Abstract
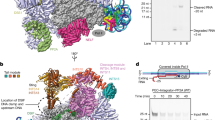
The recent emergence of highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus strains with subtype H5N1 pose a global threat to human health1. Elucidation of the underlying mechanisms of viral replication is critical for development of anti-influenza virus drugs2. The influenza RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) heterotrimer has crucial roles in viral RNA replication and transcription. It contains three proteins: PA, PB1 and PB2. PB1 harbours polymerase and endonuclease activities and PB2 is responsible for cap binding3,4; PA is implicated in RNA replication5,6,7,8,9,10 and proteolytic activity11,12,13,14, although its function is less clearly defined. Here we report the 2.9 ångström structure of avian H5N1 influenza A virus PA (PAC, residues 257–716) in complex with the PA-binding region of PB1 (PB1N, residues 1–25). PAC has a fold resembling a dragon’s head with PB1N clamped into its open ‘jaws’. PB1N is a known inhibitor that blocks assembly of the polymerase heterotrimer and abolishes viral replication. Our structure provides details for the binding of PB1N to PAC at the atomic level, demonstrating a potential target for novel anti-influenza therapeutics. We also discuss a potential nucleotide binding site and the roles of some known residues involved in polymerase activity. Furthermore, to explore the role of PA in viral replication and transcription, we propose a model for the influenza RdRp heterotrimer by comparing PAC with the λ3 reovirus polymerase structure, and docking the PAC structure into an available low resolution electron microscopy map.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taubenberger, J. K. et al. Characterization of the 1918 influenza virus polymerase genes. Nature 437, 889–893 (2005)
Ghanem, A. et al. Peptide-mediated interference with influenza A virus polymerase. J. Virol. 81, 7801–7804 (2007)
Li, M. L., Rao, P. & Krug, R. M. The active sites of the influenza cap-dependent endonuclease are on different polymerase subunits. EMBO J. 20, 2078–2086 (2001)
Guilligay, D. et al. The structural basis for cap binding by influenza virus polymerase subunit PB2. Nature Struct. Biol. 15, 500–506 (2008)
Fodor, E. et al. A single amino acid mutation in the PA subunit of the influenza virus RNA polymerase inhibits endonucleolytic cleavage of capped RNAs. J. Virol. 76, 8989–9001 (2002)
Jung, T. E. & Brownlee, G. G. A new promoter-binding site in the PB1 subunit of the influenza A virus polymerase. J. Gen. Virol. 87, 679–688 (2006)
Kawaguchi, A., Naito, T. & Nagata, K. Involvement of influenza virus PA subunit in assembly of functional RNA polymerase complexes. J. Virol. 79, 732–744 (2005)
Huarte, M. et al. Threonine 157 of influenza virus PA polymerase subunit modulates RNA replication in infectious viruses. J. Virol. 77, 6007–6013 (2003)
Fodor, E., Mingay, L. J., Crow, M., Deng, T. & Brownlee, G. G. A single amino acid mutation in the PA subunit of the influenza virus RNA polymerase promotes the generation of defective interfering RNAs. J. Virol. 77, 5017–5020 (2003)
Sugiura, A., Ueda, M., Tobita, K. & Enomoto, C. Further isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. Virology 65, 363–373 (1975)
Zurcher, T., de la Luna, S., Sanz-Ezquerro, J. J., Nieto, A. & Ortin, J. Mutational analysis of the influenza virus A/Victoria/3/75 PA protein: studies of interaction with PB1 protein and identification of a dominant negative mutant. J. Gen. Virol. 77, 1745–1749 (1996)
Hara, K. et al. Influenza virus RNA polymerase PA subunit is a novel serine protease with Ser624 at the active site. Genes Cells 6, 87–97 (2001)
Rodriguez, A., Perez-Gonzalez, A. & Nieto, A. Influenza virus infection causes specific degradation of the largest subunit of cellular RNA polymerase II. J. Virol. 81, 5315–5324 (2007)
Sanz-Ezquerro, J. J., Zurcher, T., de la Luna, S., Ortin, J. & Nieto, A. The amino-terminal one-third of the influenza virus PA protein is responsible for the induction of proteolysis. J. Virol. 70, 1905–1911 (1996)
Hara, K., Schmidt, F. I., Crow, M. & Brownlee, G. G. Amino acid residues in the N-terminal region of the PA subunit of influenza A virus RNA polymerase play a critical role in protein stability, endonuclease activity, cap binding, and virion RNA promoter binding. J. Virol. 80, 7789–7798 (2006)
Regan, J. F., Liang, Y. & Parslow, T. G. Defective assembly of influenza A virus due to a mutation in the polymerase subunit PA. J. Virol. 80, 252–261 (2006)
Toyoda, T., Adyshev, D. M., Kobayashi, M., Iwata, A. & Ishihama, A. Molecular assembly of the influenza virus RNA polymerase: determination of the subunit–subunit contact sites. J. Gen. Virol. 77, 2149–2157 (1996)
Ohtsu, Y., Honda, Y., Sakata, Y., Kato, H. & Toyoda, T. Fine mapping of the subunit binding sites of influenza virus RNA polymerase. Microbiol. Immunol. 46, 167–175 (2002)
Perez, D. R. & Donis, R. O. Functional analysis of PA binding by influenza a virus PB1: effects on polymerase activity and viral infectivity. J. Virol. 75, 8127–8136 (2001)
Gonzalez, S., Zurcher, T. & Ortin, J. Identification of two separate domains in the influenza virus PB1 protein involved in the interaction with the PB2 and PA subunits: a model for the viral RNA polymerase structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4456–4463 (1996)
Gabriel, G. et al. Differential polymerase activity in avian and mammalian cells determines host range of influenza virus. J. Virol. 81, 9601–9604 (2007)
Tao, Y., Farsetta, D. L., Nibert, M. L. & Harrison, S. C. RNA synthesis in a cage–structural studies of reovirus polymerase λ3. Cell 111, 733–745 (2002)
Area, E. et al. 3D structure of the influenza virus polymerase complex: localization of subunit domains. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 308–313 (2004)
Torreira, E. et al. Three-dimensional model for the isolated recombinant influenza virus polymerase heterotrimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 3774–3783 (2007)
Deng, T., Vreede, F. T. & Brownlee, G. G. Different de novo initiation strategies are used by influenza virus RNA polymerase on its cRNA and viral RNA promoters during viral RNA replication. J. Virol. 80, 2337–2348 (2006)
Maier, H. J., Kashiwagi, T., Hara, K. & Brownlee, G. G. Differential role of the influenza A virus polymerase PA subunit for vRNA and cRNA promoter binding. Virology 370, 194–204 (2008)
Gonzalez, S. & Ortin, J. Distinct regions of influenza virus PB1 polymerase subunit recognize vRNA and cRNA templates. EMBO J. 18, 3767–3775 (1999)
de la Luna, S., Martinez, C. & Ortin, J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of influenza virus A/Victoria/3/75 polymerase genes: sequence evolution and prediction of possible functional domains. Virus Res. 13, 143–155 (1989)
Tarendeau, F. et al. Structure and nuclear import function of the C-terminal domain of influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit. Nature Struct. Biol. 14, 229–233 (2007)
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. in Macromolecular Crystallography, part A (eds Carter C. W. Jr & Sweet, R. M.) 307–326 (Academic, New York, 1997)
Hendrickson, W. A. Determination of macromolecular structures from anomalous diffraction of synchrotron radiation. Science 254, 51–58 (1991)
Sheldrick, G. M. Direct Methods for Solving Macromolecular Structures (ed. Fortier, S.) 401–411 (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998)
Vonrhein, C., Blanc, E., Roversi, P. & Bricogne, G. Automated structure solution with autoSHARP. Methods Mol. Biol. 364, 215–230 (2007)
Cowtan, K. D. & Zhang, K. Y. Density modification for macromolecular phase improvement. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 72, 245–270 (1999)
Abrahams, J. P. & Leslie, A. G. Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D 52, 30–42 (1996)
Perrakis, A., Morris, R. & Lamzin, V. S. Automated protein model building combined with iterative structure refinement. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 458–463 (1999)
Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 58, 1948–1954 (2002)
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 2126–2132 (2004)
Brunger, A. T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998)
Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A. & Dodson, E. J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997)
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Chen and K. Yu for providing the A/goose/Guangdong/1/96 influenza PA gene; J. Ortin and O. Llorca for supplying electron microscopy maps; C. Yang, X. Su, F. Sun, L. Wang and R.-M. Xu for advice and technical assistance; and S. Harrison, P. Kuhn, X. Chen and T. Toyoda for discussion. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 30599432 and 30221003), the Ministry of Science and Technology International Cooperation Project (grant number 2006DFB32420), the Ministry of Science and Technology 863 Project (grant numbers 2006AA02A314 and 2006AA02A322) and the Ministry of Science and Technology 973 Project (grant numbers 2006CB504300 and 2007CB914300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
The file contains Supplementary Figures and Legends S1-S5; Supplementary Tables T1 and T2.
The Supplementary Figures show a multiple sequence alignment for PAC and PB1N (S1), representative electron density (S2) and known mutation sites for the PAC structure (S3), together with in vitro binding assays for PB1N to several double-point mutants of PAC (S4) and a superposition between structures of PAC and λ3 reovirus polymerase N-terminal domain (S5). The Supplementary Table T1 includes data collection, phasing and refinement statistics for PAC:PB1N. The Supplementary Table T2 includes a prediction of the effects of several known mutations in PAC. (PDF 670 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Zhou, J., Bartlam, M. et al. Crystal structure of the polymerase PAC–PB1N complex from an avian influenza H5N1 virus. Nature 454, 1123–1126 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07120
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07120
This article is cited by
-
The ubiquitination landscape of the influenza A virus polymerase
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Multiple polymerase gene mutations for human adaptation occurring in Asian H5N1 influenza virus clinical isolates
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Exploring Ugi-Azide Four-Component Reaction Products for Broad-Spectrum Influenza Antivirals with a High Genetic Barrier to Drug Resistance
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Identification of influenza polymerase inhibitors targeting C-terminal domain of PA through surface plasmon resonance screening
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Genetic and codon usage bias analyses of polymerase genes of equine influenza virus and its relation to evolution
BMC Genomics (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.