Abstract
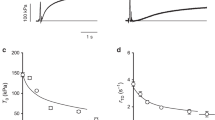
ALTHOUGH muscle constitutes almost half the body-weight in mammals, it is generally thought to be very radioresistant and to play an insignificant part in the bodily changes which follow irradiation. In excised frog muscle, changes in the resting transmembrane potential and electrolyte composition were found only after massive doses of X-rays1,2. However, transient weakness and increased fatigability have been observed in man and animals after modest doses of radiation3,4. Caster and Armstrong5 found a large negative potassium balance in rats after an LD50 of X-rays. The lost potassium appeared to originate principally in muscle. A transient post-irradiation aldolasæmia6 also occurs as well as an amino-aciduria and creatinuria7–9 which appears to be linearly dependent on the dose of radiation10. It seems likely that the creatine and other amino-acids and the aldolase were lost, in large part, by skeletal muscle and it occurred to us that subtle in vivo changes in muscle after irradiation might have been overlooked.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerstner, H. B., Lewis, R. B., and Richey, E. O., J. Gen Physiol., 37, 445 (1954).
Darden, E. B., Amer. J. Physiol., 198, 709 (1960).
Kimeldorf, D. J., Jones, D. C., and Castanera, T. J., Amer. J. Physiol., 174, 243 (1954).
Haley, T. J., Flescher, A. M., Komesu, N., McCulloh, E. F., and McCormick, W. G., Amer. J. Physiol., 193, 355 (1958).
Caster, W. O., and Armstrong, W. D., Rad. Res., 5, 189 (1956).
Albaum, H. G., Rad. Res., 12, 186 (1959).
Katz, E. J., and Hasterlik, R. J., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 15, 1085 (1955).
Haberland, G. L., Schreier, K., Bruns, F., Altman, K. I., and Hempelmann, L. H., Nature, 175, 1039 (1955).
Williams, C. M., Krise, G. M., Anderson, D. R., and Dowben, R. M., Rad. Res., 7, 176 (1957).
Gerber, G. B., Gertler, P., Altman, K. I., and Hempelmann, L. H., Rad. Res., 15, 307 (1961).
Dowben, R. M., Gordon, P., and Sniderman, S. P. (in the press).
Wilde, W. S., and Sheppard, C. W., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 88, 249 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DOWBEN, R., ZUCKERMAN, L. Alterations in Skeletal Muscle after X-Irradiation and their Similarity to Changes in Muscular Dystrophy. Nature 197, 400–401 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/197400a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/197400a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.