Abstract
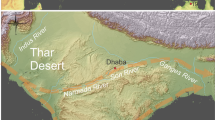
The Oldowan Stone tool industry was named for 1.8-million-year-old (Myr) artefacts found near the bottom of Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. Subsequent archaeological research in the Omo (Ethiopia) and Turkana (Kenya) also yielded stone tools dated to 2.3 Myr. Palaeoanthropological investigations in the Hadar region of the Awash Valley of Ethiopia1, revealed Oldowan assemblages in the adjacent Gona River drainage2. We conducted field work in the Gona study area of Ethiopia between 1992 and 1994 which resulted in additional archaeological discoveries as well as radio-isotopic age control and a magnetic polarity stratigraphy of the Gona sequence. These occurrences are now securely dated between 2.6–2.5 Myr. The stone tools are thus the oldest known artefacts from anywhere in the world. The artefacts show surprisingly sophisticated control of stone fracture mechanics, equivalent to much younger Oldowan assemblages of Early Pleistocene age. This indicates an unexpectedly long period of technological stasis in the Oldowan.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johanson, D. C. et al. Am. J. Phys. Anth. 57, 373–402 (1982).
Corvinus, G. & Roche, H. L'Anthropologie 80, 315–324 (1976).
Harris, J. W. K. Afr. Arch. Rev. 1, 3–31 (1983).
Harris, J. W. K. & Semaw, S. Nyame Akuma 31, 19–21 (1989).
Roche, H. & Tiercelin, J. J. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci. Paris 284D, 1871–1874 (1977).
Kimbel, W. H. et al. Nature 368, 449–451 (1994).
McDougall, I. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 2349–2352 (1992).
Leakey, M. D. Olduvai Gorge Vol. 3 (Cambridge University Press, UK, 1971).
Isaac, G. L. in Earliest Man and Environments in the Lake Rudolf Basin (eds Coppens, Y., Howell, F. C., Isaac, G. L. & Leakey, R. E. F.) 552–564 (University of Chicago Press, Illinois, 1976).
Chavaillon, J. in Earliest Man and Environments in the Lake Rudolf Basin (eds Coppens, Y., Howell, F. C., Isaac, G. L. & Leakey, R. E. F.) 565–573 (University of Chicago Press, Illinois, 1976).
Merrick, H. V. & Merrick, J. P. S. in Earliest Man and Environments in the Lake Rudolf Basin (eds Coppens, Y, Howell, F. C., Isaac, G. L. & Leakey, R. E. F.) 574–589 (University of Chicago Press, Illinois, 1976).
Kibunjia, M. J. Hum. Evol. 27, 159–171 (1994).
Toth, N. J. Archaeol. Sci. 12, 101–120 (1985).
Piperno, M. in Hominidae: Proc. 2nd Intern. Congr. Hum. Paleont. 189–195 (Jaca Books, Milan, Italy, 1989).
Gowlett, J. A. J. in Stone Age Prehistory (eds Bailey, G. N. & Callow, P.) 243–260 (Cambridge University Press, UK, 1986).
Isaac, G. LI. & Curtis, G. H. Nature 249, 624–627 (1974).
Asfaw, B. et al. Nature 360, 732–735 (1992).
Dominguez-Rodrigo, M. Complutum 7, 7–15 (1996).
Walker, A. et al. Nature 322, 517–522 (1986).
Hill, A. et al. Nature 355, 719–722 (1992).
Vrba, E. S. in Evolutionary History of the Robust Australopithecines (ed. Grine, F.) 405–426 (de Gruyter, New York, 1988).
deMenocal, P. B. Science 270, 53–59 (1995).
Renne, P. R. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1067–1070 (1993).
Deino, A. & Potts, R. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 8453–8470 (1990).
WoldeGabriel, G. et al. Nature 371, 330–333 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semaw, S., Renne, P., Harris, J. et al. 2.5-million-year-old stone tools from Gona, Ethiopia. Nature 385, 333–336 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385333a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385333a0
This article is cited by
-
Long-term behavioral adaptation of Oldowan toolmakers to resource-constrained environments at 2.3 Ma in the Lower Omo Valley (Ethiopia)
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Naïve, adult, captive chimpanzees do not socially learn how to make and use sharp stone tools
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Tool wear when using natural rocks as cutting material for the turning of aluminum alloys and plastics
Production Engineering (2023)
-
Seasonality and Lithic Investment in the Oldowan
Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology (2023)
-
Design of tool grinding processes for indexable inserts made of rocks
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.