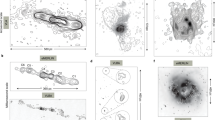
Abstract
Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope maps of faint extended emission associated with several superluminal radio sources are presented. In order to avoid exceptionally large sizes for the superluminal sources, their dominant, long-term axes must be at least 20–30° from the line of sight. This is a considerably larger angle than that demanded by the relativistic beaming interpretation of the superluminal motion in their compact cores, and implies that a wobble or precession of their ejection axes has taken place. Superluminality may thus be a temporary phenomenon.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kellermann, K. I. & Pauliny-Toth, I. I. K. Ann. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 19, 373–410 (1981).
Cohen, M. H. & Unwin, S. C. in Extragalactic Radio Sources (eds Heeschen, D. S. & Wade, C. M.) 345–354 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1982).
Phillips, R. & Mutel, R. Astrophys. J. 257, L19–22 (1982).
Walker, R. C. et al. Astrophys. J. 257, 56–62 (1982).
Pearson, T. J. et al. Nature 290, 365–368 (1981).
Readhead, A. C. S. et al. Preprint (Owens Valley Radio Observatory, Caltech, 1982).
Blandford, R. D., McKee, C. F. & Rees, M. J. Nature 267, 211–216 (1977).
Marscher, A. P. & Scott, J. S. Pub. astr. Soc. Pacif. 92, 127–133 (1980).
Scheuer, P. A. G. & Readhead, A. C. S. Nature 277, 182–185 (1979).
Blandford, R. G. & Konigl, A. Astrophys. J. 232, 34–48 (1979).
Readhead, A. C. S., Cohen, M. H., Pearson, T. J. & Wilkinson, P. N. Nature 276, 768–771 (1978).
Browne, I. W. A. et al. Nature 299, 788–793 (1982).
Perley, R. A. Astr. J. 87, 859–880 (1982).
Conway, R. G., Davis, R. J., Foley, A. R. & Ray, T. P. Nature 294, 540–542 (1981).
Noordam, J. E. & de Bruyn, A. G. Nature 299, 597–600 (1982).
Baars, J. W. M., Genzel, R., Pauliny-Toth, I. I. K. & Witzel, A. Astr. Astrophys. 61, 99–106 (1977).
Marscher, A. P. & Broderick, J. J. Astrophys. J. 249, 406–414 (1981).
Marscher, A. P. & Broderick, J. J. Astrophys. J. 255, L11–15 (1982).
Balick, B., Heckman, T. M. & Crane, P. C. Astrophys. J. 254, 483–488 (1982).
Arp, H. C. Proc. ESO/ESA Workshop SP-162, 53–61 (1981).
Reich, W. et al. Astrophys. J. 236, L61–65 (1980).
Perley, R. A., Fomalont, E. B. & Johnston, K. J. Astrophys. J. 255, L93–97 (1982).
Hooley, A., Longair, M. S. & Riley, J. M. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 182, 127–145 (1978).
Wilkinson, P. N. in Extragalactic Radio Sources (eds Heeschen, D. S. & Wade, C. M.) 149–156 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1982).
Rees, M. J. in Origin of Cosmic Rays (eds Setti, G., Spada, G. & Wolfendale, A. W.) 139–164 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1981).
Miley, G. K. Proc. NATO Advanced Study Institute on the Physics of Non-thermal Radio Sources, Urbino (ed. Setti, G.) 1–26 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1976).
Linfield, R. Astrophys. J. 250, 464–468 (1981).
Cohen, M. H. et al. Preprint (Owens Valley Radio Observatory, Caltech, 1982).
Orr, M. J. L. & Browne, I. W. A. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 200, 1067–1080 (1982).
Readhead, A. C. S. in Objects of High Redshift (eds Abell, G. O. & Peebles, P. J. E.) 165–176 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1980).
Hine, R. G. & Scheuer, P. A. G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 193, 285–293 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilizzi, R., de Bruyn, A. Large-scale radio structures of superluminal sources. Nature 303, 26–31 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/303026a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/303026a0
This article is cited by
-
Kinematical diagrams for conical relativistic jets
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2007)
-
The jets of 3C120
Nature (1989)
-
Extragalactic sources with very asymmetric radio structure: VLA and MERLIN observations
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (1989)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.