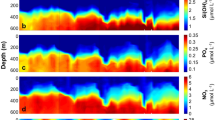
Abstract
Circumpolar surface waters dominate the circulation of the Southern Ocean and sustain one of the ocean's largest standing stocks of biomass thereby producing a significant output of biogenic components, mainly diatoms, to the bottom sediments. Generally transit of biogenic matter from the sea surface to the sea floor affects nutrient regeneration fuels benthic life and transfers signals to the sediment record1–5. Reliable quantification of the relationship between biological production, fractionation of skeletal and tissue components and bottom sediment accumulation depends on direct vertical flux measurements from sediment trap deployments6–9, which have proved to be most scientifically productive10–13. We now present data on vertical mass fluxes from the Southern Ocean and evidence for strong biogeochemical fractionation between organic carbon-, nitrogen- and phosphorus-containing compounds, siliceous and calcareous skeletal remains, and refractory aluminosilicates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schrader, H.-J. Science 174, 55–57 (1971).
Hinga, K. R., Sieburth, J. & Heath, G. R. J. mar. Res. 37, 557–579 (1979).
Cobler, R. & Dymond, J. Science 209, 801–802 (1980).
Suess, E. Nature 288, 260–263 (1980).
Thunell, R. & Honjo, S. Mar. Geol. 40, 237–253 (1981).
Honjo, S., Manganini, S. J. & Cole, J. J. Deep-Sea Res. 29, 609–625 (1982).
Deuser, W. G., Ross, E. H. & Anderson, R. F. Deep-Sea Res. 28, 495–505 (1981).
Knauer, G. A., Martin, J. H. & Bruland, K. W. Deep-Sea Res. 26, 97–108 (1979).
Starecinic, N. J. mar. Res. (in the press).
Wakeham, S. G. et al. Nature 286, 798–800 (1980).
Deuser, W. G. & Ross, E. H. Nature 283, 364–365 (1980).
Knauer, G. A. & Martin, J. H. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26, 181–186 (1981).
Urrere, M. A. & Knauer, G. A. J. Plankton Res. 3, 3–19 (1981).
Zeitzschel, B., Uhlmann, L. & Diekmann, P. Mar. Biol. 45, 285–288 (1978).
Tilzer, M. & von Bodungen, B. Berichte aus dem Institut für Meereskunde No. 80 (1981).
Whitworth, T., Nowlin, W. D. Jr & Worley, S. J. J. Phys. Oceanogr. (in the press).
Suess, E. & Ungerer, C. A. Oceanol. Acta 4, 151–160 (1980).
Berger, W. H. & Killingley, J. S. Science 197, 563–566 (1977).
Berger, W. H., Killingley, J. S. & Vincent, E. Oceanol. Acta 1, 203–216 (1978).
Epstein, S., Buchsbaum, H. A., Lowenstamm, H. A. & Urey, H. C. Bull. geol. Soc. Am. 64, 1315–1325 (1953).
Craig, H. & Gordon, L. I. Stable Isotopes in Oceanographic Studies (ed. Tongiorgi, E.) 9–130 (Consiglio Nazionale delle Richerche, Rome, 1965).
Müller, P. J. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 41, 765–776 (1977).
Handa, N. & Yanagi, K. Mar. Biol. 4, 197–207 (1969).
Black, C. A. Methods of Soil Analysis Pt II, 1038–1040 (American Society of Agronomy, Madison, 1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wefer, G., Suess, E., Balzer, W. et al. Fluxes of biogenic components from sediment trap deployment in circumpolar waters of the Drake Passage. Nature 299, 145–147 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299145a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299145a0
This article is cited by
-
Vertical fluxes and ecological significance of organic materials during the phytoplankton bloom during austral summer in Breid Bay, Antarctica
Marine Biology (1992)
-
Structure of a suprabenthic shelf sub-community of gammaridean Amphipoda in the Bay of Fundy compared with similar sub-communities in the Gulf of St. Lawrence
Hydrobiologia (1991)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.