Abstract
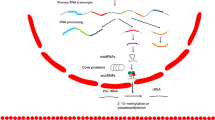
Apart from microRNAs, little is known about the regulation of expression of non-coding RNAs in cancer. We investigated whether small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) accumulation displayed specific signatures in acute myeloblastic and acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Using microarrays and high-throughput quantitative PCR (qPCR), we demonstrate here that snoRNA expression patterns are negatively altered in leukemic cells compared with controls. Interestingly, a specific signature was found in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with ectopic expression of SNORD112–114 snoRNAs located at the DLK1-DIO3 locus. In vitro experiments carried out on APL blasts demonstrate that transcription of these snoRNAs was lost under all-trans retinoic acid-mediated differentiation and induced by enforced expression of the PML–RARalpha fusion protein in negative leukemic cell lines. Further experiments revealed that the SNORD114-1 (14q(II-1)) variant promoted cell growth through cell cycle modulation; its expression was implicated in the G0/G1 to S phase transition mediated by the Rb/p16 pathways. This study thus reports three important observations: (1) snoRNA regulation is different in normal cells compared with cancer cells; (2) a relationship exists between a chromosomal translocation and expression of snoRNA loci; and (3) snoRNA expression can affect Rb/p16 cell cycle regulation. Taken together, these data strongly suggest that snoRNAs have a role in cancer development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et alMicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Calin GA, Croce CM . MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 857–866.
Kiss T . Small nucleolar RNAs: an abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions. Cell 2002; 109: 145–148.
Kiss T, Filipowicz W . Exonucleolytic processing of small nucleolar RNAs from pre-mRNA introns. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 1411–1424.
Dieci G, Preti M, Montanini B . Eukaryotic snoRNAs: a paradigm for gene expression flexibility. Genomics 2009; 94: 83–88.
Decatur WA, Fournier MJ . rRNA modifications and ribosome function. Trends Biochem Sci 2002; 27: 344–351.
Decatur WA, Fournier MJ . RNA-guided nucleotide modification of ribosomal and other RNAs. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 695–698.
Cavaille J, Buiting K, Kiefmann M, Lalande M, Brannan CI, Horsthemke B et alIdentification of brain-specific and imprinted small nucleolar RNA genes exhibiting an unusual genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 14311–14316.
Runte M, Huttenhofer A, Gross S, Kiefmann M, Horsthemke B, Buiting K . The IC-SNURF-SNRPN transcript serves as a host for multiple small nucleolar RNA species and as an antisense RNA for UBE3A. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 2687–2700.
Gallagher RC, Pils B, Albalwi M, Francke U . Evidence for the role of PWCR1/HBII-85 C/D box small nucleolar RNAs in Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 669–678.
Gee HE, Buffa FM, Camps C, Ramachandran A, Leek R, Taylor M et alThe small-nucleolar RNAs commonly used for microRNA normalisation correlate with tumour pathology and prognosis. Br J Cancer 2011; 104: 1168–1177.
Dong XY, Guo P, Boyd J, Sun X, Li Q, Zhou W et alImplication of snoRNA U50 in human breast cancer. J Genet Genomics 2009; 36: 447–454.
Dong XY, Rodriguez C, Guo P, Sun X, Talbot JT, Zhou W et alSnoRNA U50 is a candidate tumor-suppressor gene at 6q14.3 with a mutation associated with clinically significant prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 1031–1042.
Mei YP, Liao JP, Shen JP, Yu L, Liu BL, Liu L et alSmall nucleolar RNA 42 acts as an oncogene in lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2011; e-pub ahead of print 10 October 2011.
Dixon-McIver A, East P, Mein CA, Cazier JB, Molloy G, Chaplin T et alDistinctive patterns of microRNA expression associated with karyotype in acute myeloid leukaemia. PLoS One 2008; 3: e2141.
Narsinh KH, Sun N, Sanchez-Freire V, Lee AS, Almeida P, Hu S et alSingle cell transcriptional profiling reveals heterogeneity of human induced pluripotent stem cells. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 1217–1221.
Marcucci G, Radmacher MD, Maharry K, Mrozek K, Ruppert AS, Paschka P et alMicroRNA expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1919–1928.
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG, Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F et alMicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 3183–3189.
Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, Ridzon D, Moore JH, Chen C et alCharacterization of microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2456–2468.
Cavaille J, Seitz H, Paulsen M, Ferguson-Smith AC, Bachellerie JP . Identification of tandemly-repeated C/D snoRNA genes at the imprinted human 14q32 domain reminiscent of those at the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 1527–1538.
Seitz H, Royo H, Bortolin ML, Lin SP, Ferguson-Smith AC, Cavaille J . A large imprinted microRNA gene cluster at the mouse Dlk1-Gtl2 domain. Genome Res 2004; 14: 1741–1748.
Tierling S, Dalbert S, Schoppenhorst S, Tsai CE, Oliger S, Ferguson-Smith AC et alHigh-resolution map and imprinting analysis of the Gtl2-Dnchc1 domain on mouse chromosome 12. Genomics 2006; 87: 225–235.
Dulaney AM, Murgatroyd RJ . Use of trans-retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann Pharmacother 1993; 27: 211–214.
Sakajiri S, O'Kelly J, Yin D, Miller CW, Hofmann WK, Oshimi K et alDlk1 in normal and abnormal hematopoiesis. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1404–1410.
Lubbert M, Miller CW, Crawford L, Koeffler HP . p53 in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Study of mechanisms of differential expression. J Exp Med 1988; 167: 873–886.
Rui HB, Su JZ . Co-transfection of p16(INK4a) and p53 genes into the K562 cell line inhibits cell proliferation. Haematologica 2002; 7: 136–142.
Butler AP, Trono D, Coletta LD, Beard R, Fraijo R, Kazianis S et alRegulation of CDKN2A/B and retinoblastoma genes in xiphophorus melanoma. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2007; 145: 145–155.
Mizuarai S, Machida T, Kobayashi T, Komatani H, Itadani H, Kotani H . Expression ratio of CCND1 to CDKN2A mRNA predicts RB1 status of cultured cancer cell lines and clinical tumor samples. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 31.
Guo SX, Taki T, Ohnishi H, Piao HY, Tabuchi K, Bessho F et alHypermethylation of p16 and p15 genes and RB protein expression in acute leukemia. Leuk Res 2000; 24: 39–46.
Brameier M, Herwig A, Reinhardt R, Walter L, Gruber J . Human box C/D snoRNAs with miRNA like functions: expanding the range of regulatory RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 39: 675–686.
Ender C, Krek A, Friedlander MR, Beitzinger M, Weinmann L, Chen W et alA human snoRNA with microRNA-like functions. Mol Cell 2008; 32: 519–528.
Kishore S, Khanna A, Zhang ZY, Hui JY, Balwierz PJ, Stefan M et alThe snoRNA MBII-52 (SNORD 115) is processed into smaller RNAs and regulates alternative splicing. Human Molecular Genetics 2010; 19: 1153–1164.
Kishore S, Stamm S . The snoRNA HBII-52 regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C. Science 2006; 311: 230–232.
Mitchell JR, Cheng J, Collins K . A box H/ACA small nucleolar RNA-like domain at the human telomerase RNA 3′ end. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 567–576.
Ono M, Scott MS, Yamada K, Avolio F, Barton GJ, Lamond AI . Identification of human miRNA precursors that resemble box C/D snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: 3879–3891.
Martens JH, Brinkman AB, Simmer F, Francoijs KJ, Nebbioso A, Ferrara F et alPML-RARalpha/RXR alters the epigenetic landscape in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 173–185.
Figueroa ME, Lugthart S, Li Y, Erpelinck-Verschueren C, Deng X, Christos PJ et alDNA methylation signatures identify biologically distinct subtypes in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 13–27.
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA et alSpecific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 435–443.
Meng F, Wehbe-Janek H, Henson R, Smith H, Patel T . Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-370 by interleukin-6 in malignant human cholangiocytes. Oncogene 2008; 27: 378–386.
Benetatos L, Vartholomatos G, Hatzimichael E . MEG3 imprinted gene contribution in tumorigenesis. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 773–779.
Kornblau SM, Xu HJ, Zhang W, Hu SX, Beran M, Smith TL et alLevels of retinoblastoma protein expression in newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 1994; 84: 256–261.
Paggi MG, de Fabritiis P, Bonetto F, Amadio L, Santarelli G, Spadea A et alThe retinoblastoma gene product in acute myeloid leukemia: a possible involvement in promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 4552–4556.
Khan MM, Nomura T, Kim H, Kaul SC, Wadhwa R, Zhong S et alPML-RARalpha alleviates the transcriptional repression mediated by tumor suppressor Rb. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 43491–43494.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients who participated in this study and their referring physicians. We thank the Genotoul platform, Toulouse, France (Naïs Prade and Jean-José Maoret). We also thank Valerie Lallemand-Breitenbach, José Ángel Martínez Climent and Pauline Gravelle for their helpful comments on this work. This study was supported by grants from the Institut Universitaire de France, the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC) and the CITTIL program (Cooperación de Investigación Transpirenaica en la Terapia Innovadora de la Leucemia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valleron, W., Laprevotte, E., Gautier, EF. et al. Specific small nucleolar RNA expression profiles in acute leukemia. Leukemia 26, 2052–2060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.111
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
FUS regulates a subset of snoRNA expression and modulates the level of rRNA modifications
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
snoRNAs: functions and mechanisms in biological processes, and roles in tumor pathophysiology
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
SNORD89 promotes stemness phenotype of ovarian cancer cells by regulating Notch1-c-Myc pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
H/ACA box small nucleolar RNA 7B acts as an oncogene and a potential prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
Cancer Cell International (2019)
-
snoRNAs contribute to myeloid leukaemogenesis
Nature Cell Biology (2017)