Abstract
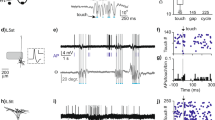
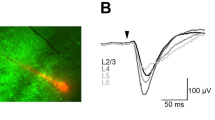
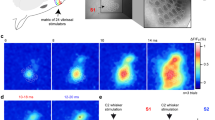
Neuronal activity in the motor cortex is understood to be correlated with movements, but the impact of action potentials (APs) in single cortical neurons on the generation of movement has not been fully determined. Here we show that trains of APs in single pyramidal cells of rat motor cortex can evoke long sequences of small whisker movements. For layer-5 pyramids, we find that evoked rhythmic movements have a constant phase relative to the AP train, indicating that single layer-5 pyramids can reset the rhythm of whisker movements. Action potentials evoked in layer-6 pyramids can generate bursts of rhythmic whisking, with a variable phase of movements relative to the AP train. An increasing number of APs decreases the latency to onset of movement, whereas AP frequency determines movement direction and amplitude. We find that the efficacy of cortical APs in evoking whisker movements is not dependent on background cortical activity and is greatly enhanced in waking rats. We conclude that in vibrissae motor cortex sparse AP activity can evoke movements.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fritsch, G. & Hitzig, E. Über die elektrische Erregbarkeit des Grosshirns. Arch. Anat. Physiol. Wiss. Med. 37, 300–332 (1870)
Asanuma, H. The Motor Cortex (Raven, New York, 1989)
Porter, R. & Lemon, R. Corticospinal Function and Voluntary Movement (Clarendon, Oxford, 1995)
Asanuma, H. & Sakata, H. Functional organization of a cortical efferent system examined with focal depth stimulation in cats. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 35–54 (1967)
Adrian, E. D. & Moruzzi, G. Impulses in the pyramidal tract. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 100, 159–191 (1939)
Evarts, E. V. Activity of pyramidal tract neurons during postural fixation. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 375–385 (1969)
Stoney, S. D. Jr, Thompson, W. D. & Asanuma, H. Excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation: effective extent of stimulating current. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 659–669 (1968)
Asanuma, H., Stoney, S. D. Jr & Abzug, C. Relationship between afferent input and motor outflow in cat motorsensory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 670–681 (1968)
Georgopoulos, A. P. Current issues in directional motor control. Trends Neurosci. 18, 506–510 (1995)
Schwartz, A. B. & Moran, D. W. Arm trajectory and representation of movement processing in motor cortical activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6, 1851–1856 (2000)
Chapin, J. K., Moxon, K. A., Markowitz, R. S. & Nicolelis, M. A. Real-time control of a robot arm using simultaneously recorded neurons in the motor cortex. Nature Neurosci. 7, 664–670 (1999)
Wessberg, J. et al. Real-time prediction of hand trajectory by ensembles of cortical neurons in primates. Nature 408, 361–365 (2000)
Taylor, D. M., Tillery, S. I. & Schwartz, A. B. Direct cortical control of 3D neuroprosthetic devices. Science 296, 1829–1832 (2002)
Schwartz, A. B., Taylor, D. M. & Tillery, S. I. Extraction algorithms for cortical control of arm prosthetics. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 701–707 (2001)
Fetz, E. E., Cheney, P. D. & German, D. C. Corticomotoneuronal connections of precentral cells detected by postspike averages of EMG activity in behaving monkeys. Brain Res. 114, 505–510 (1976)
Cheney, P. D. & Fetz, E. E. Comparable patterns of muscle facilitation evoked by individual corticomotoneuronal (CM) cells and by single intracortical microstimuli in primates: evidence for functional groups of CM cells. J. Neurophysiol. 53, 786–804 (1985)
Buys, E. J., Lemon, R. N., Mantel, G. W. H. & Muir, R. B. Selective facilitation of different hand muscles in the conscious monkey. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 381, 529–549 (1986)
Woody, C. D. & Black-Cleworth, P. Differences in excitability of cortical neurons as a function of motor projection in conditioned cats. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 1104–1116 (1973)
Lerma, J. & Garcia-Austt, E. Hippocampal theta rhythm during paradoxical sleep. Effects of afferent stimuli and phase relationships with phasic events. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 60, 46–54 (1985)
Timo-Iaria, C., Yamashita, R., Hoshino, K. & Souza-Melo, A. Rostrum movements in desynchronized sleep as a prevalent manifestation of dreaming activity in Wistar rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 23, 617–620 (1990)
Bermejo, R., Harvey, M., Gao, P. & Zeigler, H. P. Conditioned whisking in the rat. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 13, 225–233 (1996)
Bermejo, R., Vyas, A. & Zeigler, H. P. Optoelectronic monitoring of whisking trajectories in two dimensions. The topography of the rat's ‘whisking space’. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 51.8 [online] (2001)
Carvell, G. E. & Simons, D. J. Biometric analyses of vibrissal tactile discrimination in the rat. J. Neurosci. 10, 2638–2648 (1990)
Welker, W. I. Analysis of sniffing of the albino rat. Behaviour 22, 223–244 (1964)
Kleinfeld, D., Berg, R. W. & O'Connor, S. M. Anatomical loops and their electrical dynamics in relation to whisking by rat. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 16, 69–88 (1999)
Hall, R. D. & Lindholm, E. P. Organization of motor and somatosensory neocortex in the albino rat. Brain Res. 66, 23–38 (1974)
Anderson, J., Lampl, I., Reichova, I., Carandini, M. & Ferster, D. Stimulus dependence of two-state fluctuations of membrane potential in cat visual cortex. Nature Neurosci. 3, 617–621 (2000)
Cowan, R. L. & Wilson, C. J. Firing patterns and axonal projections of single corticostriatal neurons in the rat medial agranular cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 71, 17–32 (1994)
Petersen, C. C., Hahn, T. T., Mehta, M., Grinvald, A. & Sakmann, B. Interaction of sensory responses with spontaneous depolarization in layer 2/3 barrel cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13638–13643 (2003)
Leyton, A. S. F. & Sherrington, C. S. Observations on the excitable cortex of the chimpanzee, orang-utan and gorilla. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 11, 135–222 (1917)
Berg, R. W. & Kleinfeld, D. Vibrissa movement elicited by rhythmic electrical microstimulation to motor cortex in the aroused rat mimics exploratory whisking. J. Neurophysiol. 90, 2950–2963 (2003)
Eccles, J. C. Understanding of the Brain 2nd edn (McGraw Hill, New York, 1976)
Carvell, G. E., Miller, S. A. & Simons, D. J. The relationship of vibrissal motor cortex unit activity to whisking in the awake rat. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 13, 115–127 (1996)
Asanuma, H. & Ward, J. E. Patterns of contraction of distal forelimb muscles produced by intracortical stimulation in cats. Brain Res. 27, 97–109 (1971)
Hattox, A. M., Priest, C. A. & Keller, A. Functional circuitry involved in the regulation of whisker movements. J. Comp. Neurol. 442, 266–276 (2002)
Gao, P., Bermejo, R. & Zeigler, H. P. Whisker deafferentation and rodent whisking patterns: behavioral evidence for a central pattern generator. J. Neurosci. 21, 5374–5380 (2001)
Hattox, A., Li, Y. & Keller, A. Serotonin regulates rhythmic whisking. Neuron 17, 343–352 (2003)
Jones, E. G. in Cerebral Cortex Vol. 1 (eds Jones, E. G. & Peters, A.) 521–553 (Plenum, New York, 1984)
Jankowska, E., Padel, Y. & Tanaka, R. The mode of activation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical tract cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 249, 617–636 (1975)
Phillips, C. G. & Porter, R. Corticospinal Neurons. Their Role in Movement (Academic, London, 1977)
Rockel, A. J., Hiorns, R. W. & Powell, T. P. The basic uniformity in structure of the neocortex. Brain 103, 221–244 (1980)
Moore, C. I. & Nelson, S. B. Spatio-temporal subthreshold receptive fields in the vibrissa representation of rat primary somatosensory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 2882–2892 (1998)
Zhu, J. J. & Connors, B. W. Intrinsic firing patterns and whisker-evoked synaptic responses of neurons in the rat barrel cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 1171–1183 (1999)
Brecht, M. & Sakmann, B. Dynamic representation of whisker deflection by postsynaptic potentials in morphologically reconstructed spiny stellate and pyramidal cells in the barrels and septa of layer 4 in rat somatosensory cortex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 543, 49–70 (2002)
Margrie, T. W., Brecht, M. & Sakmann, B. In vivo, low-resistance, whole-cell recordings from neurons in the anaesthetized and awake mammalian brain. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 444, 491–498 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Manns, R. Friedrich, C. Schwarz, W. Denk and S. Petrou for comments and R. Erickson for inspiration; E. Heil, M. Kaiser, R. Rödel, P. Mayer and K. Schmidt for technical assistance; and A. Krauss, S. Muhammad, S. Bellanca and L. Sinai-Esfahani for help with cell staining and reconstruction. This work was supported by the Max Planck Society, the NHMRC of Australia and the Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1
Comparison of L5- and L6-cell stimulation effects. (PDF 27 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Effect of action potential frequency and number on evoked movements: averaged traces. (PDF 36 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Interaction of initiated action potentials with cortical up states and down states. (PDF 567 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
Whisker movements evoked by intracellular stimulation of an L6 cell. (MP4 2457 kb)
Supplementary Movie 2
Whisker movements evoked by intracellular stimulation of an L5 cell. (MP4 2493 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brecht, M., Schneider, M., Sakmann, B. et al. Whisker movements evoked by stimulation of single pyramidal cells in rat motor cortex. Nature 427, 704–710 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02266
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02266
This article is cited by
-
Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves the motor function of middle-aged mice by restoring the neuronal activity of the motor cortex
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Evolution of prefrontal cortex
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Neuronal hyperexcitability in Alzheimer’s disease: what are the drivers behind this aberrant phenotype?
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Population imaging discrepancies between a genetically-encoded calcium indicator (GECI) versus a genetically-encoded voltage indicator (GEVI)
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Neurogenesis of medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens continues into adulthood and is enhanced by pathological pain
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.