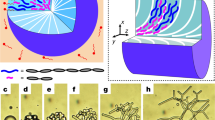
Abstract
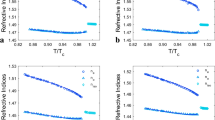
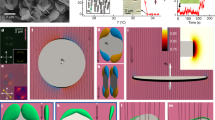
Complex fluids1,2 are usually produced by mixing together several distinct components, the interactions between which can give rise to unusual optical and rheological properties of the system as a whole. For example, the properties of microemulsions (composed of water, oil and surfactants) are determined by the microscopic structural organization of the fluid that occurs owing to phase separation of the component elements. Here we investigate the effect of introducing an additional organizing factor into such a fluid system, by replacing the oil component of a conventional water-in-oil microemulsion with an intrinsically anisotropic fluid—a nematic liquid crystal. As with the conventional case, the fluid phase-separates into an emulsion of water microdroplets (stabilized by the surfactant as inverse micelles) dispersed in the ‘oil’ phase. But the properties are further influenced by a significant directional coupling between the liquid-crystal molecules and the surfactant tails that emerge (essentially radially) from the micelles. The result is a modified bulk-liquid crystal that is an ordered nematic at the mesoscopic level, but which does not exhibit the strong light scattering generally associated with bulk nematic order2: the bulk material here is essentially isotropic and thus transparent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daoud, M. & Williams, C. E. (eds) Soft Matter Physics (Springer, Berlin, 1999).
de Gennes, P. G. & Prost, J. Physics of Liquid Crystals 2nd edn (Clarendon, Oxford, 1993).
Poulin, P., Raghunathan, V. A., Richetti, P. & Roux, D. On the dispersion of latex particles in a nematic solution. I. Experimental evidence and simple model. J. Phys. II 4, 1557–1569 (1994).
Fabre, P., Casagrande, C., Veyssie, M., Cabuil, V. & Massart, R. Ferrosmectics: A new magnetic and mesomorphic phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 539–542 (1990).
Ott, A., Urbach, W., Langevin, D., Ober, R. & Waks, M. Light scattering study of surfactant multilayers elasticity. Role of incorporated proteins. Europhys. Lett. 12, 395– 400 (1990).
Lubensky, T. C., Pettry, D., Currier, N. & Stark, H. Topological defects and interactions in nematic emulsions. Phys. Rev. B 57, 610–625 (1998).
Poulin, P. & Weitz, D. A. Inverted and multiple nematic emulsions. Phys. Rev. E 57, 626–637 (1998).
Terentjev, E. M. Stability of liquid crystalline macroemulsions. Europhys. Lett. 32, 607–612 ( 1995).
Terentjev, E. M. in Modern Aspects of Colloidal Dispersions (eds Ottewill, R. H. & Rennie, A. R.) 257–267 (Kluwer Academic, London, 1998).
Bellini, T. et al. Phase behavior of the liquid crystal 8CB in a silica aerogel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 788– 791 (1992).
Wu, L., Zhou, B., Garland, C. W., Bellini, T. & Schaefer, D. W. Heat-capacity study of nematic-isotropic and nematic-smectic-A transitions for octylcyanobiphenyl in silica aerogels. Phys. Rev. E 51, 2157–2165 ( 1995).
Copic, M. & Mertelj, A. Reorientation in random potential: A model for glasslike dynamics in confined liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1449–1452 (1998).
Clarke, S. M., Terentjev, E. M., Kundler, I. & Finkelmann, H. Texture evolution during the polydomain-monodomain transition in nematic elastomers. Macromolecules 31, 4862– 4872 (1998).
Fridrikh, S. V. & Terentjev, E. M. Order-disorder transition in an external field in random ferromagnets and nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 4661– 4664 (1997).
Kuksenok, O. V., Ruhwandl, R. W., Shiyanovskii, S. V. & Terentjev, E. M. Director structure around a colloid particle suspended in a nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 54, 5198– 5203 (1996).
Grawford, G. P., Ondris-Crawford, R. J., Doane, J. W. & Zumer, S. Systematic study of orientational wetting and anchoring at a liquid-crystal-surfactant interface. Phys. Rev. E 53, 3647– 3661 (1996).
Seo, D.-S., Kobayashi, S., Kang, D.-Y. & Yokoyama, H. Effects of rubbing and temperature dependence of polar anchoring strength of homogeneously aligned nematic liquid crystal on polyimide Langmuir-Blodgett orientation films. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 34, 3607–3611 (1995).
Iannacchione, G. S., Crawford, G. P., Zumer, S., Doane, J. W. & Finotello, D. Randomly constrained orientational order in porous glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 2595–2598 (1993).
Lammert, P. E., Rokhsar, D. S. & Toner, J. Topology and nematic ordering. I. A gauge theory. Phys. Rev. E 52, 1778–1800 (1995).
Toner, J., Lammert, P. E. & Rokhsar, D. S. Topology and nematic ordering. II. Observable critical behavior. Phys. Rev. E 52, 1801– 1810 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Takahashi for DSC measurements. H.T. is also grateful to T. C. Lubensky, E. M. Terentjev and S. Zumer for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, J., Tanaka, H. Transparent nematic phase in a liquid-crystal-based microemulsion. Nature 409, 321–325 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35053035
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35053035
This article is cited by
-
Nanoparticle-based hollow microstructures formed by two-stage nematic nucleation and phase separation
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Photopyroelectric Calorimetry Investigations of 8CB Liquid Crystal–Microemulsion System
International Journal of Thermophysics (2018)
-
Diffusion properties of liquid crystal-based microemulsions
Colloid and Polymer Science (2014)
-
Zigzag line defects and manipulation of colloids in a nematic liquid crystal in microwrinkle grooves
Nature Communications (2012)
-
Liquid-crystal-mediated self-assembly at nanodroplet interfaces
Nature (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.