Abstract
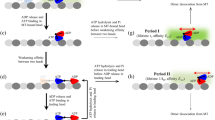
Direct measurement of the kinetics of kinesin dissociation from microtubules, the release of phosphate and ADP from kinesin, and rebinding of kinesin to the microtubule have defined the mechanism for the kinesin ATPase cycle. The processivity of ATP hydrolysis is ten molecules per site at low salt concentration but is reduced to one ATP per site at higher salt concentration. Kinesin dissociates from the microtubule after ATP hydrolysis. This step is rate-limiting. The subsequent rebinding of kinesin - ADP to the microtubule is fast, so kinesin spends only a small fraction of its duty cycle in the dissociated state. These results provide an explanation for the motility differences between skeletal myosin and kinesin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vale, R. D., Reese, T. S. & Sheetz, M. P. Cell 42, 39–50 (1985).
Brady, S. T. Nature 317, 73–75 (1985).
Scholey, J. M., Porter, M. E., Grissom, P. M. & McIntosh, J. R. Nature 318, 483–486 (1985).
Taylor, E. W. The Heart and Cardiovascular System 2nd edn 1281–1293 (Raven, New York, 1992).
Johnson, K. A. A. Rev. Biophys. biophys. Chem. 14, 161–188 (1985).
Howard, J., Hudspeth, A. J. & Vale, R. D. Nature 342, 154–158 (1989).
Uyeda, R. Q. P., Warrick, H. M., Kron, S. J. & Spudich, J. A. Nature 352, 307–311 (1991).
Greene, L. E. & Eisenberg, E. J. biol. Chem. 255, 543–548 (1980).
Gilbert, S. P. & Johnson, K. A. Biochemistry 32, 4677–4684 (1993).
Harrison, B. C. et al. Nature 362, 73–75 (1993).
Gilbert, S. P. & Johnson, K. A. Biochemistry 33, 1951–1960 (1994).
Holzbaur, E. L. F. & Johnson, K. A. Biochemistry 28, 7010–7016 (1989).
Hackney, D. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 6314–6318 (1988).
Sadhu, A. & Taylor, E. W. J. biol. Chem. 267, 11352–11359 (1992).
Brune, M., Hunter, J. L., Corrie, J. E. T. & Webb, M. R. Biochemistry 33, 8262–8271 (1994).
Woodward, S. K. A., Eccleston, J. F. & Geeves, M. A. Biochemistry 30, 422–430 (1991).
Block, S. M., Goldstein, L. S. B. & Schnapp, B. J. Nature 348, 348–352 (1990).
Romberg, L. & Vale, R. D. Nature 361, 168–170 (1993).
Stewart, R. J., Thaler, J. P. & Goldstein, L. S. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 5209–5213 (1993).
Hackney, D. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 6865–6869 (1994).
Lasek, R. J. & Brady, S. T. Nature 316, 645–647 (1985).
Barshop, B. A., Wrenn, R. F. & Frieden, C. Analyt. Biochem. 130, 134–145 (1983).
Hiratsuka, T. Biochim. biophys. Acta 742, 496–508 (1983).
Lanzetta, P. A., Alvarez, L. J., Reinach, P. S. & Candia, O. A. Analyt. Biochem. 100, 95–97 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilbert, S., Webb, M., Brune, M. et al. Pathway of processive ATP hydrolysis by kinesin. Nature 373, 671–676 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/373671a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373671a0
This article is cited by
-
Thermodynamic and mechanistic analysis of the functional properties of dengue virus NS3 helicase
Biophysical Reviews (2023)
-
New perspectives on cytoskeletal dysregulation and mitochondrial mislocalization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Translational Neurodegeneration (2021)
-
Fluorescence microscopy applied to intracellular transport by microtubule motors
Journal of Biosciences (2018)
-
Kinesin Motor Enzymology: Chemistry, Structure, and Physics of Nanoscale Molecular Machines
Biophysical Reviews (2015)
-
Kinesins with Extended Neck Linkers: A Chemomechanical Model for Variable-Length Stepping
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.