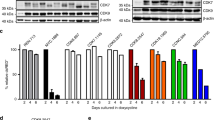
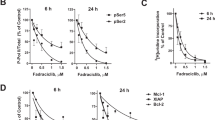
Abstract
Mixed-lineage leukemia fusion proteins activate their target genes predominantly by stimulating transcriptional elongation. A core component necessary for this activity is cyclin-dependent kinase 9. Here we explored the effectiveness of small molecules targeting this enzyme as potential therapeutics. A screen of seven compounds with anti-CDK9 activity applied to a panel of leukemia cell lines identified flavopiridol and the experimental inhibitor PC585 as superior in efficacy with inhibitory concentrations in the submicromolar range. Both substances induced rapid dephosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain, accompanied by downregulation of CDK9-dependent transcripts for MYC and HOXA9. Global gene expression analysis indicated the induction of a general stress response program, culminating in widespread apoptosis. Importantly, colony-forming activity in leukemia lines and primary patient samples could be completely inhibited under conditions that did not affect native precursors from bone marrow. In vivo application in a mouse transplant model significantly delayed disease with PC585 showing also oral activity. These results suggest CDK9 inhibition as novel treatment option for mixed-lineage leukemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krauter J, Wagner K, Schafer I, Marschalek R, Meyer C, Heil G et al. Prognostic factors in adult patients up to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and translocations of chromosome band 11q23: individual patient data-based meta-analysis of the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Intergroup. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3000–3006.
Pui CH, Carroll WL, Meshinchi S, Arceci RJ . Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: an update. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 551–565.
de Boer J, Walf-Vorderwulbecke V, Williams O . In focus: MLL-rearranged leukemia. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1224–1228.
Slany RK . The molecular biology of mixed lineage leukemia. Haematologica 2009; 94: 984–993.
Lin C, Smith ER, Takahashi H, Lai KC, Martin-Brown S, Florens L et al. AFF4, a component of the ELL/P-TEFb elongation complex and a shared subunit of MLL chimeras, can link transcription elongation to leukemia. Mol Cell 2010; 37: 429–437.
Mueller D, Bach C, Zeisig D, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Monroe S, Sreekumar A et al. A role for the MLL fusion partner ENL in transcriptional elongation and chromatin modification. Blood 2007; 110: 4445–4454.
Mueller D, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Bach C, Buhl S, Maethner E, Slany RK . Misguided transcriptional elongation causes mixed lineage leukemia. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e1000249.
Yokoyama A, Lin M, Naresh A, Kitabayashi I, Cleary ML . A higher-order complex containing AF4 and ENL family proteins with P-TEFb facilitates oncogenic and physiologic MLL-dependent transcription. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 198–212.
Zeisig BB, Milne T, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Schreiner S, Martin ME, Fuchs U et al. Hoxa9 and Meis1 are key targets for MLL-ENL-mediated cellular immortalization. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 617–628.
Adelman K, Lis JT . Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II: emerging roles in metazoans. Nat Rev Genet 2012; 13: 720–731.
Peterlin BM, Price DH . Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with P-TEFb. Mol Cell 2006; 23: 297–305.
Mohan M, Herz HM, Takahashi YH, Lin C, Lai KC, Zhang Y et al. Linking H3K79 trimethylation to Wnt signaling through a novel Dot1-containing complex (DotCom). Genes Dev 2010; 24: 574–589.
Maethner E, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Breitinger C, Takacova S, Divoky V, Hess JL et al. MLL-ENL inhibits polycomb repressive complex 1 to achieve efficient transformation of hematopoietic cells. Cell Rep 2013; 3: 1553–1566.
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Basavapathruni A, Jin L, Boriack-Sjodin PA et al. Potent inhibition of DOT1L as treatment of MLL-fusion leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 1017–1025.
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Majer CR, Sneeringer CJ, Song J et al. Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 53–65.
Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittmann A, Giotopoulos G, Bantscheff M, Chan WI et al. Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature 2011; 478: 529–533.
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB, Shi J, Jacobs HM et al. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 2011; 146: 904–917.
Mertz JA, Conery AR, Bryant BM, Sandy P, Balasubramanian S, Mele DA et al. Targeting MYC dependence in cancer by inhibiting BET bromodomains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 16669–16674.
Zuber J, Shi J, Wang E, Rappaport AR, Herrmann H, Sison EA et al. RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2011; 478: 524–528.
Lavau C, Szilvassy SJ, Slany R, Cleary ML . Immortalization and leukemic transformation of a myelomonocytic precursor by retrovirally transduced HRX-ENL. EMBO J 1997; 16: 4226–4237.
Takacova S, Slany R, Bartkova J, Stranecky V, Dolezel P, Luzna P et al. DNA damage response and inflammatory signaling limit the MLL-ENL-induced leukemogenesis in vivo. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 517–531.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 15545–15550.
Bartholomeeusen K, Xiang Y, Fujinaga K, Peterlin BM . Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibition activate transcription via transient release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 36609–36616.
Bernt KM, Zhu N, Sinha AU, Vempati S, Faber J, Krivtsov AV et al. MLL-rearranged leukemia is dependent on aberrant H3K79 methylation by DOT1L. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 66–78.
Guenther MG, Lawton LN, Rozovskaia T, Frampton GM, Levine SS, Volkert TL et al. Aberrant chromatin at genes encoding stem cell regulators in human mixed-lineage leukemia. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 3403–3408.
Wilkinson AC, Ballabio E, Geng H, North P, Tapia M, Kerry J et al. RUNX1 is a key target in t(4;11) leukemias that contributes to gene activation through an AF4-MLL complex interaction. Cell Rep 2013; 3: 116–127.
Loven J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, Lau A, Orlando DA, Vakoc CR et al. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013; 153: 320–334.
He N, Pezda AC, Zhou Q . Modulation of a P-TEFb functional equilibrium for the global control of cell growth and differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 7068–7076.
Napolitano G, Amente S, Castiglia V, Gargano B, Ruda V, Darzacq X et al. Caffeine prevents transcription inhibition and P-TEFb/7SK dissociation following UV-induced DNA damage. PLoS One 2010; 5: e11245.
Ramaswamy B, Phelps MA, Baiocchi R, Bekaii-Saab T, Ni W, Lai JP et al. A dose-finding, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of a novel schedule of flavopiridol in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs 2012; 30: 629–638.
Barr PM . Flavopiridol: Judged by the company one keeps. Leuk Res 2013; 37: 1187–1188.
Acknowledgements
We thank Renate Zimmermann for technical assistance and Ingenium Pharmaceuticals for the generous provision with CDK9 inhibitors. This work was supported by research funding from Sander Stiftung, Grant 2010.069.1 to RKS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
L Zeitlmann is an employee of Ingenium Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Cuellar, MP., Füller, E., Mäthner, E. et al. Efficacy of cyclin-dependent-kinase 9 inhibitors in a murine model of mixed-lineage leukemia. Leukemia 28, 1427–1435 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The mechanism of MYB transcriptional regulation by MLL-AF9 oncoprotein
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
CDKI-73: an orally bioavailable and highly efficacious CDK9 inhibitor against acute myeloid leukemia
Investigational New Drugs (2019)
-
Mission Possible: Advances in MYC Therapeutic Targeting in Cancer
BioDrugs (2019)
-
Recent Treatment Advances and the Role of Nanotechnology, Combination Products, and Immunotherapy in Changing the Therapeutic Landscape of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Pharmaceutical Research (2019)
-
Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2018)