Abstract
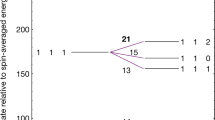
THERE has long been an interest in the study of ion-induced dipole clusters of the type H+n (n, odd integer). These positive clusters may be present in gaseous nebulae1,2, and Clampitt and Gowland3 have discovered in mass spectrometer experiments such H+n ions for 3≤n(odd)≤99. The ions are very weakly bound because of the nature of the ion-induced dipole forces involved, and thus must be produced at low temperatures. In these experiments a layer of hydrogen gas is deposited on a metal surface maintained at 3 K in a baked vacuum apparatus operating at ∼10−10 torr. The surface is swept by a 23 eV electron beam and the ions thus created are focused into a quadrapole filter and detected. The surface mechanism for production of the ions is not understood but the presence of grains in the interstellar medium might provide surfaces which could play an analogous role in similar conditions of low pressure and temperature. To study the binding energy and geometry of such clusters we performed ab initio Hartree–Fock–Roothaan calculations4, using a contracted s-type Gaussian orbital basis. Our previous use of this type of calculation4–7 for ion molecule complexes which dissociate into closed shell fragments, indicated that reliable results can be obtained. The results shown in Fig. 1 and Table 1 are all based on this type of calculation implemented with the Gaussian 70 program8,9 using four gaussians per hydrogenic s-orbital. As expected, we found the positive cluster to be quite weakly bound, that is the binding energy was of the order of 1 kcal mol−1 against dissociation according to H+n→H+n−2 + H2 5≤n(odd)≤15 (the largest and smallest binding energies found were 6.0 kcal mol−1 for H+5 and 0.3 kcal mol−1 for H+15). In our calculations the geometries of the positive clusters were dominated by the strongly bound triangular nucleating centre H+3. Each member of the series H+n 5≤n(odd)≤15 is formed by the addition of one hydrogen molecule to the basic structure of the previous member in the series. We report here calculated binding energies and geometries for the negative ion induced dipole clusters H−n, 5 ≤ n (odd) ≤ 13.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasovskii, V. I. Sov Astr. 2, 715 (1958).
Donn, B. Astrophys. J. 132, 507 (1960).
Clampitt, R. & Gowland, L. Nature 223, 815 (1969).
Harrison, S. W., Massa, L. J. & Salomon, P. Nature Phys. sci. 245, 31 (1973).
Harrison, S. W., Massa, L. J. & Salomon, P. Chem. phys. Lett. 16, 57 (1972).
Harrison, S. W., Massa, L. J. & Salomon, P. Astrophys. J. 189, 605–607 (1974).
Harrison, S. W., Massa, L. J. & Salomon, P. J. chem. Phys. 59, 263 (1973).
Hehre, W. J., Stewart, R. F. & Pople, J. A. J. chem. Phys. 51, 2657 (1969).
Ditchfield, R., Hehre, W. J. & Pople, J. A. J. chem. Phys. 54, 724 (1971).
Smith, W. H., Snow, T. P. & York, D. G. Astrophys. J. 218, 124–132 (1977).
Stevenson, D. & Hirschfelder, J. O. J. chem. Phys. 5, 933 (1937).
Macais, A. J. chem. Phys. 48, 3464 (1968).
Gillespie, R. J. J. chem. Educ. 40, 245 (1963).
Dillard & Goldberg, Chemistry, 2nd edn (Macmillan, London, 1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SAPSE, A., RAYEZ-MEAUME, M., RAYEZ, J. et al. Ion-induced dipole H−n clusters. Nature 278, 332–333 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/278332a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/278332a0
This article is cited by
-
On the topology of the electron density of H 3 + ${\mathrm {H}}_{3}^{+}$
Structural Chemistry (2017)
-
Guest Editorial: A path through quantum crystallography: a short tribute to Professor Lou Massa
Structural Chemistry (2017)
-
Odd and even numbered hydrogen ion clusters
Nature (1979)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.