Abstract
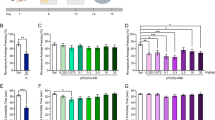
Converging evidence suggests that females and males show different responses to stress; however, little is known about the mechanism underlying the sexually dimorphic effects of stress. In this study, we found that young female rats exposed to 1 week of repeated restraint stress show no negative effects on temporal order recognition memory (TORM), a cognitive process controlled by the prefrontal cortex (PFC), which was contrary to the impairment in TORM observed in stressed males. Concomitantly, normal glutamatergic transmission and glutamate receptor surface expression in PFC pyramidal neurons were found in repeatedly stressed females, in contrast to the significant reduction seen in stressed males. The detrimental effects of repeated stress on TORM and glutamate receptors were unmasked in stressed females when estrogen receptors were inhibited or knocked down in PFC, and were prevented in stressed males with the administration of estradiol. Blocking aromatase, the enzyme for the biosynthesis of estrogen, revealed the stress-induced glutamatergic deficits and memory impairment in females, and the level of aromatase was significantly higher in the PFC of females than in males. These results suggest that estrogen protects against the detrimental effects of repeated stress on glutamatergic transmission and PFC-dependent cognition, which may underlie the stress resilience of females.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Kloet ER, Joëls M, Holsboer F . Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005; 6: 463–475.
Joëls M, Pu Z, Wiegert O, Oitzl MS, Krugers HJ . Learning under stress: how does it work? Trends Cogn Sci 2006; 10: 152–158.
McEwen BS . Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: central role of the brain. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 873–904.
Luine VN, Beck KD, Bowman RE, Frankfurt M, Maclusky NJ . Chronic stress and neural function: accounting for sex and age. J Neuroendocrinol 2007; 19: 743–751.
Luine V, Villegas M, Martinez C, McEwen BS . Repeated stress caused reversible impairments of spatial memory performance. Brain Res 1994; 639: 167–170.
Beck KD, Luine VN . Food deprivation modulates chronic stress effects on object recognition in male rats: role of monoamines and amino acids. Brain Res 1999; 830: 56–71.
Beck KD, Luine VN . Sex differences in behavioral and neurochemical profiles after chronic stress: role of housing conditions. Physiol Behav 2002; 75: 661–673.
Conrad CD, Galea LA, Kuroda Y, McEwen BS . Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav Neurosci 1996; 110: 1321–1334.
Kitraki E, Kremmyda O, Youlatos D, Alexis MN, Kittas C . Gender-dependent alterations in corticosteroid receptor status and spatial performance following 21 days of restraint stress. Neuroscience 2004; 125: 47–55.
Bowman RE, Zrull MC, Luine VN . Chronic restraint stress enhances radial arm maze performance in female rats. Brain Res 2001; 904: 279–289.
Bowman RE, Ferguson D, Luine VN . Effects of chronic restraint stress and estradiol on open field activity, spatial memory, and monoaminergic neurotransmitters in ovariectomized rats. Neuroscience 2002; 113: 401–410.
Bowman RE, Beck KD, Luine VN . Chronic stress effects on memory. Sex differences in performance and monoamines. Horm Behav 2003; 43: 48–59.
Bowman RE . Stress-induced changes in spatial memory are sexually differentiated and vary across the lifespan. J Neuroendocrinol 2005; 17: 526–535.
McLaughlin KF, Baran SE, Wright RL, Conrad CD . Chronic stress enhances spatial memory in ovariectomized female rats despite CA3 dendritic retraction. Possible involvement of CA1 neurons. Neuroscience 2005; 135: 1045–1054.
Conrad CD, Grote KD, Hobbs RJ, Ferayorni A . Sex differences in spatial and non-spatial Y-maze performance after chronic stress. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2003; 79: 32–40.
Cohen H, Yehuda R . Gender differences in animal models of posttraumatic stress disorder. Dis Markers 2011; 30: 141–150.
Woolley CS . Effects of estrogen in the CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1999; 9: 349–354.
Garcia-Segura LM, Azcortia I, DonCarlos LL . Neuroprotection by estradiol. Prog Neurobiol 2001; 63: 29–60.
McEwen BS . Sex, stress and the hippocampus: allostasis, allostatic load and the aging process. Neurobiol Aging 2002; 23: 921–939.
Kaufer D, Ogle WO, Pincus ZS, Clark KL, Nicholas AC, Dinkel KM et al. Restructuring the neuronal stress response with anti-glucocorticoid gene delivery. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 947–953.
Woolley CS . Acute effects of estrogen on neuronal physiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2007; 47: 657–680.
Roepke TA, Ronnekleiv OK, Kelly MJ . Physiological consequences of membrane-initiated estrogen signaling in the brain. Front Biosci 2011; 16: 1560–1573.
Volkmar FR . Childhood and adolescent psychosis: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996; 35: 843–851.
Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C . Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009; 10: 434–445.
Cohen H, Kaplan Z, Matar MA, Loewenthal U, Zohar J, Richter-Levin G . Long-lasting behavioral effects of juvenile trauma in an animal model of PTSD associated with a failure of the autonomic nervous system to recover. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2007; 17: 464–477.
Nemeroff CB . Early-life adversity, CRF dysregulation, and vulnerability to mood and anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacol Bull 2004; 38 (Suppl 1): 14–20.
Cerqueira JJ, Mailliet F, Almeida OF, Jay TM, Sousa N . The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 2781–2787.
Liston C, Miller MM, Goldwater DS, Radley JJ, Rocher AB, Hof PR et al. Stress-induced alterations in prefrontal cortical dendritic morphology predict selective impairments in perceptual attentional set-shifting. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 7870–7874.
Popoli M, Yan Z, McEwen BS, Sanacora G . The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 13: 22–37.
Goldman-Rakic PS . Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 1995; 14: 477–485.
Lisman JE, Fellous JM, Wang XJ . A role for NMDA-receptor channels in working memory. Nat Neurosci 1998; 1: 273–275.
Yuen EY, Wei J, Liu W, Zhong P, Li X, Yan Z . Repeated stress causes cognitive impairment by suppressing glutamate receptor expression and function in prefrontal cortex. Neuron 2012; 73: 962–977.
Yuen EY, Liu W, Karatsoreos IN, Feng J, McEwen BS, Yan Z . Acute stress enhances glutamatergic transmission in prefrontal cortex and facilitates working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 14075–14079.
Yuen EY, Liu W, Karatsoreos IN, Ren Y, Feng J, McEwen BS et al. Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission and working memory. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 156–170.
Lee JB, Wei J, Liu W, Cheng J, Feng J, Yan Z . Histone deacetylase 6 gates the synaptic action of acute stress in prefrontal cortex. J Physiol 2012; 90: 1535–11546.
Sturman DA, Moghaddam B . Reduced neuronal inhibition and coordination of adolescent prefrontal cortex during motivated behavior. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 1471–1478.
Barker GR, Bird F, Alexander V, Warburton EC . Recognition memory for objects, place, and temporal order: a disconnection analysis of the role of the medial prefrontal cortex and perirhinal cortex. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 2948–2957.
Spiteri T, Musatov S, Ogawa S, Ribeiro A, Pfaff DW, Agmo A . The role of the estrogen receptor alpha in the medial amygdala and ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus in social recognition, anxiety and aggression. Behav Brain Res 2010; 210: 211–220.
Liu W, Dou F, Feng J, Yan Z . RACK1 is involved in b-amyloid impairment of muscarinic regulation of GABAergic transmission. Neurobiol Aging 2011; 32: 1818–1826.
Alfinito PD, Chen X, Atherton J, Cosmi S, Deecher DC . ICI 182,780 penetrates brain and hypothalamic tissue and has functional effects in the brain after systemic dosing. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 5219–5226.
Arnold AP, Gorski RA . Gonadal steroid induction of structural sex differences in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 1984; 7: 413–442.
Hines M . Sex-related variation in human behavior and the brain. Trends Cogn Sci 2010; 14: 448–456.
Shors TJ, Chua C, Falduto J . Sex differences and opposite effects of stress on dendritic spine density in the male versus female hippocampus. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 6292–6297.
McEwen BS . Stress, sex, and neural adaptation to a changing environment: mechanisms of neuronal remodeling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010; 1204 (Suppl): E38–E59.
Galea LA, McEwen BS, Tanapat P, Deak T, Spencer RL, Dhabha FS . Sex differences in dendritic atrophy of CA3 pyramidal neurons in response to chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 1997; 81: 689–697.
Bowman RE, Micik R, Gautreaux C, Fernandez L, Luine VN . Sex-dependent changes in anxiety, memory, and monoamines following one week of stress. Physiol Behav 2009; 97: 21–29.
Shansky RM, Glavis-Bloom C, Lerman D, McRae P, Benson C, Miller K et al. Estrogen mediates sex differences in stress-induced prefrontal cortex dysfunction. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 531–538.
LaPlant Q, Chakravarty S, Vialou V, Mukherjee S, Koo JW, Kalahasti G et al. Role of nuclear factor kappaB in ovarian hormone-mediated stress hypersensitivity in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 65: 874–880.
Weissman MM, Bland RC, Canino GJ, Faravelli C, Greenwald S, Hwu HG et al. Cross-national epidemiology of major depression and bipolar disorder. JAMA 1996; 276: 293–299.
McCarthy MM, Konkle ATM . When is a sex difference not a sex difference? Front Neuroendocrin 2005; 26: 85–102.
Nestler EJ, Barrot M, DiLeone RJ, Eisch AJ, Gold SJ, Monteggia LM . Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 2002; 34: 13–25.
Karatsoreos IN, McEwen BS . Psychobiological allostasis: resistance, resilience and vulnerability. Trends Cogn Sci 2011; 15: 576–584.
Yu H, Wang DD, Wang Y, Liu T, Lee FS, Chen ZY . Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism alters vulnerability to stress and response to antidepressants. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 4092–4101.
Vialou V, Feng J, Robison AJ, Nestler EJ . Epigenetic mechanisms of depression and antidepressant action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2012; 53: 59–87.
Pohl J, Olmstead MC, Wynne-Edwards KE, Harkness K, Menard JL . Repeated exposure to stress across the childhood-adolescent period alters rats' anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in adulthood: the importance of stressor type and gender. Behav Neurosci 2007; 121: 462–474.
Eiland L, Ramroop J, Hill MN, Manley J, McEwen BS . Chronic juvenile stress produces corticolimbic dendritic architectural remodeling and modulates emotional behavior in male and female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012; 37: 39–47.
Woolley CS, McEwen BS . Estradiol regulates hippocampal dendritic spine density via an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 1994; 14: 7680–7687.
Woolley CS, Weiland NG, McEwen BS, Schwartzkroin PA . Estradiol increases the sensitivity of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells to NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic input: correlation with dendritic spine density. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 1848–1859.
Gould E, Woolley CS, Frankfurt M, McEwen BS . Gonadal steroids regulate dendritic spine density in hippocampal pyramidal cells in adulthood. J Neurosci 1990; 10: 1286–1291.
Hao J, Rapp PR, Janssen WG, Lou W, Lasley BL, Hof PR et al. Interactive effects of age and estrogen on cognition and pyramidal neurons in monkey prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 11465–11470.
Foy MR, Xu J, Xie X, Brinton RD, Thompson RF, Berger TW . 17Beta-estradiol enhances NMDA receptor-mediated EPSPs and long-term potentiation. J Neurophysiol 1999; 81: 925–929.
Smith CC, Vedder LC, McMahon LL . Estradiol and the relationship between dendritic spines, NR2B containing NMDA receptors, and the magnitude of long-term potentiation at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009; 34: S130–S142.
Liu F, Day M, Muñiz LC, Bitran D, Arias R, Revilla-Sanchez R et al. Activation of estrogen receptor-beta regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity and improves memory. Nat Neurosci 2008; 11: 334–343.
McLaughlin KJ, Baran SE, Conrad CD . Chronic stress- and sex-specific neuromorphological and functional changes in limbic structures. Mol Neurobiol 2009; 40: 166–182.
Liu HH, Payne HR, Wang B, Brady ST . Gender differences in response of hippocampus to chronic glucocorticoid stress: role of glutamate receptors. J Neurosci Res 2006; 83: 775–786.
Hajszan T, Szigeti-Buck K, Sallam NL, Bober J, Parducz A, Maclusky NJ et al. Effects of estradiol on learned helplessness and associated remodeling of hippocampal spine synapses in female rats. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 168–174.
Garrett JE, Wellman CL . Chronic stress effects on dendritic morphology in medial prefrontal cortex: sex differences and estrogen dependence. Neuroscience 2009; 162: 195–207.
Shansky RM, Hamo C, Hof PR, Lou W, McEwen BS, Morrison JH . Estrogen promotes stress sensitivity in a prefrontal cortex–amygdala pathway. Cereb Cortex 2010; 20: 2560–2567.
Walf AA, Frye CA . A review and update of mechanisms of estrogen in the hippocampus and amygdala for anxiety and depression behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31: 1097–1111.
Tsai G, Coyle JT . Glutamatergic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Annu Rev Pharm Toxicol 2002; 42: 165–179.
Moghaddam B . Bringing order to the glutamate chaos in schizophrenia. Neuron 2003; 40: 881–884.
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK . Synaptic dysfunction in depression: potential therapeutic targets. Science 2012; 338: 68–72.
Konkle AT, McCarthy MM . Developmental time course of estradiol, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone levels in discrete regions of male and female rat brain. Endocrinology 2011; 152: 223–235.
Hojo Y, Hattori T-a, Enami T, Furukawa A, Suzuki K, Ishii HT et al. Adult male rat hippocampus synthesizes estradiol from pregnenolone by cytochromes P45017α and P450 aromatase localized in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 101: 865–870.
Kretz O, Fester L, Wehrenberg U, Zhou L, Brauckmann S, Zhao S et al. Hippocampal synapses depend on hippocampal estrogen synthesis. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 5913–5921.
Prange-Kiel J, Rune GM . Direct and indirect effects of estrogen on rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2006; 138: 765–772.
Rune GM, Frotscher M . Neurosteroid synthesis in the hippocampus: role in synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 2005; 136: 833–842.
Nunez JL, McCarthy MM . Resting intracellular calcium concentration, depolarizing gamma-aminobutyric acid and possible role of local estradiol synthesis in the developing male and female hippocampus. Neuroscience 2009; 158: 623–634.
Dean SL, Wright CL, Hoffman JF, Wang M, Alger BE, McCarthy MM . Prostaglandin E2 stimulates estradiol synthesis in the cerebellum postnatally with associated effects on Purkinje neuron dendritic arbor and electrophysiological properties. Endocrinology 2012; 153: 5415–5427.
McCullough LD, Blizzard K, Simpson ER, Oz OK, Hurn PD . Aromatase cytochrome P450 and extragonadal estrogen play a role in ischemic neuroprotection. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 8701–8705.
Acknowledgements
We thank Xiaoqing Chen for her excellent technical support. This work was supported by NIH Grant MH85774 to ZY. None of the authors have a financial interest related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Yuen, E., Liu, W. et al. Estrogen protects against the detrimental effects of repeated stress on glutamatergic transmission and cognition. Mol Psychiatry 19, 588–598 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.83
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.83
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nrf2 activation rescues stress-induced depression-like behaviour and inflammatory responses in male but not female rats
Biology of Sex Differences (2024)
-
Effects of gestational inflammation on age-related cognitive decline and hippocampal Gdnf-GFRα1 levels in F1 and F2 generations of CD-1 Mice
BMC Neuroscience (2023)
-
Stress-related cellular pathophysiology as a crosstalk risk factor for neurocognitive and psychiatric disorders
BMC Neuroscience (2023)
-
Nucleus reuniens inactivation reverses stress-induced hypodopaminergic state and altered hippocampal-accumbens synaptic plasticity
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
The stressed synapse 2.0: pathophysiological mechanisms in stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2022)