Abstract
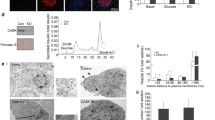
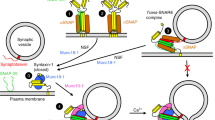
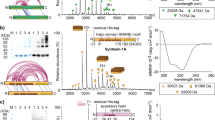
Associations between proteins present on neurotransmitter-containing vesicles and on the presynaptic membrane are thought to underlie docking and fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane, which are obligate steps in regulated neurotransmission1–4. SNAP-25 resides on the plasma membrane and interacts with syntaxin (a plasma membrane t-SNARE) and VAMP (a vesicle v-SNARE)1–9 to form a core protein complex thought to be an intermediate in a biochemical pathway that is essential for vesicular transport. We have now characterized a protein, Hrs-2, that interacts with SNAP-25. The binding of Hrs-2 to SNAP-25 is inhibited by calcium in the physiological concentration range that supports synaptic transmission. Furthermore, Hrs-2 binds and hydrolyses nucleoside triphosphates with kinetics that suggest that ATP is the physiological substrate for this enzyme. Hrs-2 is expressed throughout the brain and is present in nerve terminals. Moreover, recombinant Hrs-2 inhibits calcium-triggered 3H-noradrenaline release from permeabilized PC 12 cells. Our results suggest a role for Hrs-2 in regulating secretory processes through calcium- and nucleotide-dependent modulation of vesicle-trafficking protein complexes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, M. K. & Scheller, R. H. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 63, 63–100 (1994).
Scheller, R. H. Neuron 14, 893–897 (1995).
Söllner, T. et al. Nature 362, 318–324 (1993).
Sollner, T., Bennett, M. K., Whiteheart, S. W., Scheller, R. H. & Rothman, J. E. Cell 75, 409–418 (1993).
Chapman, E. R., An, S., Barton, N. & Jahn, R. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 27427–27432 (1994).
Südhof, T. C. Nature 375, 645–653 (1995).
Pevsner, J. et al. Neuron 13, 353–361 (1994).
Rothman, J. E. Nature 372, 55–63 (1994).
Oyler, G. A. et al. J. Cell. Biol. 109, 3039–3052 (1989).
Fields, S. & Song, O. Nature 340, 245–246 (1989).
Komada, M. & Kitamura, N. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 6213–6221 (1995).
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. Nature 349, 117–127 (1991).
Nishimura, M. Br. J. Pharmacol. 93, 430–436 (1988).
Wang, Y. X. & Quastel, D. M. Pflugers Arch. 415, 582–587 (1990).
Smith, S. & Augustine, G. Trends Neurosci. 11, 458–464 (1988).
Whiteheart, S. W. et al. J. Cell. Biol. 126, 945–954 (1994).
Tagaya, M., Wilson, D. W., Brunner, M., Arango, N. & Rothman, J. E. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 2662–26666 (1993).
Morgan, A., Dimaline, R. & Burgoyne, R. D. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 29347–29350 (1994).
Hay, J. C. & Martin, T. F. J. Cell. Biol. 119, 139–151 (1992).
Kemler, R. Trends Genet. 9, 317–321 (1993).
Parsons, T. D., Coorssen, J. R., Horstmann, H. & Almers, W. Neuron 15, 1085–1096 (1995).
Gietz, R. D. & Schiestl, R. H. Yeast 7, 253–263 (1991).
Kozak, M. Cell 44, 283–292 (1986).
Lomneth, R., Martin, T. F. & DasGupta, B. R. J. Neurochem. 57, 1413–1421 (1991).
Dever, T. E., Glynias, M. J. & Merrick, W. C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 1814–1818 (1987).
Cheng, Y.-S. E., Patterson, C. & Staeheli, P. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 4717–4725 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bean, A., Seifert, R., Chen, Y. et al. Hrs-2 is an ATPase implicated in calcium-regulated secretion. Nature 385, 826–829 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385826a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385826a0
This article is cited by
-
Growth factor receptor trafficking as a potential therapeutic target in pediatric cancer
Frontiers in Biology (2012)
-
Hrs inhibits citron kinase-mediated HIV-1 budding via its FYVE domain
Protein & Cell (2011)
-
The Chediak-Higashi Protein Interacts with SNARE Complex and Signal Transduction Proteins
Molecular Medicine (2002)
-
SNARE-mediated membrane fusion
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2001)
-
Snapin: a SNARE–associated protein implicated in synaptic transmission
Nature Neuroscience (1999)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.