Abstract
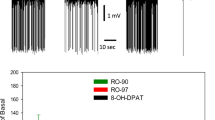
D-Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) given pareriterally produces a reversible cessation of the spontaneous activity of neuronal units in the midbrain raphe nuclei of the rat1. Threshold doses of LSD required to produce this effect are extremely small in relation to those typically used in rats (10–20 µg/kg, intravenously). Substances the behavioural effects of which are similar to those of LSD (for example, N,N-dimethyltryptamine and mescaline) also inhibit raphe units, although none is as potent as LSD2. A variety of other types of drugs (for example, atropine, phencyclidine, chlorpromazine) do not affect the activity of raphe units2. The inhibitory effect of LSD is specific for units in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei; in other mid-brain areas (for example, reticular formation), the drug either has no effect or accelerates unit activity1. According to the fluorescence histochemical method the midbrain raphe nuclei are comprised of serotonin-containing neurones3. Axons of the raphe neurones supply the principal serotonin input to the forebrain4. Large doses of LSD induce a prolonged inhibition of the serotonin-containing neurones1; this inhibition may account for the reduced metabolism of brain serotonin observed after injections of LSD5–8.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian, G. K., Foote, W. E., and Sheard, M. H., Science, 161, 706 (1968).
Aghajanian, G. K., Sheard, M. H., and Foote, W. E., Psychotomimetics (edit. by Efron, D. H.), (US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, in the press).
Dahlstrom, A., and Fuxe, K., Acta Physiol. Scand., 62, 232 (1965).
Andén, N. E., Dahlstrom, A., Fuxe, K., Larson, K., Olson, L., and Ungerstedt, U., Acta Physiol. Scand., 67, 313 (1966).
Freedman, D. X., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 134, 169 (1961).
Rosecrans, J. A., Lovell, R. A., and Freedman, D. X., Biochem. Pharmacol., 16, 2011 (1967).
Diaz, P., Ngai, S. H., and Costa, E., Pharmacologist, 9, 372 (1967).
Andén, N. E., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., and Hokfelt, T., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 34, 1 (1968).
Bradley, P. B., and Key, B. J., Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol., 10, 97 (1958).
Rosenberg, D. E., Wolbach, A. B., Miner, E. J., and Isbell, H., Psychopharmacologia, 5, 1 (1963).
Konig, J. F. R., and Klippel, R. A., The Rat Brain (Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1963).
Fuxe, K., Acta Physiol. Scand., 64, Suppl. 247, 39 (1965).
Aghajanian, G. K., and Freedman, D. X., in Psychopharmacology: A Review of Progress (edit. by Efron, D. H.), 1185 (US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, 1968).
Roberts, M. H. T., and Straughan, D. W., J. Physiol., 193, 269 (1967).
Phillis, J. W., and Tebecis, A. K., J. Physiol., 192, 715 (1967).
Bloom, F. E., Costa, E., and Salmoiraghi, G. C., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 146, 16 (1964).
Bradley, P. B., and Wolstencroft, J. H., Brit. Med. Bull., 21, 15 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FOOTE, W., SHEARD, M. & AGHAJANIAN, G. Comparison of Effects of LSD and Amphetamine on Midbrain Raphe Units. Nature 222, 567–569 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/222567a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/222567a0
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition by oxytocin of methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity related to dopamine turnover in the mesolimbic region in mice
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2008)
-
Evidence that central 5‐HT2A and 5‐HT2B/C receptors regulate 5‐HT cell firing in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the anaesthetised rat
British Journal of Pharmacology (2003)
-
Differential effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists on behaviors resulting from activation of different pathways arising from the raphe nuclei
Psychopharmacology (1983)
-
Effects of mescaline and amphetamine on simultaneous visual discrimination in two inbred strains of mice
Psychopharmacology (1979)
-
Studies of various amphetamines, apomorphine and clonidine on body temperature and brain 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism in rats
Psychopharmacologia (1974)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.