Abstract
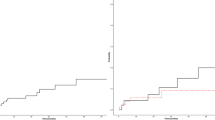
The optimal duration of treatment with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) after venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) is uncertain. To tackle this issue, we retrospectively studied 206 patients with MPN-related VTE (deep venous thrombosis of the legs and/or pulmonary embolism). After this index event, we recorded over 695 pt-years 45 recurrences, venous in 36 cases, with an incidence rate (IR) of 6.5 per 100 pt-years (95% confidence interval (CI): 4.9–8.6). One hundred fifty-five patients received VKA; the IR of recurrent thrombosis per 100 pt-years was 4.7 (95% CI: 2.8–7.3) on VKA and 8.9 (95% CI: 5.7–13.2) off VKA (P=0.03). In patients receiving VKA, the IR of recurrent thrombosis per 100 pt-years was 5.3 (95% CI: 3.2–8.4) among 108 patients on long-term VKA and 12.8 (95% CI: 7.3–20.7) after discontinuation among the 47 who ceased treatment (P=0.008), with a doubled risk of recurrence after stopping VKA (hazard ratio: 2.21, 95% CI: 1.19–5.30). The IR of major bleeding per 100 pt-years was 2.4 (95%: CI: 1.1–4.5) on VKA and 0.7 (95% CI: 0.08–2.5) off VKA (P=0.08). In conclusion, in MPN patients with VTE recurrent thrombosis is significantly reduced by VKA and caution should be adopted in discontinuation; however, the incidence of recurrence on treatment remains high, calling for clinical trials aimed to improve prophylaxis in this setting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patrono C, Rocca B, De Stefano V . Platelet activation and inhibition in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2013; 121: 1701–1711.
Landolfi R, Marchioli R, Kutti J, Gisslinger H, Tognoni G, Patrono C et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose aspirin in polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 114–124.
Marchioli R, Finazzi G, Landolfi R, Kutti J, Gisslinger H, Patrono C et al. Vascular and neoplastic risk in a large cohort of patients with polycythemia vera. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 2224–2232.
Marchioli R, Finazzi G, Specchia G, Cacciola R, Cavazzina R, Cilloni D et al. Cardiovascular events and intensity of treatment in polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 22–33.
Harrison CN, Campbell PJ, Buck G, Wheatley K, East CL, Bareford D et al. Hydroxyurea compared with anagrelide in high-risk essential thrombocythemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 33–45.
Gisslinger H, Gotic M, Holowiecki J, Penka M, Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM et al. Anagrelide compared with hydroxyurea in WHO- classified essential thrombocythemia: the ANAHYDRET Study, a randomized controlled trial. Blood 2013; 121: 1720–1728.
Goldhaber SZ . Venous thromboembolism: epidemiology and magnitude of the problem. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2012; 25: 235–242.
De Stefano V, Za T, Rossi E, Vannucchi AM, Ruggeri M, Elli E et al. Recurrent thrombosis in patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: incidence, risk factors, and effect of treatments. Haematologica 2008; 93: 372–380.
Hernández-Boluda JC, Arellano-Rodrigo E, Cervantes F, Alvarez-Larrán A, Gómez M, Barba P et al. Oral anticoagulation to prevent thrombosis recurrence in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Ann Hematol 2015; 94: 911–918.
Barbui T, Barosi G, Birgegard G, Cervantes F, Finazzi G, Griesshammer M et al. Philadelphia-negative classical myeloproliferative neoplasms: critical concepts and management recommendations from European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 761–770.
Kreher S, Ochsenreither S, Trappe RU, Pabinger I, Bergmann F, Petrides PE et al. Prophylaxis and management of venous thromboembolism in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms: consensus statement of the Haemostasis Working Party of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO), the Austrian Society of Hematology and Oncology (ÖGHO) and Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis Research (GTH e.V.). Ann Hematol 2014; 93: 1953–1963.
Tefferi A, Barbui T . Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 2015; 90: 162–173.
Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, Prandoni P, Bounameaux H, Goldhaber SZ et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012; 141 (2 Suppl): e419S–e4194.
Ellis MH, Lavi N, Vannucchi A, Harrison C . Treatment of thromboembolic events coincident with the diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms: a physician survey. Thromb Res 2014; 134: 251–254.
Tefferi A, Vardiman JW . Classification and diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms: the 2008 World Health Organization criteria and point-of-care diagnostic algorithms. Leukemia 2008; 22: 14–22.
Schulman S, Kearon C Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost 2005; 3: 692–694.
Boutitie F, Pinede L, Schulman S, Agnelli G, Raskob G, Julian J et al. Influence of preceding length of anticoagulant treatment and initial presentation of venous thromboembolism on risk of recurrence after stopping treatment: analysis of individual participants' data from seven trials. BMJ 2011; 342: d3036.
Prandoni P, Noventa F, Ghirarduzzi A, Pengo V, Bernardi E, Pesavento R et al. The risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism after discontinuing anticoagulation in patients with acute proximal deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. A prospective cohort study in 1,626 patients. Haematologica 2007; 92: 199–205.
van Es N, Coppens M, Schulman S, Middeldorp S, Büller HR . Direct oral anticoagulants compared with vitamin K antagonists for acute venous thromboembolism: evidence from phase 3 trials. Blood 2014; 124: 1968–1975.
Prandoni P . Links between arterial and venous disease. J Intern Med 2007; 262: 341–350.
EINSTEIN Investigators EINSTEIN Investigators Bauersachs R EINSTEIN Investigators Berkowitz SD EINSTEIN Investigators Brenner B EINSTEIN Investigators Buller HR EINSTEIN Investigators Decousus H EINSTEIN Investigators Gallus AS et al. Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 2499–2510.
EINSTEIN–PE Investigators EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Büller HR EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Prins MH EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Lensin AW EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Decousus H EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Jacobson BF EINSTEIN–PE Investigators Minar E et al. Oral rivaroxaban for the treatment of symptomatic pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1287–1297.
Agnelli G, Buller HR, Cohen A, Curto M, Gallus AS, Johnson M et al. Oral apixaban for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 799–808.
Hokusai-VTE Investigators Hokusai-VTE Investigators Büller HR Hokusai-VTE Investigators Décousus H Hokusai-VTE Investigators Grosso MA Hokusai-VTE Investigators Mercuri M Hokusai-VTE Investigators Middeldorp S Hokusai-VTE Investigators Prins MH et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 1406–1415.
Paul A Kyrle . How I manage recurrent deep-vein thrombosis. Blood 2015; 27: 696–702.
Oger E . Incidence of venous thromboembolism: a community-based study in Western France EPI-GETBP Study Group. Groupe d'Etude de la Thrombose de Bretagne Occidentale. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: 657–660.
Naess IA, Christiansen SC, Romundstad P, Cannegieter SC, Rosendaal FR, Hammerstrøm J . Incidence and mortality of venous thrombosis: a population-based study. J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: 692–699.
Acknowledgements
TB and AMV were supported by a grant from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC, Milano) 'Special Program Molecular Clinical Oncology 5 × 1000' to AGIMM (AIRC-Gruppo Italiano Malattie Mieloproliferative). VDS was supported by an unrestricted grant from Bruno Farmaceutici Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Stefano, V., Ruggeri, M., Cervantes, F. et al. High rate of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms and effect of prophylaxis with vitamin K antagonists. Leukemia 30, 2032–2038 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.85
This article is cited by
-
Essential Thrombocythemia in Adolescents and Young Adults: Clinical Aspects, Treatment Options and Unmet Medical Needs
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2023)
-
Machine learning analyses constructed a novel model to predict recurrent thrombosis in adults with essential thrombocythemia
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2023)
-
Cytoreductive treatment in real life: a chart review analysis on 1440 patients with polycythemia vera
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2022)
-
Advances in Risk Stratification and Treatment of Polycythemia Vera and Essential Thrombocythemia
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2022)
-
Pathogenesis of cardiovascular events in BCR-ABL1-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms
Leukemia (2021)