Abstract
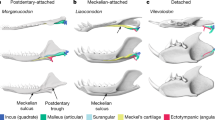
ALL described fossil and Recent cetaceans have relatively similar ear bones (malleus, incus and stapes) that strongly diverge from those of land mammals1–4. Here we report that the hearing organ of the oldest whale, Pakicetus, is the only known intermediate between that of land mammals and aquatic cetaceans (whales, dolphins and porpoises). The incus of Pakicetus is intermediate with respect to inflation, crural proportions, and position of the mallear joint. The incus and mandible of Pakicetus indicate that the path of soundwaves to its ear resembled that of land mammals. These fossils suggest that the first whale was amphibious, and corroborate the hypothesis that artiodactyls (for example, pigs, camels and ruminants) are the closest extant relatives of cetaceans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fraser, F. C. & Purves, P. E. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 152, 62–78 (1960).
Purves, P. E. in Whales, Dolphins, and Porposes (ed. Norris, K. S.) 320–378 (Univ. California Press, Berkeley, 1966).
Reysenbach de Haan, F. W. Acta otolar. Suppl. 134, 1 (1957).
Fleischer, G. Adv. Anat. embryol. Cell Biol. 55, 1–70 (1978).
Gingerich, P. D. & Russell, D. E. Contr. Mus. Paleont. Univ. Mich. 25, 235–246 (1981).
Gingerich, P. D., Wells, N. A., Russell, D. E. & Shah, S. M. I. Science 220, 402–406 (1983).
West, R. M. & Lukacs, J. R. Contr. Biol. Geol. Milwaukee Publ. Mus. 26, 1–20 (1979).
Slijper, E. J. Whales (Cornell Univ. Press, Ithaca, 1979).
Norris, K. S. in Animal Sonar Systems (eds Busnel, R.-G. & Fish, J. F.) 495–509 (Plenum, New York and London, 1980).
Doran, A. H. G. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond 1, 371–497 (1879).
Wyss, A. R. Am. Mus. Novit. 2871, 1–31 (1987).
Repenning C. A. in Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals (ed. Harrison, R. J.) 307–331 (Academic, New York, 1972).
McCormick, J. G., Wever, E. G., Palin, J. & Ridgway, S. H. J. acoust. Soc. Am. 48, 1418–1428 (1970).
McMormick, J. G., Wever, E. G., Ridgway, S. H. & Palin, J. in Animal Sonar Systems (eds Busnel R.-G. & Fish, J. F.) 449–467 (Plenum, New York and London, 1980).
Purves, P. E. & Pllleri, G. E. Echolocation in Whales and Dolphins 1–261 (Academic, London, 1983).
Ketten, D. R. in The Biology of Hearing (eds Webster, D., Fay, R., & Popper, A.) 717–750 (Springer, Berlin, 1991).
Lancaster, W. C. J. vert. Pal. 10, 117–127 (1990).
Van Valen, L. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 132, 10–126 (1966).
Miyamoto, M. M., & Goodman, M. Syst. Zool. 35, 230–240 (1986)
Goodman, M., Czelusniak, J. & Beeber, J. E. Cladistics 1, 171–185 (1985).
Novacek, M. J. Nature 356, 121–125 (1992).
Wyss, A. Nature 347, 428–429 (1990).
Oelschlager, H. A. Am. J. Anat. 177, 353–368 (1986).
Oelschlager, H. A. Gegenbaurs Morph. Jahrb. 133, 673–685 (1987).
Watkins, W. A. & Wartzok, D. Mar. mam. Sci. 1, 219–260 (1985).
Moore, P. W. B. & Schusterman, R. J. Mar. mam. Sci. 3, 31–53 (1987).
Ramprashad, F., Corey, S. & Ronald, K. Can. J. Zool. 49, 241–248 (1971).
Ramprashad, F., Corey, S. & Ronald, R. Can. J. Zool. 51, 589–600 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thewissen, J., Hussain, S. Origin of underwater hearing in whales. Nature 361, 444–445 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361444a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361444a0
This article is cited by
-
Astragali of Pakicetidae and other early-to-middle Eocene archaeocetes (Mammalia, Cetacea) of Pakistan: locomotion and habitat in the initial stages of whale evolution
PalZ (2017)
-
Anatomy and physics of the exceptional sensitivity of dolphin hearing (Odontoceti: Cetacea)
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2010)
-
The origin and early evolution of whales: macroevolution documented on the Indian Subcontinent
Journal of Biosciences (2009)
-
Eocene evolution of whale hearing
Nature (2004)
-
Skeletons of terrestrial cetaceans and the relationship of whales to artiodactyls
Nature (2001)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.