Abstract
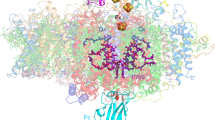
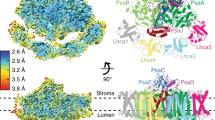
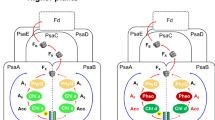
Oxygenic photosynthesis is the principal producer of both oxygen and organic matter on Earth. The conversion of sunlight into chemical energy is driven by two multisubunit membrane protein complexes named photosystem I and II. We determined the crystal structure of the complete photosystem I (PSI) from a higher plant (Pisum sativum var. alaska) to 4.4 Å resolution. Its intricate structure shows 12 core subunits, 4 different light-harvesting membrane proteins (LHCI) assembled in a half-moon shape on one side of the core, 45 transmembrane helices, 167 chlorophylls, 3 Fe–S clusters and 2 phylloquinones. About 20 chlorophylls are positioned in strategic locations in the cleft between LHCI and the core. This structure provides a framework for exploration not only of energy and electron transfer but also of the evolutionary forces that shaped the photosynthetic apparatus of terrestrial plants after the divergence of chloroplasts from marine cyanobacteria one billion years ago.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chitnis, P. R. Photosystem I: Function and physiology. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant. Mol. Biol. 52, 593–626 (2001)
Barber, J. Photosystem II: a multisubunit membrane protein that oxidises water. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12, 523–530 (2002)
Junge, W. ATP synthase and other motor proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4735–4737 (1999)
Cramer, W. A. et al. Some new structural aspects and old controversies concerning the cytochrome b(6)f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 47, 477–508 (1996)
Herrmann, R. G. Biogenesis and evolution of photosynthetic (thylakoid) membranes. Biosci. Rep. 19, 355–365 (1999)
Trissl, H.-W. & Wilhelm, C. Why do thylakoid membranes from higher plants form grana stacks? Trends Biochem. Sci. 18, 415–419 (1993)
Bailey, S., Walters, R. G., Jansson, S. & Horton, P. Acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to the light environment: the existence of separate low light and high light responses. Planta 213, 794–801 (2001)
Durnford, D. G. et al. A phylogenetic assessment of the eukaryotic light-harvesting antenna proteins, with implications for plastid evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 48, 59–68 (1999)
Croce, R., Morosinotto, T., Castelletti, S., Breton, J. & Bassi, R. The Lhca antenna complexes of higher plants photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1556, 29–40 (2002)
Jordan, P. et al. Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 411, 909–917 (2001)
Ben-Shem, A., Nelson, N. & Frolow, F. Crystallization and initial X-ray diffraction studies of higher plant photosystem I. Acta Crystallogr. D 59, 1824–1827 (2003)
Scheller, H. V., Jensen, P. E., Haldrup, A., Lunde, C. & Knoetzel, J. Role of subunits in eukaryotic Photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1507, 41–60 (2001)
Jansson, S., Andersen, B. & Scheller, H. V. Nearest-neighbor analysis of higher-plant photosystem I holocomplex. Plant Physiol. 112, 409–420 (1996)
Kargul, J., Nield, J. & Barber, J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of a light-harvesting complex I-photosystem I (LHCI-PSI) supercomplex from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Insights into light harvesting for PSI. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 16135–16141 (2003)
Ihalainen, J. A. et al. Pigment organization and energy transfer dynamics in isolated photosystem I (PSI) complexes from Arabidopsis thaliana depleted of the PSI-G, PSI-K, PSI-L, or PSI-N subunit. Biophys. J. 83, 2190–2201 (2002)
Schmid, V. H., Paulsen, H. & Rupprecht, J. Identification of N- and C-terminal amino acids of Lhca1 and Lhca4 required for formation of the heterodimeric peripheral photosystem I antenna LHCI-730. Biochemistry 41, 9126–9131 (2002)
Ganeteg, U., Strand, A., Gustafsson, P. & Jansson, S. The properties of the chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins Lhca2 and Lhca3 studied in vivo using antisense inhibition. Plant Physiol. 127, 150–158 (2001)
Knoetzel, J., Mant, A., Haldrup, A., Jensen, P. E. & Scheller, H. V. PSI-O, a new 10-kDa subunit of eukaryotic photosystem I. FEBS Lett. 510, 145–148 (2002)
Lunde, C. P., Jensen, P. E., Haldrup, A., Knoetzel, J. & Scheller, H. V. The PSI-H subunit of photosystem I is essential for state transitions in plant photosynthesis. Nature 408, 613–615 (2000)
Hippler, M. et al. The plastocyanin binding domain of photosystem I. EMBO J. 15, 6374–6384 (1996)
Raymond, J., Zhaxybayeva, O., Gogarten, J. P., Gerdes, S. Y. & Blankenship, R. E. Whole-genome analysis of photosynthetic prokaryotes. Science 298, 1616–1620 (2002)
Xiong, J. & Bauer, C. E. Complex evolution of photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 53, 503–521 (2002)
Kuhlbrandt, W., Wang, D. N. & Fujiyoshi, Y. Atomic model of plant light-harvesting complex by electron crystallography. Nature 367, 614–621 (1994)
Jansson, S. A. Guide to the Lhc genes and their relatives in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 4, 236–240 (1999)
Morosinotto, T., Castelletti, S., Breton, J., Bassi, R. & Croce, R. Mutation analysis of Lhca1 antenna complex. Low energy absorption forms originate from pigment–pigment interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 36253–36261 (2002)
Moseley, J. L. et al. Adaptation to Fe-deficiency requires remodeling of the photosynthetic apparatus. EMBO J. 21, 6709–6720 (2002)
Schmid, V. H. et al. Pigment binding of photosystem I light-harvesting proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 37307–37314 (2002)
Croce, R., Zucchelli, G., Garlaschi, F. M. & Jennings, R. C. A thermal broadening study of the antenna chlorophylls in PSI-200, LHCI, and PSI core. Biochemistry 37, 17355–17360 (1998)
Rivadossi, A., Zucchelli, G., Garlaschi, F. M. & Jennings, R. C. The importance of PSI chlorophyll red forms in light-harvesting by leaves. Photosynth. Res. 60, 209–215 (1999)
Jennings, R. C., Zucchelli, G., Croce, R. & Garlaschi, F. M. The photochemical trapping rate from red spectral states in PSI-LHCI is determined by thermal activation of energy transfer to bulk chlorophylls. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1557, 91–98 (2003)
Bengis, C. & Nelson, N. Subunit structure of chloroplast photosystem I reaction center. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 4564–4569 (1977)
Xue, Y., Okvist, M., Hansson, O. & Young, S. Crystal structure of spinach plastocyanin at 1.7 Å resolution. Protein Sci. 7, 2099–2105 (1998)
Sommer, F., Drepper, F. & Hippler, M. The luminal helix l of PsaB is essential for recognition of plastocyanin or cytochrome c6 and fast electron transfer to photosystem I in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6573–6581 (2002)
Chitnis, P. R., Purvis, D. & Nelson, N. Molecular cloning and targeted mutagenesis of the gene psaF encoding subunit III of photosystem I from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp PCC 6803. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 20146–20151 (1991)
Hippler, M., Drepper, F., Haehnel, W. & Rochaix, J. D. The N-terminal domain of PsaF: precise recognition site for binding and fast electron transfer from cytochrome c6 and plastocyanin to photosystem I of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7339–7344 (1998)
Bibby, T. S., Nield, J. & Barber, J. Iron deficiency induces the formation of an antenna ring around trimeric photosystem I in cyanobacteria. Nature 412, 743–745 (2001)
Boekema, E. J. et al. A giant chlorophyll–protein complex induced by iron deficiency in cyanobacteria. Nature 412, 745–748 (2001)
Nield, J., Morris, E. P., Bibby, T. S. & Barber, J. Structural analysis of the photosystem I supercomplex of cyanobacteria induced by iron deficiency. Biochemistry 42, 3180–3188 (2003)
Melkozernov, A. N., Lin, S., Bibby, T. S., Barber, J. & Blankenship, R. E. Time-resolved absorption and emission show that the CP43′ antenna ring of iron-stressed Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 is efficiently coupled to the photosystem I reaction center core. Biochemistry 42, 3893–3903 (2003)
Nelson, N. & Ben-Shem, A. Photosystem I reaction center: Past and future. Photosynth. Res. 73, 193–206 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the ESRF for synchrotron beam time, and staff scientists of the ID14 stations cluster for their assistance. We thank W. Kuhlbrandt for LHCII coordinates. A.B. is a recipient of a Charles Clore Foundation Ph.D. student scholarship. This work was supported by a grant from The Israel Science Foundation to N.N. and F.F.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Shem, A., Frolow, F. & Nelson, N. Crystal structure of plant photosystem I. Nature 426, 630–635 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02200
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02200
This article is cited by
-
Nanosecond time-resolved infrared spectroscopy for the study of electron transfer in photosystem I
Photosynthesis Research (2024)
-
Uphill energy transfer mechanism for photosynthesis in an Antarctic alga
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Analysis of Lhc family genes reveals development regulation and diurnal fluctuation expression patterns in Cyperus esculentus, a Cyperaceae plant
Planta (2023)
-
The location of the low-energy states in Lhca1 favors excitation energy transfer to the core in the plant PSI-LHCI supercomplex
Photosynthesis Research (2023)
-
Spectral diversity of photosystem I from flowering plants
Photosynthesis Research (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.