Abstract
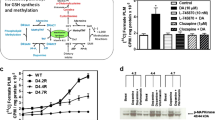
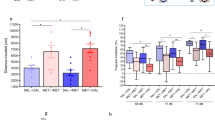
Methylation events play a critical role in the ability of growth factors to promote normal development. Neurodevelopmental toxins, such as ethanol and heavy metals, interrupt growth factor signaling, raising the possibility that they might exert adverse effects on methylation. We found that insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)- and dopamine-stimulated methionine synthase (MS) activity and folate-dependent methylation of phospholipids in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, via a PI3-kinase- and MAP-kinase-dependent mechanism. The stimulation of this pathway increased DNA methylation, while its inhibition increased methylation-sensitive gene expression. Ethanol potently interfered with IGF-1 activation of MS and blocked its effect on DNA methylation, whereas it did not inhibit the effects of dopamine. Metal ions potently affected IGF-1 and dopamine-stimulated MS activity, as well as folate-dependent phospholipid methylation: Cu2+ promoted enzyme activity and methylation, while Cu+, Pb2+, Hg2+ and Al3+ were inhibitory. The ethylmercury-containing preservative thimerosal inhibited both IGF-1- and dopamine-stimulated methylation with an IC50 of 1 nM and eliminated MS activity. Our findings outline a novel growth factor signaling pathway that regulates MS activity and thereby modulates methylation reactions, including DNA methylation. The potent inhibition of this pathway by ethanol, lead, mercury, aluminum and thimerosal suggests that it may be an important target of neurodevelopmental toxins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sweetman L, Nyhan WL . Excretion of hypoxanthine and xanthine in a genetic disease of purine metabolism. Nature 1967; 215: 859–860.
Stone RL, Aimi J, Barshop BA, Jaeken J, Van den Berghe G, Zalkin H et al. A mutation in adenylosuccinate lyase associated with mental retardation and autistic features. Nat Genet 1992; 1: 59–63.
Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY . Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 185–188.
Rousseau F, Heitz D, Mandel JL . The unstable and methylatable mutations causing the fragile X syndrome. Hum Mutat 1992; 1: 91–96.
Olney JW, Wozniak DF, Farber NB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Bittigau P, Ikonomidou C . The enigma of fetal alcohol neurotoxicity. Ann Med 2002; 34: 109–119.
Lidsky TI, Schneider JS . Lead neurotoxicity in children: basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Brain 2003; 126: 5–19.
Bernard S, Enayati A, Redwood L, Roger H, Binstock T . Autism: a novel form of mercury poisoning. Med Hypotheses 2001; 56: 462–471.
Vaudry D, Stork PJ, Lazarovici P, Eiden LE . Signaling pathways for PC12 cell differentiation: making the right connections. Science 2002; 296: 1648–1649.
Ehrlich M . Expression of various genes is controlled by DNA methylation during mammalian development. J Cell Biochem 2003; 88: 899–910.
Acheson A, Thoenen H . Both short- and long-term effects of nerve growth factor on tyrosine hydroxylase in calf adrenal chromaffin cells are blocked by S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitors. J Neurochem 1987; 48: 1416–1424.
Cimato TR, Ettinger MJ, Zhou X, Aletta JM . Nerve growth factor-specific regulation of protein methylation during neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J Cell Biol 1997; 138: 1089–1103.
Cantoni GL . The role of S-adenosylhomocysteine in the biological utilization of S-adenosylmethionine. Prog Clin Biol Res 1985; 198: 47–65.
Yi P, Melnyk S, Pogribna M, Pogribny IP, Hine RJ, James SJ . Increase in plasma homocysteine associated with parallel increases in plasma S-adenosylhomocysteine and lymphocyte DNA hypomethylation. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 29318–29323.
de la Haba G, Cantoni GL . The enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine from adenosine and homocysteine. J Biol Chem 1959; 234: 603–608.
Sharma A, Kramer ML, Wick PF, Liu D, Chari S, Shim S et al. D4 dopamine receptor-mediated phospholipid methylation and its implications for mental illnesses such as schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 235–246.
Zhao R, Chen Y, Tan W, Waly M, Sharma A, Stover P et al. Relationship between dopamine-stimulated phospholipid methylation and the single-carbon folate pathway. J Neurochem 2001; 78: 788–796.
Sharma A, Waly M, Deth RC . Protein kinase C regulates dopamine D4 receptor-mediated phospholipid methylation. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 427: 83–90.
LaHoste GJ, Swanson JM, Wigal SB, Glabe C, Wigal T, King N et al. Dopamine D4 receptor gene polymorphism is associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1996; 1: 121–124.
Deth RC . Molecular Origins of Human Attention. Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, 2003.
Banerjee R, Chen Z, Gulati S . Methionine synthase from pig liver. Methods Enzymol 1997; 281: 189–196.
Friso S, Choi SW, Dolnikowski GG, Selhub J . A method to assess genomic DNA methylation using high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 2002; 74: 4526–4531.
Evron E, Umbricht CB, Korz D, Raman V, Loeb DM, Niranjan B et al. Loss of cyclin D2 expression in the majority of breast cancers is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2782–2787.
Kurihara S, Hakuno F, Takahashi S . Insulin-like growth factor-I-dependent signal transduction pathways leading to the induction of cell growth and differentiation of human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y: the roles of MAP kinase pathway and PI 3-kinase pathway. Endocr J 2000; 47: 739–751.
Seiler AE, Ross BN, Rubin R . Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and IRS-2 signaling by ethanol in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 2001; 76: 573–581.
Strong MJ, Garruto RM, Joshi JG, Mundy WR, Shafer TJ . Can the mechanisms of aluminum neurotoxicity be integrated into a unified scheme? J Toxicol Environ Health 1996; 48: 599–613.
Mendola P, Selevan SG, Gutter S, Rice D . Environmental factors associated with a spectrum of neurodevelopmental deficits. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2002; 8: 188–197.
Bellinger D, Dietrich KN . Low-level lead exposure and cognitive function in children. Pediatr Ann 1994; 23: 600–605.
Canfield RL, Henderson Jr CR, Cory-Slechta DA, Cox C, Jusko TA, Lanphear BP . Intellectual impairment in children with blood lead concentrations below 10 microg per deciliter. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1517–1526.
Ostrakhovitch EA, Lordnejad MR, Schliess F, Sies H, Klotz LO . Copper ions strongly activate the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt pathway independent of the generation of reactive oxygen species. Arch Biochem Biophys 2002; 397: 232–239.
Bernard S, Enayati A, Roger H, Binstock T, Redwood L . The role of mercury in the pathogenesis of autism. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: S42–43.
Geier MR, Geier DA . Thimerosal in childhood vaccines, neurodevelopment disorders and heart disease in the United States. J Am Physicians Surg 2003; 8: 6–11.
Sinclair AJ, Palmero I, Holder A, Peters G, Farrell PJ . Expression of cyclin D2 in Epstein–Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines is related to methylation status of the gene. J Virol 1995; 69: 1292–1295.
Evron E, Umbricht CB, Korz D, Raman V, Loeb DM, Niranjan B et al. Loss of cyclin D2 expression in the majority of breast cancers is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2782–2787.
Conover JC, Yancopoulos GD . Neurotrophin regulation of the developing nervous system: analyses of knockout mice. Rev Neurosci. 1997; 8: 13–27.
Arsenijevic Y, Weiss S, Schneider B, Aebischer P . Insulin-like growth factor-I is necessary for neural stem cell proliferation and demonstrates distinct actions of epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 7194–7202.
Riaz SS, Jauniaux E, Stern GM, Bradford HF . The controlled conversion of human neural progenitor cells derived from foetal ventral mesencephalon into dopaminergic neurons in vitro. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 2002; 136: 27–34.
Jaboin J, Kim CJ, Kaplan DR, Thiele CJ . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6756–6763.
Zheng WH, Kar S, Quirion R . Insulin-like growth factor-1-induced phosphorylation of transcription factor FKHRL1 is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt kinase and role of this pathway in insulin-like growth factor-1-induced survival of cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 2002; 62: 225–233.
Nusser N, Gosmanova E, Zheng Y, Tigyi G . Nerve growth factor signals through TrkA, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Rac1 to inactivate RhoA during the initiation of neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 35840–35846.
D'Ercole AJ, Ye P, O'Kusky JR . Mutant mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central nervous system. Neuropeptides 2002; 36: 209–220.
Ye P, Li L, Richards RG, DiAugustine RP, D'Ercole AJ . Myelination is altered in insulin-like growth factor-I null mutant mice. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6041–6051.
Komoly S, Hudson LD, Webster HD, Bondy CA . Insulin-like growth factor I gene expression is induced in astrocytes during experimental demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 1894–1898.
Jurevics H, Largent C, Hostettler J, Sammond DW, Matsushima GK, Kleindienst A et al. Alterations in metabolism and gene expression in brain regions during cuprizone-induced demyelination and remyelination. J Neurochem 2002; 82: 126–136.
Surtees R . Biochemical pathogenesis of subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord and brain. J Inherit Metab Dis 1993; 16: 762–770.
Scott JM, Dinn JJ, Wilson P, Weir DG . Pathogenesis of subacute combined degeneration: a result of methyl group deficiency. Lancet 1981; 2: 334–337.
Courchesne E, Karns CM, Davis HR, Ziccardi R, Carper RA, Tigue ZD et al. Unusual brain growth patterns in early life in patients with autistic disorder: an MRI study. Neurology 2001; 57: 245–254.
Carper RA, Moses P, Tigue ZD, Courchesne E . Cerebral lobes in autism: early hyperplasia and abnormal age effects. Neuroimage 2002; 16: 1038–10351.
Herbert MR, Ziegler DA, Deutsch CK, O'Brien LM, Lange N, Bakardjiev A et al. Dissociations of cerebral cortex, subcortical and cerebral white matter volumes in autistic boys. Brain 2003; 126: 1182–1192.
Vanhala R, Turpeinen U, Riikonen R . Low levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in cerebrospinal fluid in children with autism. Dev Med Child Neurol 2001; 43: 614–616.
Halmesmaki E, Valimaki M, Karonen SL, Ylikorkala O . Low somatomedin C and high growth hormone levels in newborns damaged by maternal alcohol abuse. Obstet Gynecol 1989; 74: 366–370.
Breese CR, D'Costa A, Ingram RL, Lenham J, Sonntag WE . Long-term suppression of insulin-like growth factor-1 in rats after in utero ethanol exposure: relationship to somatic growth. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993; 264: 448–456.
Stickel F, Choi SW, Kim YI, Bagley PJ, Seitz HK, Russell RM et al. Effect of chronic alcohol consumption on total plasma homocysteine level in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2000; 24: 259–264.
Bleich S, Spilker K, Kurth C, Degner D, Quintela-Schneider M, Javaheripour K et al. Oxidative stress and an altered methionine metabolism in alcoholism. Neurosci Lett 2000; 293: 171–174.
Barak AJ, Beckenhauer HC, Tuma DJ, Badakhsh S . Effects of prolonged ethanol feeding on methionine metabolism in rat liver. Biochem Cell Biol 1987; 65: 230–233.
Mirpuri E, Garcia-Trevijano ER, Castilla-Cortazar I, Berasain C, Quiroga J, Rodriguez-Ortigosa C et al. Altered liver gene expression in CCl4-cirrhotic rats is partially normalized by insulin-like growth factor-I. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2002; 34: 242–252.
Toxicological Profile for Lead. US Department of Health and Human Services, P.H.S., Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; Washington, DC, 1999.
Sanfeliu C, Sebastia J, Cristofol R, Rodriguez-Farre E . Neurotoxicity of organomercurial compounds. Neurotoxicol Res 2003; 5: 283–305.
Mercury Study Report to Congress: Volume I. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC, 1997.
Alonso-Aperte E, Ubeda N, Achon M, Perez-Miguelsanz J, Varela-Moreiras G . Impaired methionine synthesis and hypomethylation in rats exposed to valproate during gestation. Neurology 1999; 52: 750–756.
Paz MF, Avila S, Fraga MF, Pollan M, Capella G, Peinado MA et al. Germ-line variants in methyl-group metabolism genes and susceptibility to DNA methylation in normal tissues and human primary tumors. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4519–4524.
Immunization Safety Review: Thimerosal-containing Vaccines and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Stratton K, Gable A, McCormick MC (Eds.), Institute of Medicine, Washington, DC, 2001 pp 51–54.
Makani S, Gollapudi S, Yel L, Chiplunkar S, Gupta S . Biochemical and molecular basis of thimerosal-induced apoptosis in T cells: a major role of mitochondrial pathway. Genes Immun 2002; 3: 270–278.
Baskin DS, Ngo H, Didenko VV . Thimerosal induces DNA breaks, caspase-3 activation, membrane damage, and cell death in cultured human neurons and fibroblasts. Toxicol Sci 2003; 74: 361–368.
Stajich GV, Lopez GP, Harry SW, Sexson WR . Iatrogenic exposure to mercury after hepatitis B vaccination in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2000; 136: 679–681.
Pichichero ME, Cernichiari E, Lopreiato J, Treanor J . Mercury concentrations and metabolism in infants receiving vaccines containing thiomersal: a descriptive study. Lancet 2002; 360: 1737–1741.
Stubbs G, Litt M, Lis E, Jackson R, Voth W, Lindberg A, Litt R . Adenosine deaminase activity decreased in autism. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 1982; 21: 71–74.
Persico AM, Militerni R, Bravaccio C, Schneider C, Melmed R, Trillo S et al. Adenosine deaminase alleles and autistic disorder: case–control and family-based association studies. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 784–790.
Bottini N, De Luca D, Saccucci P, Fiumara A, Elia M, Porfirio MC et al. Autism: evidence of association with adenosine deaminase genetic polymorphism. Neurogenetics 2001; 3: 111–113.
Page T, Yu A, Fontanesi J, Nyhan WL . Developmental disorder associated with increased cellular nucleotidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 11601–11606.
Page T, Coleman M . De novo purine synthesis is increased in the fibroblasts of purine autism patients. Adv Exp Med Biol 1998; 431: 793–796.
Nyhan WL . The recognition of Lesch–Nyhan syndrome as an inborn error of purine metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis 1997; 20: 171–178.
Yeargin-Allsopp M, Rice C, Karapurkar T, Doernberg N, Boyle C, Murphy C . Prevalence of autism in a US metropolitan area. JAMA 2003; 289: 49–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waly, M., Olteanu, H., Banerjee, R. et al. Activation of methionine synthase by insulin-like growth factor-1 and dopamine: a target for neurodevelopmental toxins and thimerosal. Mol Psychiatry 9, 358–370 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001476
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001476
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systemic review of genetic and epigenetic factors underlying differential toxicity to environmental lead (Pb) exposure
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
-
Toxoplasmosis: Targeting neurotransmitter systems in psychiatric disorders
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Methylation-related metabolic effects of D4 dopamine receptor expression and activation
Translational Psychiatry (2019)
-
Components of the folate metabolic pathway and ADHD core traits: an exploration in eastern Indian probands
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
-
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signalling (IIS) based regulation of lifespan across species
Biogerontology (2017)