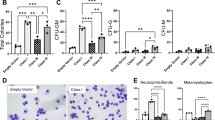
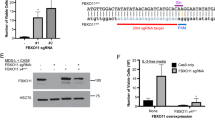
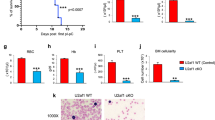
Abstract
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a malignancy of the human hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) caused by the p210BCR/ABL oncoprotein. Although alternative splicing of pre-mRNA is a critical determinant of a cell's protein repertoire, it has not been associated with CML pathogenesis. We identified a BCR/ABL-dependent increase in expression of multiple genes involved in pre-mRNA splicing (eg SRPK1, RNA Helicase II/Gu, and hnRNPA2/B1) by subtractive hybridization of cDNA from p210BCR/ABL-eGFP vs eGFP-transduced umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells. β1-integrin signaling is important to HSC maintenance and proliferation/differentiation, and is abnormal in CML. As an example of how changes in pre-mRNA processing might contribute to CML pathogenesis, we observed alternative splicing of a gene for a β1-integrin-responsive nonreceptor tyrosine kinase (PYK2), resulting in increased expression of full-length Pyk2 in BCR/ABL-containing cells. Treatment of p210BCR/ABL-positive cells with the Abl-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 reverted PYK2 splicing to a configuration more consistent with normal cells, and correlated with decreased expression of BCR/ABL-induced proteins involved in pre-mRNA processing. Whether altered PYK2 splicing contributes to CML pathogenesis remains undetermined; however, we propose that generic changes in pre-mRNA splicing as a result of p210BCR/ABL kinase activity may contribute to CML pathogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldstrohm AC, Greenleaf AL, Garcia-Blanco MA . Co-transcriptional splicing of pre-messenger RNAs: considerations for the mechanism of alternative splicing. Gene 2001; 277: 31–47.
Black DL . Protein diversity from alternative splicing: a challenge for bioinformatics and post-genome biology. Cell 2000; 103: 367–370.
Modrek B, Lee C . A genomic view of alternative splicing. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 13–19.
Hanamura A, Caceres JF, Mayeda A, Franza Jr BR, Krainer AR . Regulated tissue-specific expression of antagonistic pre-mRNA splicing factors. RNA 1998; 4: 430–444.
Hastings ML, Krainer AR . Pre-mRNA splicing in the new millennium. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 302–309.
Shyu AB, Wilkinson MF . The double lives of shuttling mRNA binding proteins. Cell 2000; 102: 135–138.
Yeakley JM, Tronchere H, Olesen J, Dyck JA, Wang HY, Fu XD . Phosphorylation regulates in vivo interaction and molecular targeting of serine/arginine-rich pre-mRNA splicing factors. J Cell Biol 1999; 145: 447–455.
Gui JF, Lane WS, Fu XD . A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature 1994; 369: 678–682.
Allemand E, Gattoni R, Bourbon HM, Stevenin J, Caceres JF, Soret J et al. Distinctive features of Drosophila alternative splicing factor RS domain: implication for specific phosphorylation, shuttling, and splicing activation. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 1345–1359.
Rowley JD . Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature 1973; 243: 290–293.
Dowding CR, Gordon MY, Goldman JM . Primitive progenitor cells in the blood of patients with chronic granulocytic leukemia. Int J Cell Cloning 1986; 4: 331–340.
de Klein A, van Kessel AG, Grosveld G, Bartram CR, Hagemeijer A, Bootsma D et al. A cellular oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 1982; 300: 765–767.
McWhirter JR, Wang JY . Activation of tyrosinase kinase and microfilament-binding functions of c-abl by bcr sequences in bcr/abl fusion proteins. Mol Cell Biol 1991; 11: 1553–1565.
Van Etten RA, Jackson P, Baltimore D . The mouse type IV c-abl gene product is a nuclear protein, and activation of transforming ability is associated with cytoplasmic localization. Cell 1989; 58: 669–678.
Wetzler M, Talpaz M, Van Etten RA, Hirsh-Ginsberg C, Beran M, Kurzrock R . Subcellular localization of Bcr, Abl, and Bcr-Abl proteins in normal and leukemic cells and correlation of expression with myeloid differentiation. J Clin Invest 1993; 92: 1925–1939.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV . The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000; 96: 3343–3356.
Daley GQ, Baltimore D . Transformation of an interleukin 3-dependent hematopoietic cell line by the chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210bcr/abl protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 9312–9316.
Daley GQ, Van Etten RA, Baltimore D . Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science 1990; 247: 824–830.
Gishizky ML, Johnson-White J, Witte ON . Efficient transplantation of BCR-ABL-induced chronic myelogenous leukemia-like syndrome in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 3755–3759.
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB . Differentiation of primitive human multipotent hematopoietic progenitors into single lineage clonogenic progenitors is accompanied by alterations in their interaction with fibronectin. J Exp Med 1991; 174: 693–703.
Teixido J, Hemler ME, Greenberger JS, Anklesaria P . Role of beta 1 and beta 2 integrins in the adhesion of human CD34hi stem cells to bone marrow stroma. J Clin Invest 1992; 90: 358–367.
Williams DA, Rios M, Stephens C, Patel VP . Fibronectin and VLA-4 in haematopoietic stem cell-microenvironment interactions. Nature 1991; 352: 438–441.
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB . Mechanisms underlying abnormal trafficking of malignant progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Decreased adhesion to stroma and fibronectin but increased adhesion to the basement membrane components laminin and collagen type IV. J Clin Invest 1992; 90: 1232–1241.
Bhatia R, McCarthy JB, Verfaillie CM . Interferon-alpha restores normal beta 1 integrin-mediated inhibition of hematopoietic progenitor proliferation by the marrow microenvironment in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 1996; 87: 3883–3891.
Bhatia R, Munthe HA, Verfaillie CM . Role of abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in impaired beta1 integrin function in chronic myelogenous leukemia hematopoietic progenitors. Exp Hematol 1999; 27: 1384–1396.
Salgia R, Li JL, Ewaniuk DS, Pear W, Pisick E, Burky SA et al. BCR/ABL induces multiple abnormalities of cytoskeletal function. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 46–57.
Giancotti FG . Integrin signaling: specificity and control of cell survival and cell cycle progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997; 9: 691–700.
Dikic I, Schlessinger J . Identification of a new Pyk2 isoform implicated in chemokine and antigen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 14301–14308.
Li X, Hunter D, Morris J, Haskill JS, Earp HS . A calcium-dependent tyrosine kinase splice variant in human monocytes. Activation by a two-stage process involving adherence and a subsequent intracellular signal. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 9361–9364.
Xiong WC, Macklem M, Parsons JT . Expression and characterization of splice variants of PYK2, a focal adhesion kinase-related protein. J Cell Sci 1998; 111: 1981–1991.
Gesbert F, Griffin JD . Bcr/Abl activates transcription of the Bcl-X gene through STAT5. Blood 2000; 96: 2269–2276.
Mermoud JE, Cohen PT, Lamond AI . Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J 1994; 13: 5679–5688.
Watari K, Tojo A, Nagamura-Inoue T, Nagamura F, Takeshita A, Fukushima T et al. Identification of a melanoma antigen, PRAME, as a BCR/ABL-inducible gene. FEBS Lett 2000; 466: 367–371.
Daheron L, Zenz T, Siracusa LD, Brenner C, Calabretta B . Molecular cloning of Ian4: a BCR/ABL-induced gene that encodes an outer membrane mitochondrial protein with GTP-binding activity. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 1308–1316.
Zhao RC, Jiang Y, Verfaillie CM . A model of human p210(bcr/ABL)-mediated chronic myelogenous leukemia by transduction of primary normal human CD34(+) cells with a BCR/ABL-containing retroviral vector. Blood 2001; 97: 2406–2412.
Long H, Gaffney P, Mortari F, Miller JS . CD3 gamma, CD3 delta, and CD3 zeta mRNA in adult human marrow hematopoietic progenitors correlates with surface CD2 and CD7 expression. Exp Hematol 1996; 24: 1402–1408.
Jiang Y, Zhao RC, Verfaillie CM . Abnormal integrin-mediated regulation of chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cell proliferation: BCR/ABL up-regulates the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27Kip, which is relocated to the cell cytoplasm and incapable of regulating cdk2 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10538–10543.
Salesse S, Verfaillie CM . BCR/ABL-mediated increased expression of multiple known and novel genes that may contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 2003; 2: 173–182.
Prasad J, Colwill K, Pawson T, Manley JL . The protein kinase Clk/Sty directly modulates SR protein activity: both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit splicing. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6991–7000.
Krecic AM, Swanson MS . hnRNP complexes: composition, structure, and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11: 363–371.
Caceres JF, Stamm S, Helfman DM, Krainer AR . Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science 1994; 265: 1706–1709.
Valdez BC, Henning D, Perlaky L, Busch RK, Busch H . Cloning and characterization of Gu/RH-II binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 234: 335–340.
Arai Y, Hosoda F, Kobayashi H, Arai K, Hayashi Y, Kamada N et al. The inv(11)(p15q22) chromosome translocation of de novo and therapy-related myeloid malignancies results in fusion of the nucleoporin gene, NUP98, with the putative RNA helicase gene, DDX10. Blood 1997; 89: 3936–3944.
Savitsky K, Ziv Y, Bar-Shira A, Gilad S, Tagle DA, Smith S et al. A human gene (DDX10) encoding a putative DEAD-box RNA helicase at 11q22–q23. Genomics 1996; 33: 199–206.
Das BK, Xia L, Palandjian L, Gozani O, Chyung Y, Reed R . Characterization of a protein complex containing spliceosomal proteins SAPs 49, 130, 145, and 155. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6796–6802.
Watakabe A, Tanaka K, Shimura Y . The role of exon sequences in splice site selection. Genes Dev 1993; 7: 407–418.
Dylla SJ, Deyle DR, Theunissen K, Padurean AM, Verfaillie CM . Integrin engagement-induced inhibition of human myelopoiesis is mediated by proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 gene products. Exp Hematol 2004; in press.
Ohba T, Ishino M, Aoto H, Sasaki T . Interaction of two proline-rich sequences of cell adhesion kinase beta with SH3 domains of p130Cas-related proteins and a GTPase-activating protein, Graf. Biochem J 1998; 330: 1249–1254.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr M Garcia-Blanco for valuable comments and Janet Peller, Brad Anderson, and members of the Stem Cell Lab for technical assistance. Additional thanks to Drs B Valdez, B Turner, I Dikic, and Novartis for reagents critical to these studies. This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (RO1 HL-49930 and RO1 DK-53673), Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of America H6377-97; the Tulloch Family Foundation and the McKnight Foundation to CMV, and the Bone Marrow Transplant Research Fund and NCI-awarded Cancer Biology Training Grant (CA09138) to SJD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salesse, S., Dylla, S. & Verfaillie, C. p210BCR/ABL-induced alteration of pre-mRNA splicing in primary human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Leukemia 18, 727–733 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403310
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403310
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of SRPK1, a key splicing regulator, exhibits antitumor and chemotherapeutic-sensitizing effects on extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma cells
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
SRSF1 mediates cytokine-induced impaired imatinib sensitivity in chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2020)
-
Apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest of pladienolide B in erythroleukemia cell lines
Investigational New Drugs (2020)
-
Serine arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1): a moonlighting protein with theranostic ability in cancer prevention
Molecular Biology Reports (2019)
-
BCR-ABL mediated repression of miR-223 results in the activation of MEF2C and PTBP2 in chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2013)