Abstract
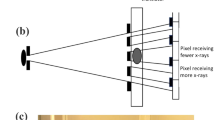
Fresnel zone plates consisting of alternating transmissive and opaque circular rings can be used to focus X-rays1. The spatial resolution that can be achieved with these devices is of the order of the width of the outermost zone and is therefore limited by the smallest structure (20–40 nm) that can be fabricated by lithography today2. Here we show that a large number of pinholes distributed appropriately over the Fresnel zones make it possible to focus soft X-rays to spot sizes smaller than the diameter of the smallest pinhole. In addition, higher orders of diffraction and secondary maxima can be suppressed by several orders of magnitude. In combination with the next generation of synchrotron light sources (free-electron lasers) these ‘photon sieves’ offer new opportunities for high-resolution X-ray microscopy and spectroscopy in physical and life sciences.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thieme, J., Schmahl, G., Rudolph, D. & Umbach, E. X-Ray Microscopy and Spectroscopy IV-3–IV-110 (Springer, Berlin, 1996).
Anderson, E. H., Boegli, V. & Muray, L. P. Electron beam lithography digital pattern generator and electronics for generalized curvilinear structures. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 13, 2529–2534 (1995).
Attwood, D. Soft X-Rays and Extreme Ultraviolet Radiation (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2000).
Bilderback, D. H. & Thiel, D. J. Microbeam generation with capillary optics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66, 2059–2063 (1995).
Snigirev, A., Kohn, V., Snigireva, I. & Lengeler, B. A compound refractive lens for focusing high-energy X-rays. Nature 384, 49–51 (1996).
Schmahl, G., Rudolph, D., Guttmann, P. & Christ, O. in Zone Plates for X-ray Microscopy Vol. 43 X-ray Microscopy (eds Schmahl, G. & Rudolph, D.) 63–74 (Springer Series in Optical Sciences, Academic, London, 1984).
Michette, A. G. Optical Systems for Soft X-Rays 193–194 (Plenum, New York, 1986).
Spector, S. J., Jacobsen, C. J. & Tennant, D. M. Process optimization for production of sub-20 nm soft X-ray zone plates. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 15, 2872–2876 (1997).
Cappellini, V., Constantinides, A. G. & Emiliani, P. Digital Filters and their Applications Vol. 4 Techniques of Physics (eds March, N. H. & Daglish, H. N.) 65–74 (Springer, Berlin, 1981).
Acknowledgements
Discussions with B. Niemann and G. Schmahl are gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported in part by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kipp, L., Skibowski, M., Johnson, R. et al. Sharper images by focusing soft X-rays with photon sieves. Nature 414, 184–188 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35102526
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35102526
This article is cited by
-
Free light-shape focusing in extreme-ultraviolet radiation with self-evolutionary photon sieves
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Economical generation of high-quality optical vortices with gradual-width Fermat spiral slit mask
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
Transparent and Flexible Photon Sieve Made with Cellulose Nanofiber by Micro-Nano Structure Molding
International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology (2022)
-
A new trifocal corneal inlay for presbyopia
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Single shot multispectral multidimensional imaging using chaotic waves
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.