Abstract
We investigated whether FNIII14, a 22-mer peptide derived from fibronectin (FN) that potently impairs interaction of FN with β1-integrin, could overcome cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) induced by very late antigen (VLA)-4-to-FN interaction in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Two AML cell lines, U937 cells and HL-60 cells, and fresh leukemic cells from six AML patients with high α4-integrin expression exhibited CAM-DR to cytosine arabinoside (Ara C) through VLA-4-to-FN interaction, while fresh leukemic cells from two AML patients with low α4-integrin expression did not display CAM-DR to Ara C. FNIII14 impaired VLA-4-to-FN interaction and restored sensitivity to Ara C in the CAM-DR leukemic cells. In these CAM-DR leukemic cells, upregulation of Bcl-2, which was induced through the focal adhesion kinase/Akt signal pathway upon VLA-4-to-FN interaction, was inhibited by FNIII14 treatment. In a mouse model of minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow, 100% survival was achieved by combining FNIII14 with Ara C, whereas Ara C alone prolonged survival only slightly. The myelosuppression induced by Ara C was not augmented by the combination of FNIII14 in mouse experiments. Thus, the combination of anticancer drugs and FNIII14 holds promise to eradicate MRD in bone marrow after chemotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohno R, Kobayashi T, Tanimoto M, Hiraoka A, Imai K, Asou N et al. Randomized study of individualized induction therapy with or without vincristine, and of maintenance-intensification therapy between 4 or 12 courses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. AML-87 Study of the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. Cancer 1993; 71: 3888–3895.
Hann IM, Stevens RF, Goldstone AH, Rees JK, Wheatley K, Gray RG et al. Randomized comparison of DAT versus ADE as induction chemotherapy in children and younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Results of the Medical Research Council's 10th AML trial (MRC AML10). Adult and Childhood Leukaemia Working Parties of the Medical Research Council. Blood 1997; 89: 2311–2318.
Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A . Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1051–1062.
Matsunaga T, Takemoto N, Sato T, Takimoto R, Tanaka I, Fujimi A et al. Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin is a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute myelogenous leukemia. Nat Med 2003; 91: 1158–1165.
Feller N, van der Pol MA, van Stijn A, Weijers GW, Westra AH, Evertse BW et al. MRD parameters using immunophenotypic detection methods are highly reliable in predicting survival in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1380–1390.
Kern W, Voskova D, Schoch C, Hiddemann W, Schnittger S, Haferlach T . Determination of relapse risk based on assessment of minimal residual disease during complete remission by multiparameter flow cytometry in unselected patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 3078–3085.
Gazitt Y . Homing and mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoietic cancer cells are mirror image processes, utilizing similar signaling pathways and occurring concurrently: circulating cancer cells constitute an ideal target for concurrent treatment with chemotherapy and antilineage-specific antibodies. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1–10.
Mudry RE, Fortney JE, York T, Hall BM, Gibson LF . Stromal cells regulate survival of B-lineage leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood 2000; 96: 1926–1932.
de la Fuente MT, Casanova B, Moyano JV, Garcia-Gila M, Sanz L, Garcia-Marco J et al. Engagement of α4β1 integrin by fibronectin induces in vitro resistance of B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to fludarabine. J Leuk Biol 2002; 71: 495–502.
Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA, Shtil AA, Dalton WS . Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines. Blood 1999; 93: 1658–1667.
Taylor ST, Hickman JA, Dive C . Epigenetic determinants of resistance to etoposide regulation of Bcl-xL and Bax by tumor microenvironment factors. J Nat Cancer Inst 2000; 92: 18–23.
Aoudjit F, Vuori K . Integrin signaling inhibits paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4995–5004.
Fridman R, Giaccone G, Kanemoto T, Martin GR, Gazdar AF, Mulshine JL . Reconstituted basement membrane (matrigel) and laminin can enhance the tumorigenicity and the drug resistance of small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 6698–6702.
Tsurutani J, West KA, Sayyah J, Gills JJ, Dennis PA . Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway but not the MEK/ERK pathway attenuates laminin-mediated small cell lung cancer cellular survival and resistance to imatinib mesylate or chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8423–8432.
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C et al. Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5: 662–668.
Hartmann TN, Burger JA, Glodek A, Fujii N, Burger M . CXCR4 chemokine receptor and integrin signaling co-operate in mediating adhesion and chemoresistance in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4462–4471.
Uhm JH, Dooley NP, Kyritsis AP, Rao JS, Gladson CL . Vitronectin, a glioma-derived extracellular matrix protein, protects tumor cells from apoptotic death. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1587–1594.
Fukai F, Takahashi H, Habu Y, Kubushiro N, Katayama T . Fibronectin harbors antiadhesive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 220: 394–398.
Fukai F, Hasebe S, Ueki M, Mutoh M, Ohgi C, Takahashi H et al. Identification of the antiadhesive site buried within the heparin-binding domain of fibronectin. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1997; 121: 189–192.
Fukai F, Mashimo M, Akiyama K, Goto T, Tanuma S, Katayama T . Modulation of apoptotic cell death by extracellular matrix proteins and a fibronectin-derived antiadhesive peptide. Exp Cell Res 1998; 242: 92–99.
Kato R, Ishikawa T, Kamiya S, Oguma F, Ueki K, Goto S et al. A new type antimetastatic peptide derived from fibronectin. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 2455–2462.
Fukai F, Kamiya S, Ohwaki T, Goto S, Akiyama K, Goto T et al. The fibronectin derived anti-adhesive peptide FNIII14 suppresses adhesion and apoptosis of leukemic cell lines through down-regulation of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell Mol Biol 2000; 46: 145–152.
Kamiya S, Kato R, Wakabayashi M, Tohyama T, Enami I, Ueki M et al. Fibronectinpeptides derived from two distinct regions stimulate adipocyte differentiation by preventing fibronectin matrix assembly. Biochemistry 2002; 41: 3270–3277.
Sugahara H, Kanakura Y, Furitsu T, Ishihara K, Oritani K, Ikeda H et al. Induction of programmed cell death in human hematopoietic cell lines by fibronectin via its interaction with very late antigen 5. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 1757–1766.
Miyake K, Hasunuma Y, Yagita H, Kimoto M . Requirement for VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrins in lymphoma cells binding to and migration beneath stromal cells in culture. J Cell Biol 1992; 119: 653–662.
Hemler M . VLA proteins in the integrin family: structure, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol 1990; 8: 365–400.
Kamata T, Puzon W, Takada Y, Kamata T . Identification of putative ligand-binding sites of the integrin alpha 4 beta 1 (VLA-4, CD49d/CD29). Biochem J 1995; 305: 945–951.
Akiyama SK, Yamada SS, Chen WT, Yamada KM . Analysis of fibronectin receptor function with monoclonal antibodies: roles in cell adhesion, migration, matrix assembly, and cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Biol 1989; 109: 863–875.
Irie A, Kamata T, Puzon-McLaughlin W, Takada Y . Critical amino acid residues for ligand bindings are clustered in a predicted beta-turn of the third N-terminal repeat in the integrin alpha 4 and alpha 5 subunits. EMBO J 1995; 14: 5550–5556.
Lacombe F, Durrieu F, Briais A, Dumain P, Belloc F, Bascans E et al. Flow cytometry CD45 gating for immunophenotyping of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1878–1886.
Kawano Y, Kobune M, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura K, Ito Y, Sasaki K et al. Ex vivo expansion of human umbilical cord hematopoietic progenitor cells using a coculture system with human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT)-transfected human stromal cells. Blood 2003; 101: 532–540.
Yonemura Y, Ku H, Hirayama F, Souza LM, Ogawa M . Interleukin 3or interleukin 1 abrogates the reconstituting ability of hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 4040–4044.
Heinze G, Schemper M . Comparing the importance of prognostic factors in Cox and logistic regression using SAS. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2003; 71: 155–163.
Maguire JE, Danahey KM, Burkly LC, van Seventer GA . T cell receptor- and beta 1 integrin-mediated signals synergize to induce tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) in human T cells. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 2079–2090.
Rabinowich H, Manciulea M, Herberman RB, Whiteside TL . 1 integrin-mediated activation of focal adhesion kinase and its association with Fyn and Zap-70 in human NK cells. J Immunol 1996; 157: 3860–3868.
Gilmore AP, Metcalfe AD, Romer LH, Streuli CH . Integrin-mediated survival signals regulate the apoptotic function of Bax through its conformation and subcellualr localization. J Cell Biol 2000; 149: 431–436.
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennstrom S, Warne PH, Downward J . Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J 1997; 16: 2783–2793.
King WG, Mattaliano MD, Chan TO, Tsichlis PN, Brugge JS . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for integrin-stimulated AKT and Raf-1/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 4406–4418.
Chen Q, Kinch MS, Lin TH, Burridge K, Juliano RL . Integrin-mediated cell adhesion activates mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 26602–26605.
Moro L, Venturino M, Bozzo C, Silengo L, Altruda F, Beguinot L et al. Integrins induce activation of EGF receptor: role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion-dependent cell survival. EMBO J 1998; 17: 6622–6632.
Aoudjit F, Vuori K . Matrix attachment regulates Fas-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells: a role for c-flip and implications for anoikis. J Cell Biol 2001; 152: 633–643.
Visser JW, Bauman JG, Mulder AH, Eliason JF, de Leeuw AM . Isolation of murine pluripotent hemopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 1984; 159: 1576–1590.
Ogawa M . Differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 1993; 11: 2844–2853.
Chaudhary PM, Roninson IB . Expression and activity of P-glycoprotein, a multidrug efflux pump, in human hematopoietic stem cells. Cell 1991; 66: 85–94.
Damiano JS, Hazlehurst LA, Dalton WS . Cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) protects the K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line from apoptosis induced by BCR/ABL inhibition, cytotoxic drugs, and gamma-irradiation. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1232–1239.
Warle M, Bernkop-Schnurch A . Strategies to improve plasma half life time of peptide and protein drugs. Amino Acids 2006; 30: 351–367.
Manning MC, Patel K, Borchardt TR . Stability of protein pharmaceuticals. Pharm Res 1989; 6: 903–918.
Veronese FM, Pasut G . PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 2005; 10: 1451–1458.
Frohman LA, Downs TR, Williams TC, Heimer EP, Pan Y-CE, Felix AM . Rapid enzymatic degradation of growth hormone-releasing hormone by plasma in vitro and in vivo to a biologically inactive product cleaved at the NH2 terminus. J Clin Invest 1986; 78: 906–913.
Walensky LD, Kung AL, Escher I, Malia TJ, Barbuto S, Wright RD et al. Activation of apoptosis in vivo by a hydrocarbon-stapled BH3 helix. Science 2004; 305: 1466–1470.
Kamiya S, Kato R, Goto S, Fukai F . Cell regulation by the extracellular matrix-integrin system. Recent Res Dev Biophys Biochem 2003; 3: 13–20.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr Kevin Litton (BA in English) for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsunaga, T., Fukai, F., Miura, S. et al. Combination therapy of an anticancer drug with the FNIII14 peptide of fibronectin effectively overcomes cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance of acute myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 22, 353–360 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2405017
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2405017
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
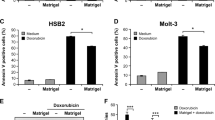
Cell adhesion to collagen promotes leukemia resistance to doxorubicin by reducing DNA damage through the inhibition of Rac1 activation
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Beta1 integrin blockade overcomes doxorubicin resistance in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling causes malignant melanoma cells to differentially alter extracellular matrix biosynthesis to promote cell survival
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
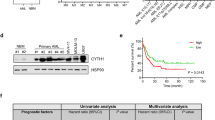
VLA-4 and CXCR4 expression levels show contrasting prognostic impact (favorable and unfavorable, respectively) in acute myeloid leukemia
Annals of Hematology (2015)
-
SP/drug efflux functionality of hematopoietic progenitors is controlled by mesenchymal niche through VLA-4/CD44 axis
Leukemia (2014)