Abstract
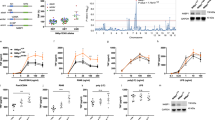
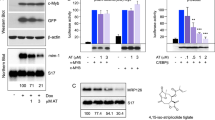
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) is mutated in 10% of acute myeloid leukemias, resulting in either a truncated protein or an altered leucine zipper (C/EBPαLZ) that prevents DNA binding. C/EBPα induces bcl-2 in cooperation with nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p50 to inhibit apoptosis. We now demonstrate that C/EBPα or a C/EBPαLZ oncoprotein binds the bcl-2 P2 promoter in chromatin immunoprecipitation assays and induces the promoter dependent on the integrity of a κB site. C/EBPα expressed as a transgene in B cells binds and activates the bcl-2 promoter, but not in nfkb1−/− mice lacking NF-κB p50. Bcl-2 is central to the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, whereas FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP) modulates caspase-8, the initiator caspase of the extrinsic pathway. C/EBPα and C/EBPαLZ also bind the FLIP promoter and induce its expression dependent upon NF-κB p50. Moreover, induction of FLIP by C/EBPα protects splenocytes from Fas ligand-induced apoptosis, but only if p50 is present. We also demonstrate the direct interaction between bacterially produced C/EBPα and NF-κB p50, mediated by the C/EBPα basic region. These findings indicate that C/EBPα or its oncoproteins activate the bcl-2 and FLIP genes by tethering to their promoters through bound NF-κB p50. Targeting their interaction may favor apoptosis of transformed cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman AD, McKnight SL . Identification of two polypeptide segments of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein required for transcriptional activation of the serum albumin gene. Genes Dev 1990; 4: 1416–1426.
Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, McKnight SL . The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 1988; 240: 1759–1764.
Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, McKnight SL . The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science 1989; 243: 1681–1688.
Friedman AD . Transcriptional control of granulocyte and monocyte development. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6816–6828.
Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P, Friedman AD . A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood 1992; 80: 1725–1735.
Wang D, D'Costa J, Civin CI, Friedman AD . C/EBPα directs monocytic commitment of primary myeloid progenitors. Blood 2006; 108: 1223–1229.
Zhang DE, Zhang P, Wang ND, Hetherington CJ, Darlington GJ, Tenen DG . Absence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in CCAAT enhancer binding protein α-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 569–574.
Zhang P, Iwasaki-Arai J, Iwasaki H, Fenyus ML, Dayaram T, Owens BM et al. Enhancement of hematopoietic stem cell repopulating capacity and self-renewal in the absence of the transcription factor C/EBPα. Immunity 2004; 21: 853–863.
Frohling S, Schlenk RF, Stolze I, Bihlmayr J, Benner A, Kreitmeier S et al. CEBPA mutations in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: prognostic relevance and analysis of cooperating mutations. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 624–633.
Gombart AF, Hofmann WK, Kawano S, Takeuchi S, Krug U, Kwok SH et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. Blood 2002; 99: 1332–1340.
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Narravula S, Schnittger S et al. Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 263–270.
Preudhomme C, Sagot C, Boissel N, Cayuela JM, Tigaud I, de Botton S et al. Favorable prognostic significance of CEBPA mutations in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA). Blood 2002; 100: 2717–2723.
Liang DC, Shih LY, Huang CF, Hung IJ, Yang CP, Liu HC et al. CEBPα mutations in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 410–414.
Cleaves R, Wang QF, Friedman AD . C/EBPαp30, a myeloid leukemia oncoprotein, limits G-CSF receptor expression but not terminal granulopoiesis via site-selective inhibition of C/EBP DNA binding. Oncogene 2004; 23: 716–725.
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Harakawa N, Schoch C, Haferlach T, Behre G et al. AML1-ETO downregulates the granulocytic differentiation factor C/EBPα in t(8;21) myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 2001; 7: 444–451.
Zheng R, Friedman AD, Levis M, Li L, Weir EG, Small D . Internal tandem duplication mutation of FLT3 blocks myeloid differentiation through suppression of C/EBPα expression. Blood 2004; 103: 1883–1890.
Perrotti D, Cesi V, Trotta R, Guerzoni C, Santilli G, Campbell K et al. BCR-ABL suppresses C/EBPα expression through inhibitory action of hnRNP E2. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 48–58.
Pabst T, Mueller BU . Transcriptional dysregulation during myeloid transformation in AML. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6829–6837.
Paz-Priel I, Cai DH, Wang D, Kowalski J, Blackford A, Liu H et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) and C/EBPα myeloid oncoproteins induce bcl-2 via interaction of their basic regions with nuclear factor-κB p50. Mol Cancer Res 2005; 3: 585–596.
Campos L, Rouault JP, Sabido O, Oriol P, Roubi N, Vasselon C et al. High expression of bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood 1993; 81: 3091–3096.
Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Del Principe MI, Maurillo L, Buccisano F, Tamburini A et al. Amount of spontaneous apoptosis detected by Bax/Bcl-2 ratio predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2003; 101: 2125–2131.
Del Princip MI, Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Buccisano F, Maurillo L, Mazzone C et al. Apoptosis and immaturity in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology 2005; 10: 25–34.
Meyer LH, Queudeville M, Eckhoff SM, Creutzig U, Reinhardt D, Karawajew L et al. Intact apoptosis signalling in myeloid leukaemia cells determines treatment outcome in childhood AML. Blood 2008; 111: 2899–2903.
Otten HG, van Ginkel WG, Hagenbeek A, Petersen EJ . Prevalence and clinical significance of resistance to perforin- and FAS-mediated cell death in leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1401–1405.
Calvo KR, Sykes DB, Pasillas M, Kamps MP . Hoxa9 immortalizes a granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent promyelocyte capable of biphenotypic differentiation to neutrophils or macrophages, independent of enforced meis expression. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 3274–3285.
Agre P, Johnson PF, McKnight SL . Cognate DNA binding specificity retained after leucine zipper exchange between GCN4 and C/EBP. Science 1989; 246: 922–926.
Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Boxer LM . NF-κB activates Bcl-2 expression in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 2002; 21: 3898–3908.
Sha WC, Liou HC, Tuomanen EI, Baltimore D . Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-κB leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell 1995; 80: 321–330.
Watanabe D, Suda T, Nagata S . Expression of Fas in B cells of the mouse germinal center and Fas-dependent killing of activated B cells. Int Immunol 1995; 7: 1949–1956.
Oelgeschlager M, Nuchprayoon I, Luscher B, Friedman AD . C/EBP, c-Myb, and PU.1 cooperate to regulate the neutrophil elastase promoter. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 4717–4725.
Stein B, Cogswell PC, Baldwin Jr AS . Functional and physical associations between NF-κB and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain–bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13: 3964–3974.
Stein B, Baldwin Jr AS . Distinct mechanisms for regulation of the interleukin-8 gene involve synergism and cooperativity between C/EBP and NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13: 7191–7198.
Hu HM, Tian Q, Baer M, Spooner CJ, Williams SC, Johnson PF et al. The C/EBP bZIP domain can mediate lipopolysaccharide induction of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 16373–16381.
Kim H, Whartenby KA, Georgantas III RW, Wingard J, Civin CI . Human CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells express high levels of FLIP and are resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Stem Cells 2002; 20: 174–182.
Dutton A, O'Neil JD, Milner AE, Reynolds GM, Starczynski J, Crocker J et al. Expression of the cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) protects Hodgkin's lymphoma cells from autonomous Fas-mediated death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6611–6616.
Thomas RK, Kallenborn A, Wickenhauser C, Schultze JL, Draube A, Vockerodt M et al. Constitutive expression of c-FLIP in Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 1521–1528.
Jundt F, Raetzel N, Muller C, Calkhoven CF, Kley K, Mathas S et al. A rapamycin derivative (everolimus) controls proliferation through down-regulation of truncated CCAAT enhancer binding protein β and NF-κB activity in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Blood 2005; 106: 1801–1807.
Zhang X, Jin TG, Yang H, DeWolf WC, Khosravi-Far R, Olumi AF . Persistent c-FLIP(L) expression is necessary and sufficient to maintain resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7086–7091.
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J, Sjoblom T, Leary RJ et al. The genomic landscape of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2007; 318: 1108–1113.
Zahnow CA, Younes P, Laucirica R, Rosen JM . Overexpression of C/EBPβ-LIP a naturally occurring, dominant-negative transcription factor, in human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1997; 89: 1887–1891.
Ditsworth D, Zong WX . NF-κB: key mediator of inflammation-associated cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2004; 3: 1214–1216.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation and the Children's Cancer Foundation (ADF), the Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation (IPP) and by NIH Grant R01 HL082948 (ADF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paz-Priel, I., Ghosal, A., Kowalski, J. et al. C/EBPα or C/EBPα oncoproteins regulate the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways by direct interaction with NF-κB p50 bound to the bcl-2 and FLIP gene promoters. Leukemia 23, 365–374 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.297
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PHF6 maintains acute myeloid leukemia via regulating NF-κB signaling pathway
Leukemia (2023)
-
Homodimer-mediated phosphorylation of C/EBPα-p42 S16 modulates acute myeloid leukaemia differentiation through liquid-liquid phase separation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
The AML-associated K313 mutation enhances C/EBPα activity by leading to C/EBPα overexpression
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
C/EBPα in normal and malignant myelopoiesis
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
HTLV-1 bZIP factor supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells through suppression of C/EBPα signaling
Retrovirology (2013)