Abstract
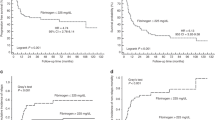
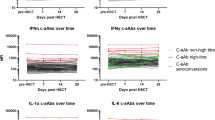
Serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha were frequently measured during the first 30 days after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) in 84 consecutive adult patients. Major transplant-related complications (MTCs) occurred in 33% of cases and included veno-occlusive liver disease, idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, severe endothelial leakage syndrome and >grade II acute graft-versus-host disease. Compared with patients having minor complications, those with MTCs developed higher levels at times of maximal clinical signs (all cytokines, P<0.001), between days 0–5 post-BMT (IL-6 and IL-8, P<0.05) and days 6–10 (L-6, P<0.001; IL-8 and TNF, P<0.01) post-BMT. We could not discriminate patterns of cytokine release that were specific for any subtype of MTC. Higher levels of IL-8 during days 0–5 were associated (P=0.044) with early (<40 days) death. Multivariate analysis including patient and transplant characteristics as well as post-BMT levels of C-reactive protein showed that high average levels of one or more of the cytokines within the first 10 days post-BMT were independently associated with MTC (Odd's ratio: 2.3 [1.2–4.5], P=0.011). This study shows that systemic release of proinflammatory cytokines contributes to the development of MTC and provides a rationale for pre-emptive anti-inflammatory treatment in selected patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carreras E, Bertz H, Arcese W, Vernant JP, Tomas JF, Hagglund H et al. Incidence and outcome of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after blood or marrow transplantation: a prospective cohort study of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Chronic Leukemia Working Party. Blood 1998; 92: 3599–3604.
Bearman SI . The syndrome of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after marrow transplantation. Blood 1995; 85: 3005–3020.
Kantrow SP, Hackman RC, Boeckh M, Myerson D, Crawford SW . Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome: changing spectrum of lung injury after marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1997; 63: 1079–1086.
Cahill RA, Spitzer TR, Mazumder A . Marrow engraftment and clinical manifestations of capillary leak syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 18: 177–184.
Schots R, Kaufman L, Van Riet I, Lacor P, Trullemans F, De Waele M et al. Monitoring of C-reactive protein after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation identifies patients at risk of severe transplant-related complications and mortality. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 79–85.
Gabay C, Kushner I . Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 448–454.
Antin JH, Ferrara JL . Cytokine dysregulation and acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1992; 80: 2964–2968.
Gugliotta L, Catani L, Vianelli N, Gherlinzoni F, Miggiano MC, Bandini G et al. High plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha may be predictive of veno-occlusive disease in bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1994; 83: 2385–2386.
Holler E, Kolb HJ, Moller A, Kempeni J, Liesenfeld S, Pechumer H et al. Increased serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha precede major complications of bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1990; 75: 1011–1016.
Remberger M, Ringden O . Serum levels of cytokines after bone marrow transplantation: increased IL-8 levels during severe veno-occlusive disease of the liver. Eur J Haematol 1997; 59: 254–262.
Symington FW, Symington BE, Liu PY, Viguet H, Santhanam U, Sehgal PB . The relationship of serum IL-6 levels to acute graft-versus-host disease and hepatorenal disease after human bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1992; 54: 457–462.
McDonald GB, Hinds MS, Fisher LD, Schoch HG, Wolford JL, Banaji M et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver and multiorgan failure after bone marrow transplantation: a cohort study of 355 patients. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: 255–267.
Clark JG, Madtes DK, Martin TR, Hackman RC, Farrand AL, Crawford SW . Idiopathic pneumonia after bone marrow transplantation: cytokine activation and lipopolysaccharide amplification in the bronchoalveolar compartment. Crit Care Med 1999; 27: 1800–1806.
Gaynor ER, Vitek L, Sticklin L, Creekmore SP, Ferraro ME, Thomas Jr JX et al. The hemodynamic effects of treatment with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Ann Intern Med 1988; 109: 953–958.
Thijs LG, Hack CE, Strack van Schijndel RJ, Nuijens JH, Wolbink GJ, Eerenberg-Belmer AJ et al. Activation of the complement system during immunotherapy with recombinant IL-2. Relation to the development of side effects. J Immunol 1990; 144: 2419–2424.
Storb R, Thomas ED . Graft-versus-host disease in dog and man: the Seattle experience. Immunol Rev 1985; 88: 215–238.
Schots R, Trullemans F, Van Riet I, Kaufman L, Hafsia A, Meddeb B et al. The clinical impact of early gram-positive bacteremia and the use of vancomycin after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 2000; 69: 1511–1514.
Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Fabra R, Trullenque R, Heinrich PC . Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology 1990; 12: 1179–1186.
Vachino G, Gelfand JA, Atkins MB, Tamerius JD, Demchak P, Mier JW . Complement activation in cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy with interleukin-2 (IL-2): binding of complement and C-reactive protein by IL-2-activated lymphocytes. Blood 1991; 78: 2505–2513.
Charreau B, Coupel S, Goret F, Pourcel C, Soulillou JP . Association of glucocorticoids and cyclosporin A or rapamycin prevents E-selectin and IL-8 expression during LPS- and TNFalpha-mediated endothelial cell activation. Transplantation 2000; 69: 945–953.
Faioni EM, Krachmalnicoff A, Bearman SI, Federici AB, Decarli A, Gianni AM et al. Naturally occurring anticoagulants and bone marrow transplantation: plasma protein C predicts the development of venocclusive disease of the liver. Blood 1993; 81: 3458–3462.
Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim S, Lee JS, Kim WK, Park CJ et al. Relevance of proteins C and S, antithrombin III, von Willebrand factor, and factor VIII for the development of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a prospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 883–888.
Rio B, Bauduer F, Arrago JP, Zittoun R . N-terminal peptide of type III procollagen: a marker for the development of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after BMT and a basis for determining the timing of prophylactic heparin. Bone Marrow Transplant 1993; 11: 471–472.
Tanikawa S, Mori S, Ohhashi K, Akiyama H, Sasaki T, Kaku H et al. Predictive markers for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults: a prospective single center study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 881–886.
Fried MW, Duncan A, Soroka S, Connaghan DG, Farrand A, Peter J et al. Serum hyaluronic acid in patients with veno-occlusive disease following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 635–639.
van Hinsbergh VW, Bauer KA, Kooistra T, Kluft C, Dooijewaard G, Sherman ML et al. Progress of fibrinolysis during tumor necrosis factor infusions in humans. Concomitant increase in tissue-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1, and fibrin(ogen) degradation products. Blood 1990; 76: 2284–2289.
Salat C, Holler E, Kolb HJ, Reinhardt B, Pihusch R, Wilmanns W et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 confirms the diagnosis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in patients with hyperbilirubinemia after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1997; 89: 2184–2188.
Donnelly SC, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Walz A, Robertson CR, Carter DC et al. Interleukin-8 and development of adult respiratory distress syndrome in at-risk patient groups. Lancet 1993; 341: 643–647.
Ferrara JL . Pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease: cytokines and cellular effectors. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 2000; 9: 299–306.
Khoury H, Adkins D, Brown R, Trinkaus K, Vij R, Miller G, Goodnough LT et al. Does early treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone alter the course of hepatic regimen-related toxicity? Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 737–743.
Chopra R, Eaton JD, Grassi A, Potter M, Shaw B, Salat C et al. Defibrotide for the treatment of hepatic veno-occlusive disease: results of the European compassionate-use study. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 1122–1129.
Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF, LaRosa SP, Dhainaut JF, Lopez-Rodriguez A et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 699–709.
Bacigalupo A, Oneto R, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, Bregante S, Raiola AM et al. Pre-emptive therapy of acute graft-versus-host disease: a pilot study with antithymocyte globulin (ATG). Bone Marrow Transplant JID-8702459 2001; 28: 1093–1096.
Carpenter PA, Appelbaum FR, Corey L, Deeg HJ, Doney K, Gooley T et al. A humanized non-FcR-binding anti-CD3 antibody, visilizumab, for treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2002; 99: 2712–2719.
Deeg HJ, Blazar BR, Bolwell BJ, Long GD, Schuening F, Cunningham J et al. Treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody ABX-CBL. Blood 2001; 98: 2052–2058.
Herve P, Flesch M, Tiberghien P, Wijdenes J, Racadot E, Bordigoni P et al. Phase I-II trial of a monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody for the treatment of refractory severe acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1992; 79: 3362–3368.
Holler E, Kolb HJ, Mittermuller J, Kaul M, Ledderose G, Duell T et al. Modulation of acute graft-versus-host-disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) release in the course of pretransplant conditioning: role of conditioning regimens and prophylactic application of a monoclonal antibody neutralizing human TNF alpha (MAK 195F). Blood 1995; 86: 890–899.
Tse JC, Moore TB . Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease. Pharmacotherapy 1998; 18: 988–1000.
Kobbe G, Schneider P, Rohr U, Fenk R, Neumann F, Aivado M et al. Treatment of severe steroid refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with infliximab, a chimeric human/mouse antiTNFalpha antibody. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 47–49.
Przepiorka D, Kernan NA, Ippoliti C, Papadopoulos EB, Giralt S, Khouri I et al. Daclizumab, a humanized anti-interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain antibody, for treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2000; 95: 83–89.
Verbon A, Dekkers PE, ten Hove T, Hack CE, Pribble JP, Turner T et al. IC14, an anti-CD14 antibody, inhibits endotoxin-mediated symptoms and inflammatory responses in humans. J Immunol 2001; 166: 3599–3605.
Hill GR, Crawford JM, Cooke KR, Brinson YS, Pan L, Ferrara JL . Total body irradiation and acute graft-versus-host disease: the role of gastrointestinal damage and inflammatory cytokines. Blood 1997; 90: 3204–3213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schots, R., Kaufman, L., Van Riet, I. et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and their role in the development of major transplant-related complications in the early phase after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Leukemia 17, 1150–1156 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402946
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402946
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Galectin-3 predicts acute GvHD and overall mortality post reduced intensity allo-HCT: a BMT-CTN biorepository study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Late cardiac events after allogeneic stem cell transplant: incidence, risk factors, and impact on overall survival
Cardio-Oncology (2023)
-
Endothelial function testing before conditioning therapy is useful for predicting transplant-related complications after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Co-infections of human herpesviruses (CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7 and EBV) in non-transplant acute leukemia patients undergoing chemotherapy
Virology Journal (2020)
-
Tumor necrosis factor α in aGVHD patients contributed to the impairment of recipient bone marrow MSC stemness and deficiency of their hematopoiesis-promotion capacity
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020)