Abstract
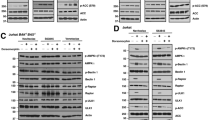
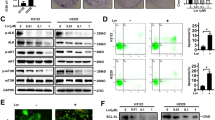
p53 is expressed frequently, but is rarely mutated in anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)–positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) tumours. Nutlin-3a is a recently developed small molecule that targets Mdm2, a critical negative regulator of p53, and disrupts the p53–Mdm2 interaction resulting in p53 stabilization and activation. We show that nutlin-3a activates p53 in ALK+ ALCL cells carrying a wild type (wt) or mutated but partially functional p53 gene resulting in p53-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cell-cycle arrest was associated with upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Nutlin-3a-induced apoptotic cell death was accompanied by Bax and Puma upregulation, downregulation of Bcl-xl, survivin, and caspase-3 cleavage, and this was reduced when p53-dependent transactivation activity was inhibited by pifithrin-α, or when pifithrin-μ was used to inhibit direct p53 targeting of mitochondria. Nutlin-3a sensitized the activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in wt-p53 ALK+ ALCL cells, in part, through upregulation of DR-5 and downregulation of c-FlipS/L, and was synergistic with TRAIL in cell death induction. In addition, nutlin-3a treatment enhanced doxorubicin cytotoxicity against ALK+ ALCL cells harbouring mt p53, and this was associated with p73 upregulation. These data suggest that disruption of the p53–mdm2 interaction by nutlin-3a offers a novel therapeutic approach for ALK+ ALCL patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delsol G, Falini B, Muller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Gascoyne RD, et al., World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H., Thiele J, Vardiman JW (eds). IARC Press: Lyon, France, 4th edn 2008, 312–316.
Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G . The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 11–23.
Stein H, Foss HD, Durkop H, Marafioti T, Delsol G, Pulford K et al. CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood 2000; 96: 3681–3695.
Gascoyne RD, Aoun P, Wu D, Chhanabhai M, Skinnider BF, Greiner TC et al. Prognostic significance of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein expression in adults with anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 1999; 93: 3913–3921.
Falini B, Pileri S, Zinzani PL, Carbone A, Zagonel V, Wolf-Peeters C et al. ALK+lymphoma: clinico-pathological findings and outcome. Blood 1999; 93: 2697–2706.
Savage KJ, Harris NL, Vose JM, Ullrich F, Jaffe ES, Connors JM et al. ALK- anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: report from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 2008; 111: 5496–5504.
Brugieres L, Deley MC, Pacquement H, Meguerian-Bedoyan Z, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Robert A et al. CD30(+) anaplastic large-cell lymphoma in children: analysis of 82 patients enrolled in two consecutive studies of the French Society of Pediatric Oncology. Blood 1998; 92: 3591–3598.
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ . Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000; 408: 307–310.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC . p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 1991; 253: 49–53.
Ventura A, Kirsch DG, McLaughlin ME, Tuveson DA, Grimm J, Lintault L et al. Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. Nature 2007; 445: 661–665.
Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, Dickins RA, Hernando E, Krizhanovsky V et al. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature 2007; 445: 656–660.
Martins CP, Brown-Swigart L, Evan GI . Modeling the therapeutic efficacy of p53 restoration in tumors. Cell 2006; 127: 1323–1334.
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004; 303: 844–848.
Tovar C, Rosinski J, Filipovic Z, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Hilton H et al. Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in cancer: implications for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 1888–1893.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, McQueen T, O'Brien S, Plunkett W, Andreeff M . Mdm2 inhibitor nutlin-3a induces p53-mediated apoptosis by transcription-dependent and transcription-independent mechanisms and may overcome Atm-mediated resistance to fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 993–1000.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Samudio IJ, Shikami M, Cabreira-Hansen M, McQueen T et al. MDM2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy. Blood 2005; 106: 3150–3159.
Drakos E, Thomaides A, Medeiros LJ, Li J, Leventaki V, Konopleva M et al. Inhibition of p53-murine double minute 2 interaction by nutlin-3A stabilizes p53 and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 3380–3387.
Stuhmer T, Chatterjee M, Hildebrandt M, Herrmann P, Gollasch H, Gerecke C et al. Nongenotoxic activation of the p53 pathway as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma. Blood 2005; 106: 3609–3617.
Sarek G, Kurki S, Enback J, Iotzova G, Haas J, Laakkonen P et al. Reactivation of the p53 pathway as a treatment modality for KSHV-induced lymphomas. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 1019–1028.
Gu L, Zhu N, Findley HW, Zhou M . MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3 is a potent inducer of apoptosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells with wild-type p53 and overexpression of MDM2. Leukemia 2008; 22: 730–739.
Janz M, Stuhmer T, Vassilev LT, Bargou RC . Pharmacologic activation of p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptotic pathways in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells. Leukemia 2007; 21: 772–779.
Secchiero P, Barbarotto E, Tiribelli M, Zerbinati C, di Iasio MG, Gonelli A et al. Functional integrity of the p53-mediated apoptotic pathway induced by the nongenotoxic agent nutlin-3 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 2006; 107: 4122–4129.
Coll-Mulet L, Iglesias-Serret D, Santidrian AF, Cosialls AM, de Frias M, Castano E et al. MDM2 antagonists activate p53 and synergize with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2006; 107: 4109–4114.
Tabe Y, Sebasigari D, Jin L, Rudelius M, Davies-Hill T, Miyake K et al. MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3 displays antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 933–942.
Drakos E, Atsaves V, Li J, Leventaki V, Andreeff M, Medeiros LJ et al. Stabilization and activation of p53 downregulates mTOR signaling through AMPK in mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2009; 23: 784–790.
Rassidakis GZ, Thomaides A, Wang S, Jiang Y, Fourtouna A, Lai R et al. p53 gene mutations are uncommon but p53 is commonly expressed in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1663–1669.
Hubinger G, Muller E, Scheffrahn I, Schneider C, Hildt E, Singer BB et al. CD30-mediated cell cycle arrest associated with induced expression of p21(CIP1/WAF1) in the anaplastic large cell lymphoma cell line Karpas 299. Oncogene 2001; 20: 590–598.
Turturro F, Heineke HL, Drevyanko TF, Link Jr CJ, Seth P . Adenovirus-p 53-mediated gene therapy of anaplastic large cell lymphoma with t(2;5) in a nude mouse model. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 930–933.
Inga A, Storici F, Darden TA, Resnick MA . Differential transactivation by the p53 transcription factor is highly dependent on p53 level and promoter target sequence. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 8612–8625.
Resnick MA, Inga A . Functional mutants of the sequence-specific transcription factor p53 and implications for master genes of diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 9934–9939.
Komarov PG, Komarova EA, Kondratov RV, Christov-Tselkov K, Coon JS, Chernov MV et al. A chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side effects of cancer therapy. Science 1999; 285: 1733–1737.
Strom E, Sathe S, Komarov PG, Chernova OB, Pavlovska I, Shyshynova I et al. Small-molecule inhibitor of p53 binding to mitochondria protects mice from gamma radiation. Nat Chem Biol 2006; 2: 474–479.
Oyarzo MP, Medeiros LJ, Atwell C, Feretzaki M, Leventaki V, Drakos E et al. c-FLIP confers resistance to FAS-mediated apoptosis in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006; 107: 2544–2547.
Kitagawa M, Aonuma M, Lee SH, Fukutake S, McCormick F . E2F-1 transcriptional activity is a critical determinant of Mdm2 antagonist-induced apoptosis in human tumor cell lines. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5303–5314.
Lau LM, Nugent JK, Zhao X, Irwin MS . HDM2 antagonist nutlin-3 disrupts p73-HDM2 binding and enhances p73 function. Oncogene 2008; 27: 997–1003.
Ambrosini G, Sambol EB, Carvajal D, Vassilev LT, Singer S, Schwartz GK . Mouse double minute antagonist nutlin-3a enhances chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in cancer cells with mutant p53 by activating E2F1. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3473–3481.
Cui YX, Kerby A, McDuff FK, Ye H, Turner SD . NPM-ALK inhibits the p53 tumour suppressor pathway in an MDM2 and JNK-dependent manner. Blood 2009; 113: 5217–5227.
Rassidakis GZ, Sarris AH, Herling M, Ford RJ, Cabanillas F, McDonnell TJ et al. Differential expression of BCL-2 family proteins in ALK-positive and ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma of T/null-cell lineage. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 527–535.
Rassidakis GZ, Jones D, Lai R, Ramalingam P, Sarris AH, McDonnell TJ et al. BCL-2 family proteins in peripheral T-cell lymphomas: correlation with tumour apoptosis and proliferation. J Pathol 2003; 200: 240–248.
Drakos E, Rassidakis GZ, Lai R, Herling M, O'Connor SL, Schmitt-Graeff A et al. Caspase-3 activation in systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 2004; 17: 109–116.
Oyarzo MP, Drakos E, Atwell C, Amin HM, Medeiros LJ, Rassidakis GZ . Intrinsic apoptotic pathway in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Hum Pathol 2006; 37: 874–882.
Schlette EJ, Medeiros LJ, Goy A, Lai R, Rassidakis GZ . Survivin expression predicts poorer prognosis in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1682–1688.
Steele AJ, Prentice AG, Hoffbrand AV, Yogashangary BC, Hart SM, Nacheva EP et al. p53-mediated apoptosis of CLL cells: evidence for a transcription-independent mechanism. Blood 2009; 112: 3827–3834, 2009.
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L, Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD, Green DR . PUMA couples the nuclear and cytoplasmic proapoptotic function of p53. Science 2005; 309: 1732–1735.
Schuler M, Green DR . Transcription, apoptosis and p53: catch-22. Trends Genet 2005; 21: 182–187.
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Humphreys R, Andreeff M, O'Brien S, Younes M et al. Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of doxorubicin- and bortezomib-induced cell death. Br J Haematol 2005; 130: 501–510.
Secchiero P, Zerbinati C, di Iasio MG, Melloni E, Tiribelli M, Grill V et al. Synergistic cytotoxic activity of recombinant TRAIL plus the non-genotoxic activator of the p53 pathway nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Curr Drug Metab 2007; 8: 395–403.
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Schober WD, Dietrich MF, Pinilla C, Vassilev LT et al. Triptolide sensitizes AML cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via decrease of XIAP and p53-mediated increase of DR5. Blood 2008; 111: 3742–3750.
Carvajal D, Tovar C, Yang H, Vu BT, Heimbrook DC, Vassilev LT . Activation of p53 by MDM2 antagonists can protect proliferating cells from mitotic inhibitors. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1918–1924.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drakos, E., Atsaves, V., Schlette, E. et al. The therapeutic potential of p53 reactivation by nutlin-3a in ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma with wild-type or mutated p53. Leukemia 23, 2290–2299 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.180
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Resistance mechanisms to inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interactions in cancer therapy: can we overcome them?
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2021)
-
PUMA Protein in p53 Regulatory Molecule Pattern Determines the Prognosis for Patients with Lymphoproliferative Diseases
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2014)
-
Targeting p53 by small molecules in hematological malignancies
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2013)
-
MDM2 Inhibitor Nutlin-3a Induces Apoptosis and Senescence in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma: Role of p53
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2012)
-
Activation of the p53 pathway by the MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3a overcomes BCL2 overexpression in a preclinical model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with t(14;18)(q32;q21)
Leukemia (2011)