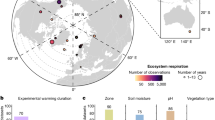
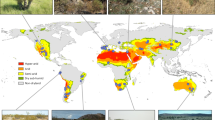
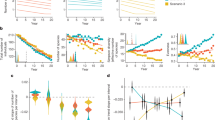
Abstract
THE suggestion that the densities of organisms are regulated by interactions involving entire food chains1 has resurfaced into a new debate about the role of population regulation in environments that vary in productivity2–5. Past work has shown that density responses of organisms to enhanced productivity should be strongly affected by the number of trophic levels in the food chain6–11 but more recent theoretical work on this question has suggested that heterogeneity within a trophic level can be just as important12–15. Here we present direct experimental evidence for such an interaction between environmental productivity and the species composition of herbivores. Our results illustrate that differences in food-web structure similar to those documented in natural communities16,17 can dramatically alter how organisms will respond to abiotic factors such as nutrients that regulate primary productivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hairston, N. G., Smith, F. E. & Slobodkin, L. B. Am. Nat. 94, 421–425 (1960).
Hunter, M. D. & Price, P. W. Ecology 73, 724–732 (1992).
Power, M. E. Ecology 73, 733–746 (1992).
Strong, D. R. Ecology 73, 747–754 (1992).
Menge, B. A. Ecology 73, 755–765 (1992).
Smith, F. E. in Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, Correctives 631–645 (Natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A., Washington DC, 1969).
Rosenzweig, M. L. Science 171, 385–387 (1971).
Wollkind, D. V. Am. Nat. 110, 431–447 (1976).
Oksanen, L., Fretwell, S., Arruda, J. & Niemala, P. Am. Nat 118, 240–261 (1981).
Mittelbach, G. G., Osenberg, C. W. & Leibold, M. A. In Size Structured Populations (eds Ebenman B. & Persson, L.) 219–235 (Springer, New York, 1988).
DeAngelis, D. L. Dynamics of Nutrient Cycling and Food Webs (Chapman and Hall, London, 1991).
Phillips, O. M. Arch. Hydorbiol. 73, 301–333 (1974).
Tilman, D. Plant Strategies and the Dynamics and Structure of Plant Communities (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, 1988).
Leibold, M. A. Am. Nat. 134, 922–949 (1989).
Abrams, P. A. Am. Nat. (in the press).
Pimm, S. L., Lawton, J. H. & Cohen, J. E. Nature 350, 669–674 (1991).
Cohen, J. E., Briand, F. & Newman, C. M. Community Food Webs: Data and Theory (Springer, New York, 1990).
Morin, P., Wilbur, H. M. & Harris, R. Ecology 64, 1430–1436 (1983).
Wilbur, H. M. Ecology 68, 1437–1452 (1987).
Seale, D. B. Ecology 61, 1531–1550 (1980).
Oksanen, L. Am. Nat. 131, 424–444 (1988).
Arditi, R., Perrin, N. & Saiah, H. Oikos 60, 69–75 (1991).
Lund, J. W. G., Kipling, C. & LeCren, E. D. Hydrobiology 11, 143–170 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leibold, M., Wilbur, H. Interactions between food-web structure and nutrients on pond organisms. Nature 360, 341–343 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/360341a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/360341a0
This article is cited by
-
Relative strength of top-down effects of an invasive fish and bottom-up effects of nutrient addition in a simple aquatic food web
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
Effects of experimental warming and nutrient enrichment on wetland communities at the Arctic’s edge
Hydrobiologia (2020)
-
Joint effects of resources and amphibians on pond ecosystems
Oecologia (2017)
-
Different Anuran Species Show Different Relationships to Agricultural Intensity
Wetlands (2016)
-
Effects of Roundup formulations, nutrient addition, and Western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) on aquatic communities
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.