
L’Ralph: A Visible/Infrared Spectral Imager for the Lucy Mission to the Trojans
Space Science Reviews (2023)
-
Asteroid families: properties, recent advances, and future opportunities
Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy (2022)
-
Shapes, structures, and evolution of small bodies
Astrodynamics (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.