Abstract
Tumour-necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is an important protein that regulates inflammation, immunity, cell survival and cell death in response to infection or chronic stress1,2,3,4,5. De Smaele et al. report that the gene encoding an inducible cellular factor, Gadd45β (for 'growth arrest and DNA damage'), is essential for promoting TNF-α-mediated cell survival6. However, we show here that neither TNF-α signalling nor cell survival is affected in mice lacking gadd45β, a fact which demonstrates that genes other than gadd45β (refs 5, 7) might regulate cell survival in response to TNF-α.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
TNF-α concomitantly activates two signalling pathways — a cell-survival pathway regulated by the transcription factor NF-κB and a cell-death pathway associated with the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) cascade1,2,3,5. Understanding the molecular basis for the cell's choice between life and death in response to TNF-α is a topic of intense investigation4,5. The fate of a cell exposed to TNF-α is determined by cross-talk between these two signalling pathways4,5,6,7: NF-κB activation switches on genes that blunt the pro-cell-death activity of the JNK pathway4,6,7.
De Smaele et al. propose that one such NF-κB target that is essential in TNF-α-mediated cell survival is the gadd45β gene6. Gadd45β (also termed MyD118) encodes one of the family of Gadd45 proteins, which are implicated in growth arrest, DNA-damage repair and programmed cell death8,9. De Smaele et al. showed that ectopic overexpression of Gadd45β in mouse-embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) and in NF-κB-deficient cell lines antagonizes TNF-α-induced cell death and increases cell survival. In addition, ectopic expression of antisense gadd45β messenger RNA, which presumably blocks Gadd45β expression, was found to decrease cell survival and prolong JNK activity; this is similar to the response in cells lacking NF-κB. The authors conclude6 that TNF-α-mediated activation of NF-κB induces Gadd45β, which inhibits TNF-α-mediated cell death and JNK signalling and promotes cell survival; however, this conclusion contradicts an earlier study10 that implicates Gadd45β as an activator of JNK.
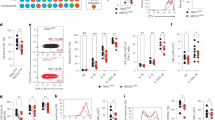
We used gadd45β-null mice, in which the gadd45β gene is ablated (D.L. and A.F., unpublished results), to assess further the effect of gadd45β deficiency on TNF-α-mediated cellular responses, including cell survival and JNK signalling. We found that TNF-α induced gadd45β expression in wild-type but not in gadd45β-deficient MEFs (Fig. 1a). Like wild-type MEFs, gadd45β-deficient (gadd45β−/−) MEFs were not susceptible to TNF-α-mediated cell death (Fig. 1b). However, in the presence of the protein-synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide, which prevents the expression of the pro-survival genes induced by NF-κB, both gadd45β−/− and wild-type MEFs were equally susceptible to TNF-α-mediated cell death.
a, TNF-α induces expression of gadd45β in wild-type (WT) but not in gadd45−/− mouse-embryo fibroblasts (MEFs). RNA from cells collected at different times after treatment with TNF-α (1,000 U ml−1) was resolved on a 2% agarose–formaldehyde gel and analysed by northern blotting using a 32P-labelled gadd45β probe. 28S RNA, loading control. b, gadd45β−/− cells are not susceptible to TNF-α-mediated cell death in the absence of cycloheximide (CHX). Viability of WT (left bars) and gadd45β−/− MEFs (right bars) was determined by trypan-blue staining after 14-h treatment with TNF-α (1,000 U ml−1), CHX (1 mg ml−1) or both. c, Gadd45β is not required for rapid downregulation of JNK after TNF-α treatment. MEFs from WT and gadd45β−/− mice were treated with TNF-α (1,000 U ml−1) and, at the indicated times, cell lysates were resolved by SDS–PAGE and western blotted (antibody probes: antiphospho-JNK, anti-JNK; Cell Signaling, Inc). A fusion protein of glutathione-S-transferase and c-Jun was used as substrate in the JNK assay (bottom).
Our findings indicate that gadd45β expression is not essential for the NF-κB pro-survival function. Furthermore, the kinetics of downregulation of JNK activity were similarly rapid in gadd45β−/− MEFs and in wild-type cells (Fig.1c), as well as in another cell type, splenic lymphocytes (data not shown).
Our results indicate that other NF-κB target genes5,7 are more likely than gadd45β to be primary mediators of the survival function of NF-κB. The discrepancy between our observations and those of De Smaele et al.6 might reflect limitations in their experimental approach — for example, ectopic overexpression of gadd45β or of its antisense RNA in cells stimulated with TNF-α might have affected cell survival and JNK activity in some indirect or nonspecific way. Further work is needed to assess what role, if any, Gadd45β has in the cell's response to TNF-α.
References
Baud, V. & Karin, M. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 372–377 (2001).
Locksley, R. M., Killeen, N. & Lenardo, M. J. Cell 104, 487–501 (2001).
Chen, G. & Goeddel, D.V. Science 296, 1634–1635 (2002).
Kyriakis, J. M. Nature 414, 265–266 (2001).
Karin, M. & Lin, A. Nature Immunol. 3, 221–227 ( 2002).
De Smaele, E. et al. Nature 414, 308–313 (2001).
Tang, G. et al. Nature 414, 313–317 (2001).
Liebermann, D. A. & Hoffman, B. Leukemia 16, 527–541 (2002).
Fornace, A. J. Jr, Jackman, J., Hollander, M. C., Hoffman-Liebermann, B. & Liebermann, D. A. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 663, 139–153 (1992).
Takekawa, M. & Saito, H. Cell 95, 521–530 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amanullah, A., Azam, N., Balliet, A. et al. Cell survival and a Gadd45-factor deficiency. Nature 424, 741 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/424741b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/424741b
This article is cited by
-
Burn injury induces elevated inflammatory traffic: the role of NF-κB
Inflammation Research (2021)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiR-362-5p promotes the malignancy of chronic myelocytic leukaemia via down-regulation of GADD45α
Molecular Cancer (2015)
-
Gadd45α as an upstream signaling molecule of p38 MAPK triggers oxidative stress-induced sFlt-1 and sEng upregulation in preeclampsia
Cell and Tissue Research (2011)
-
Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Cell Signaling
Molecules and Cells (2011)
-
Protective effects of selenocystine against γ-radiation-induced genotoxicity in Swiss albino mice
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.