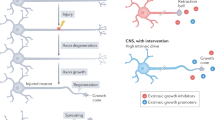
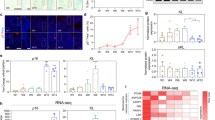
Abstract
Developing vertebrate neurons are thought to depend for their survival on specific neurotrophic proteins present in their target fields1. The limited availability of these proteins does not allow the survival of all neurons initially innervating a target, resulting in the widely observed phenomenon of naturally occurring neuronal death1. Although a variety of proteins have been reported to promote the survival of neurons in tissue culture2–4, the demonstration that these proteins increase neuronal numbers and/or decrease neuronal death in vivo has only been possible with nerve growth factor (NGF)5–7. The generalization of the concept that neurotrophic proteins regulate neuronal survival during normal development critically depends on the demonstration that the survival of neurons in vivo can be increased by the administration of a neurotrophic protein different from NGF. We report here that this is the case with brain-derived neurotrophic factor, a protein of extremely low abundance purified from the central nervous system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowan, W. M., Fawcett, J. W., O'Leary, D. D. M. & Stanfield, B. B. Science 225, 1258–1265 (1984).
Barbin, G., Manthorpe, M. & Varon, S. J. Neurochemistry 43, 1468–1478 (1984).
Walicke, P., Cowan, W. M., Ueno, N. & Guillemin, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3012–3016 (1986).
Gurney, M. E., Heinrich, S. A., Lee, M. R. & Yin, H.-S. Science 234, 566–573 (1986).
Levi-Montalcini, R. & Angeletti, P. U. Physiol. Rev. 48, 534–569 (1968).
Hamburger, V., Brunso-Bechtold, J. K. & Yip, J. W. J. Neurosci. 1, 60–71 (1981).
Oppenheim, R. W., Marderdrut, J. L. & Wells, D. J. J. Comp. Neurol. 210, 174–189 (1982).
Barde, Y.-A., Edgar, D. & Thoenen, H. EMBO J. 1, 549–553 (1982).
Lindsay, R. M., Thoenen, H. & Barde, Y.-A. Devl Biol. 112, 319–328 (1985).
Zacchei, A. M. Archo ital. Anat. Embriol. 66, 36–62 (1961).
Ayer-Le Lièvre, C. & Le Douarin, N. M. Devl Biol. 94, 291–310 (1982).
Davies, A. M., Thoenen, H. & Barde, Y.-A. Nature 319, 497–499 (1986).
Korsching, S. & Thoenen, H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 3513–3516 (1983).
Teillet, M.-A. & Le Douarin, N. M. Devl Biol. 98, 192–211 (1983).
Kalcheim, C. & Le Douarin, N. M. Devl Biol. 116, 461–466 (1986).
Kalcheim, C., Barde, Y.-A., Thoenen, H. & Le Douarin, N. M. EMBO J. 6, 2811–2813 (1987).
Lindsay, R. M. & Rohrer, H. Devl Biol. 112, 30–48 (1985).
Palladini, G. Riv. Neurobiol. 7, 383–400 (1961).
Johnson, J. E., Barde, Y.-A., Schwab, M. E. & Thoenen, H. J. Neurosci. 6, 3031–3038 (1986).
Konigsmark, B. W. in Contemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (eds Nauta, W. J. H. & Ebbesson, S. O. E.) 315–348 (Springer, New York, 1970).
Suda, K., Barde, Y.-A. & Thoenen, H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4042–4046 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofer, M., Barde, YA. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents neuronal death in vivo. Nature 331, 261–262 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/331261a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/331261a0
This article is cited by
-
Proteasomal Stimulation by MK886 and Its Derivatives Can Rescue Tau-Induced Neurite Pathology
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Synucleinopathy-associated pathogenesis in Parkinson’s disease and the potential for brain-derived neurotrophic factor
npj Parkinson's Disease (2021)
-
Sleep quality, autonomic dysfunction and renal function in diabetic patients with pre-CKD phase
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Dietary Protein Source Influences Brain Inflammation and Memory in a Male Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Model of Dementia
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Fingolimod Increases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Level Secretion from Circulating T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
CNS Drugs (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.