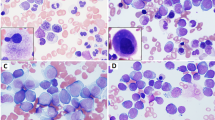
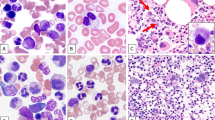
Abstract
The role of the nucleophosmin (NPM1) mutations in de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is well analyzed, but the impact in secondary AML (s-AML) following myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or transformed myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) remains unclear. We investigated 350 patients—283 s-AML after MDS and 67 transformed MPNs—for NPM1mut. NPM1mut was detected in 43/350 patients (12.3%) at diagnosis of s-AML (transformed MDS: 37/283; 13.1%; transformed MPNs: 6/67; 9.0%). Cytogenetic alterations were present in 12/40 cases (30.0%) with available karyotypes. Additional molecular mutations were found in 23/43 NPM1mut s-AML after MDS (53.5%) and in transformed MPN in 18/37 (48.6%): FLT3-ITD: 14/37 (37.8%); FLT3-TKD: 3/28 (10.7%); NRASmut: 4/37 (10.8%), RUNX1mut: 1/16 (6.3%). In NPM1mut-transformed MPNs, five out of six cases showed 1–2 additional molecular mutations (2 × KITD816V, ETV6-PDGFRB, 2 × JAK2V617F, 2 × FLT3-ITD). Backtracking of nine of these cases by quantitative real time PCR showed the NPM1mut already at diagnosis of MDS/MPN, at variable levels and up to 14 months before diagnosis of AML, and at transformation often being preceded or accompanied by other genetic alterations. Thus, NPM1 mutations are involved in the transformation from MDS to AML or MPN to blast phase in single cases, which should be further confirmed in larger studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falini B, Nicoletti I, Martelli MF, Mecucci C . Acute myeloid leukemia carrying cytoplasmic/mutated nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML): biologic and clinical features. Blood 2007; 109: 874–885.
Falini B, Bolli N, Liso A, Martelli MP, Mannucci R, Pileri S et al. Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1731–1743.
Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B, Pandolfi PP . Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 493–505.
Bolli N, De Marco MF, Martelli MP, Bigerna B, Pucciarini A, Rossi R et al. A dose-dependent tug of war involving the NPM1 leukaemic mutant, nucleophosmin, and ARF. Leukemia 2009; 23: 501–509.
Döhner K, Schlenk RF, Habdank M, Scholl C, Rucker FG, Corbacioglu A et al. Mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) predicts favorable prognosis in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: interaction with other gene mutations. Blood 2005; 106: 3740–3746.
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Rosati R, Pasqualucci L et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 254–266.
Schnittger S, Schoch C, Kern W, Mecucci C, Tschulik C, Martelli MF et al. Nucleophosmin gene mutations are predictors of favorable prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. Blood 2005; 106: 3733–3739.
Verhaak RG, Goudswaard CS, van Putten W, Bijl MA, Sanders MA, Hugens W et al. Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and their favorable prognostic significance. Blood 2005; 106: 3747–3754.
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Krauter J, Fröhling S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1909–1918.
Swerdlow S, Campo E, Lee Harris N, Jaffe E, Pileri S, Stein H et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th edn. IARC press: Lyon, 2008.
Falini B . Any role for the nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia with chromosome 5 abnormalities? Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 2093–2095.
Shiseki M, Kitagawa Y, Wang YH, Yoshinaga K, Kondo T, Kuroiwa H et al. Lack of nucleophosmin mutation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia with chromosome 5 abnormalities. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 2141–2144.
Gale RE, Green C, Allen C, Mead AJ, Burnett AK, Hills RK et al. The impact of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutant level, number, size, and interaction with NPM1 mutations in a large cohort of young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 2776–2784.
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Kern W, Haferlach C, Schnittger S . A comparative study of molecular mutations in 381 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and in 4130 patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2007; 92: 744–752.
Pinheiro RF, de Sa Moreira E, Silva MR, Alberto FL, Chauffaille ML . FLT3 internal tandem duplication during myelodysplastic syndrome follow-up: a marker of transformation to acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2008; 183: 89–93.
Kaeferstein A, Krug U, Tiesmeier J, Aivado M, Faulhaber M, Stadler M et al. The emergence of a C/EBPalpha mutation in the clonal evolution of MDS towards secondary AML. Leukemia 2003; 17: 343–349.
Dicker F, Haferlach C, Sundermann J, Wendland N, Weiss T, Kern W et al. Mutation analysis for RUNX1, MLL-PTD, FLT3-ITD, NPM1 and NRAS in 269 patients with MDS or secondary AML. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1528–1532.
Löffler H, Raststetter J, Haferlach T . Atlas of Clinical Hematology, 6th edn. Springer: Berlin, 2004.
Schoch C, Schnittger S, Bursch S, Gerstner D, Hochhaus A, Berger U et al. Comparison of chromosome banding analysis, interphase- and hypermetaphase-FISH, qualitative and quantitative PCR for diagnosis and for follow-up in chronic myeloid leukemia: a study on 350 cases. Leukemia 2002; 16: 53–59.
Schnittger S, Kern W, Tschulik C, Weiss T, Dicker F, Falini B et al. Minimal residual disease levels assessed by NPM1 mutation specific RQ-PCR provide important prognostic information in AML. Blood 2009; 114: 2220–2231.
Schnittger S, Schoch C, Dugas M, Kern W, Staib P, Wuchter C et al. Analysis of FLT3 length mutations in 1003 patients with acute myeloid leukemia: correlation to cytogenetics, FAB subtype, and prognosis in the AMLCG study and usefulness as a marker for the detection of minimal residual disease. Blood 2002; 100: 59–66.
Bacher U, Haferlach C, Kern W, Haferlach T, Schnittger S . Prognostic relevance of FLT3-TKD mutations in AML: the combination matters—an analysis of 3082 patients. Blood 2008; 111: 2527–2537.
Schnittger S, Kinkelin U, Schoch C, Heinecke A, Haase D, Haferlach T et al. Screening for MLL tandem duplication in 387 unselected patients with AML identify a prognostically unfavorable subset of AML. Leukemia 2000; 14: 796–804.
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Schoch C, Kern W, Schnittger S . Implications of NRAS mutations in AML: a study of 2502 patients. Blood 2006; 107: 3847–3853.
Schnittger S, Bacher U, Kern W, Schroder M, Haferlach T, Schoch C . Report on two novel nucleotide exchanges in the JAK2 pseudokinase domain: D620E and E627E. Leukemia 2006; 20: 2195–2197.
Schnittger S, Kohl TM, Haferlach T, Kern W, Hiddemann W, Spiekermann K et al. KIT-D816 mutations in AML1-ETO-positive AML are associated with impaired event-free and overall survival. Blood 2006; 107: 1791–1799.
Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J et al. A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1201–1214.
Kroschinsky FP, Schakel U, Fischer R, Mohr B, Oelschlaegel U, Repp R et al. Cup-like acute myeloid leukemia: new disease or artificial phenomenon? Haematologica 2008; 93: 283–286.
Kern W, Voskova D, Schoch C, Hiddemann W, Schnittger S, Haferlach T . Determination of relapse risk based on assessment of minimal residual disease during complete remission by multiparameter flow cytometry in unselected patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 3078–3085.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Büchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 4642–4649.
Liso A, Castiglione F, Cappuccio A, Stracci F, Schlenk RF, Amadori S et al. A one-mutation mathematical model can explain the age incidence of acute myeloid leukemia with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1). Haematologica 2008; 93: 1219–1226.
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Yang L, Xiao Z . NPM1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Leuk Res 2007; 31: 109–111.
Thiede C, Koch S, Creutzig E, Steudel C, Illmer T, Schaich M et al. Prevalence and prognostic impact of NPM1 mutations in 1485 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2006; 107: 4011–4020.
Ernst T, Chase A, Zoi K, Waghorn K, Hidalgo-Curtis C, Score J et al. Transcription factor mutations in myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Haematologica 2010; 95: 1473–1480.
Falini B, Macijewski K, Weiss T, Bacher U, Schnittger S, Kern W et al. Multilineage dysplasia has no impact on biologic, clinicopathologic, and prognostic features of AML with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1). Blood 2010; 115: 3776–3786.
Chen W, Konoplev S, Medeiros LJ, Koeppen H, Leventaki V, Vadhan-Raj S et al. Cuplike nuclei (prominent nuclear invaginations) in acute myeloid leukemia are highly associated with FLT3 internal tandem duplication and NPM1 mutation. Cancer 2009; 115: 5481–5489.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Brunangelo Falini (Institute of Hematology, University of Perugia) for fruitful discussion of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
SS, CH, WK and TH are part owners of the Munich Leukemia Laboratory. TA, FD and JS are employed by the MLL. UB has nothing to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnittger, S., Bacher, U., Haferlach, C. et al. Characterization of NPM1-mutated AML with a history of myelodysplastic syndromes or myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 25, 615–621 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.299
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.299
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic pitfalls in NPM1-mutated AML: notes from the field
Leukemia (2021)
-
NPM1 Biology in Myeloid Neoplasia
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2020)
-
Sequentially inducible mouse models reveal that Npm1 mutation causes malignant transformation of Dnmt3a-mutant clonal hematopoiesis
Leukemia (2019)
-
Biological and clinical consequences of NPM1 mutations in AML
Leukemia (2017)
-
Dynamics of clonal evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes
Nature Genetics (2017)