Abstract
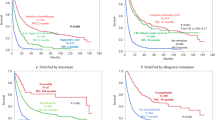
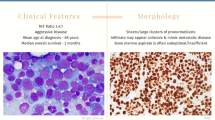
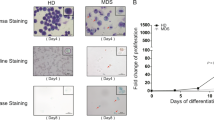
Acute erythroleukemia (AML-M6) is an uncommon subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML); it is considered to have a poor prognosis. From 1 January 1980 to 21 May 2008, 91 patients with newly diagnosed AML-M6 were seen at the University of Texas–M.D. Anderson Cancer Center (UT–MDACC). Forty-five patients (50%) had a history of myelodysplatic syndrome (MDS), compared with 41% in our control group (patients with other AML subtypes) (P=0.08). Poor-risk cytogenetics were more common in patients with AML-M6 (61% versus 38%, P=0.001). Complete remission rates were 62% for patients with AML-M6, comparing with 58% for the control group (P=0.35). Median disease free survival (DFS) for patients with AML-M6 was 32 weeks, versus 49 weeks for the control group (P=0.05). Median overall survival (OS) of patients with AML-M6 was 36 weeks, compared with 43 weeks for the control group (P=0.60). On multivariate analysis for DFS and OS, AML-M6 was not an independent risk factor. AML-M6 is commonly associated with a previous diagnosis of MDS and poor-risk karyotype. The diagnosis of AML-M6 does not impart by itself a worse prognosis, and treatment decisions on this disease should be guided by well known AML prognostic factors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copelli M . Di una emopatia sistemizzata rapresentata da una imperplasia eritroblastica (eritronatosis). Pathologica 1912; 4: 460.
Di Guglielmo G . Richerche di ematologia. I. Un caso di eritroleucemia. Megacariociti in circolo e loro funzione piastrinopoietico. Folia Medica (Pavia) 1917; 13: 386.
Bain BJ . Di Guglielmo and his syndromes. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 939–943.
Di Guglielmo G . Eritremie acute. XXIX Congr Italiano Medical International; Roma, 1923.
Dameshek W, Baldini M . The Di Guglielmo syndrome. Blood 1958; 13: 192–194.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French–American–British (FAB) co-operative group. Br J Haematol 1976; 33: 451–458.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French–American–British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med 1985; 103: 620–625.
Brunning RD, Matutes E, Flandrin G, Vardiman JW, Bennett JM, Head DR et al. Acute myeloid leukemia not otherwise categorized. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001, pp 91–105.
Davey FR, Abraham Jr N, Brunetto VL, MacCallum JM, Nelson DA, Ball ED et al. Morphologic characteristics of erythroleukemia (acute myeloid leukemia; FAB-M6): a CALGB study. Am J Hematol 1995; 49: 29–38.
Peterson BA, Levine EG . Uncommon subtypes of acute nonlymphocytic leukemia: clinical features and management of FAB M5, M6 and M7. Semin Oncol 1987; 14: 425–434.
Olopade OI, Thangavelu M, Larson RA, Mick R, Kowal-Vern A, Schumacher HR et al. Clinical, morphologic, and cytogenetic characteristics of 26 patients with acute erythroblastic leukemia. Blood 1992; 80: 2873–2882.
Bennett JM, Begg CB . Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study of the cytochemistry of adult acute myeloid leukemia by correlation of subtypes with response and survival. Cancer Res 1981; 41: 4833–4837.
Lowenberg B . Prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract Res 2001; 14: 65–75.
Barnard DR, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Lange B, Woods WG . Comparison of childhood myelodysplastic syndrome, AML FAB M6 or M7, CCG 2891: report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007; 49: 17–22.
Malkin D, Freedman MH . Childhood erythroleukemia: review of clinical and biological features. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1989, Fall 11: 348–359.
Lazure T, Beauchamp A, Croisille L, Ferlicot S, Feneux D, Fabre M . Congenital anerythremic erythroleukemia presenting as hepatic failure. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003; 127: 1362–1365.
Novik Y, Marino P, Makower DF, Wiernik PH . Familial erythroleukemia: a distinct clinical and genetic type of familial leukemias. Leuk Lymphoma 1998; 30: 395–401.
Nakamura H . Cytogenetic heterogeneity in erythroleukemia defined as M6 by the French–American–British (FAB) Cooperative Group criteria. Leukemia 1989; 3: 305–309.
Atkinson J, Hrisinko MA, Weil SC . Erythroleukemia: a review of 15 cases meeting 1985 FAB criteria and survey of the literature. Blood Rev 1992; 6: 204–214.
Lessard M, Struski S, Leymarie V, Flandrin G, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Mozziconacci MJ et al. Cytogenetic study of 75 erythroleukemias. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2005; 163: 113–122.
Garand R, Duchayne E, Blanchard D, Robillard N, Kuhlein E, Fenneteau O et al. Minimally differentiated erythroleukaemia (AML M6 ‘variant’): a rare subset of AML distinct from AML M6. Groupe Francais d'Hematologie Cellulaire. Br J Haematol 1995; 90: 868–875.
Greaves MF, Sieff C, Edwards PA . Monoclonal antiglycophorin as a probe for erythroleukemias. Blood 1983; 61: 645–651.
Shichishima T . Minimally differentiated erythroleukemia: recognition of erythroid precursors and progenitors. Intern Med (Tokyo, Japan) 2000; 39: 761–762.
Villeval JL, Cramer P, Lemoine F, Henri A, Bettaieb A, Bernaudin F et al. Phenotype of early erythroblastic leukemias. Blood 1986; 68: 1167–1174.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children's Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood 1998; 92: 2322–2333.
Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Cassileth PA, Harrington DH, Theil KS, Mohamed A et al. Karyotypic analysis predicts outcome of preremission and postremission therapy in adult acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Blood 2000; 96: 4075–4083.
Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, Carroll AJ, Edwards CG, Arthur DC et al. Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood 2002; 100: 4325–4336.
Cheson BD, Cassileth PA, Head DR, Schiffer CA, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD et al. Report of the National Cancer Institute-sponsored workshop on definitions of diagnosis and response in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1990; 8: 813–819.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Buchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 4642–4649.
Snedecor G, Cochran W . Statistical Methods, 7th edn, Iowa State University Press: Armes, IA, 1980.
Kaplan EL, Meire P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Cox D . Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc 1972; 34: 187–202.
Colita A, Belhabri A, Chelghoum Y, Charrin C, Fiere D, Thomas X . Prognostic factors and treatment effects on survival in acute myeloid leukemia of M6 subtype: a retrospective study of 54 cases. Ann Oncol 2001; 12: 451–455.
Cuneo A, Van Orshoven A, Michaux JL, Boogaerts M, Louwagie A, Doyen C et al. Morphologic, immunologic and cytogenetic studies in erythroleukaemia: evidence for multilineage involvement and identification of two distinct cytogenetic-clinicopathological types. Br J Haematol 1990; 75: 346–354.
Cigudosa JC, Odero MD, Calasanz MJ, Sole F, Salido M, Arranz E et al. De novo erythroleukemia chromosome features include multiple rearrangements, with special involvement of chromosomes 11 and 19. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003; 36: 406–412.
Park S, Picard F, Dreyfus F . Erythroleukemia: a need for a new definition. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1399–1401.
Domingo-Claros A, Larriba I, Rozman M, Irriguible D, Vallespi T, Aventin A et al. Acute erythroid neoplastic proliferations. A biological study based on 62 patients. Haematologica 2002; 87: 148–153.
Hayhoe FGJ, Quaglino D . Haematological Cytochemistry, 2nd edn, Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, 1988.
Frydecka I, Brodzka W, Lawinska B, Sciborski R . Clinical course and results of treatment of erythroleukaemia. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch 1984; 111: 283–289.
Fouillard L, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Polge E, Prentice HG, Meloni G et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for de novo erythroleukemia: a study of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Blood 2002; 100: 3135–3140.
Killick S, Matutes E, Powles RL, Min T, Treleaven JG, Rege KP et al. Acute erythroid leukemia (M6): outcome of bone marrow transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma 1999; 35: 99–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, F., Faderl, S., Garcia-Manero, G. et al. Adult acute erythroleukemia: an analysis of 91 patients treated at a single institution. Leukemia 23, 2275–2280 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.181
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A rare de novo pure erythroid leukemia with JAK2 R683S mutation
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Erythroleukemia: an Update
Current Oncology Reports (2021)
-
Molecular evidence of JAK2 p.V617F mutated pure erythroid leukemia arising from polycythemia vera
Virchows Archiv (2018)
-
Antiproliferative effect of upregulation of hsa-let-7c-5p in human acute erythroleukemia cells
Cytotechnology (2018)
-
An analysis of 97 previously diagnosed de novo adult acute erythroid leukemia patients following the 2016 revision to World Health Organization classification
BMC Cancer (2017)