Abstract
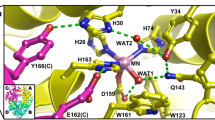
Copper, zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyses the very rapid two-step dismutation of the toxic superoxide radical (O−2) to molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide through the alternate reduction and oxidation of the active-site copper1. We report here that after refitting and further refinement of the previous 2 Å structure of SOD2, analysis of the new model and its calculated molecular surface shows an extensive surface topography of sequence-conserved residues stabilized by underlying tight packing and H-bonding. There is a single, highly complementary position for O−2 to bind to both the Cu(II) and activity-important Arg 141 with correct geometry; two water molecules form a ghost of the superoxide in this position. The geometry and molecular surface of the active site, together with biochemical data, suggest a specific model for the enzyme mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fridovich, I. Adv. inorg. Biochem. 1, 67–90 (1979).
Tainer, J. A., Getzoff, E. D., Beem, K. M., Richardson, J. S. & Richardson, D. C. J. molec. Biol. 160, 181–217 (1982).
Richardson, J. S. Nature 268, 495–500 (1977).
Hermans, J. & McQueen, J. E. Acta crystallogr. A30, 730–739 (1974).
Wlodawer, A. & Hendrickson, W. A. Acta crystallogr. A38, 239–247 (1982).
Getzoff, E. D. thesis, Duke Univ. (1982).
Connolly, M. L. Science 221, 709–713 (1983).
Connolly, M. L. Quantum Chemistry Program Exchange Bull. 1, 75 (1981).
Richards, F. M. A. Rev. Biophys. Bioengng 6, 151–176 (1977).
Steinman, H. M., Naik, V. R., Abernethy, J. L. & Hill, R. L. J. biol. Chem. 249, 7326–7338 (1974).
Steinman, H. M. J. biol. Chem. 255, 6758–6765 (1980).
Jabusch, J. R., Farb, D. L., Kerschensteiner, D. A. & Deutsch, H. F. Biochemistry 19, 2310–2316 (1980).
Lerch, K. & Ammer, D. J. biol. Chem. 256, 11545–11551 (1981).
Klug, D., Rabani, J. & Fridovich, I. J. biol. Chem. 247, 4839–4842 (1972).
Valentine, J. S. & Pantoliano, M. W. in Metal Ions in Biology Vol. 3 (ed. Spiro, T. G.), 291–358 (Wiley, New York, 1981).
Lawrence, G. D. & Sawyer, D. T. Biochemistry 18, 3045–3050 (1979).
Morpurgo, L., Giovagnoli, C. & Rotilio, G. Biochim. biophys. Acta 322, 204–210 (1973).
Margerum, D. W., Cayley, G. R., Weatherburn, D. C. & Pagenkopf, G. K. in Coordination Chemistry Vol. 12 (ed. Martell, A. E.) 1–220 (American Chemical Society, Washington DC, 1978).
Rigo, A., Stevanato, R., Viglino, P. & Rotilio, G. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 79, 776–783 (1977).
Boden, N., Holmes, M. C. & Knowles, P. F. Biochem. J. 177, 303–309 (1979).
Blumberg, W. E., Peisach, J., Eisenberger, P. & Fee, J. A. Biochemistry 17, 1842–1846 (1978).
McAdam, M. E. et al. Biochem. J. 167, 271–274 (1977).
Rotilio, G., Calabrese, L., Mondovi, B. & Blumberg, W. E. J. biol. Chem. 249, 3157–3160 (1974).
Burger, A. R. thesis, Columbia Univ. (1979).
Beem, K. M., Richardson, D. C. & Rajagopalan, K. V. Biochemistry 16, 1930–1936 (1977).
Lieberman, R. A., Sands, R. H. & Fee, J. A. J. biol. Chem. 257, 336–344 (1982).
Van Camp, H. L., Sands, R .H. & Fee, J. A. Biochim. biophys. Acta 704, 75–89 (1982).
Johnson, C. K. Oak Ridge natn. Rep. ORNL-3794 (1965).
Valentine, J. S., Sheridan, R. P., Allen, L. C. & Kahn, P. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 1009–1013 (1979).
Malinowski, D. P. & Fridovich, I. Biochemistry 18, 5909–5917 (1979).
Martin, R. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4346–4347 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tainer, J., Getzoff, E., Richardson, J. et al. Structure and mechanism of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. Nature 306, 284–287 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/306284a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/306284a0
This article is cited by
-
The essential liaison of two copper proteins: the Cu-sensing transcription factor Mac1 and the Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase Sod1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Current Genetics (2023)
-
Homeostatic alterations related to total antioxidant capacity, elemental concentrations and isotopic compositions in aqueous humor of glaucoma patients
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2022)
-
Nanocomposite-based dual enzyme system for broad-spectrum scavenging of reactive oxygen species
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Curcumin Ameliorates Copper-Induced Neurotoxicity Through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells
Neurochemical Research (2021)
-
Effects of transcranial photobiomodulation and methylene blue on biochemical and behavioral profiles in mice stress model
Lasers in Medical Science (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.