Abstract
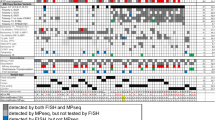
The value of dual-color fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for the detection of inv(16), using two contigs of cosmid probes mapping on both sides of the chromosome 16p breakpoint region, was evaluated in 23 acute myeloid leukemias (AML) in different phases of the disease. At diagnosis interphase FISH detected inv(16) in 19/19 (100%) cases with conventional cytogenetics (CC) evident aberration and excluded the rearrangement in two patients with CC suspected inv(16). Moreover, it also identified an associated del(16p) in two patients. At relapse, it revealed the inv(16) in 8/8 (100%) studied cases. These results were concordant with those of reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). From 13 patients who obtained at least one complete remission (CR), 31 follow-up samples were analyzed using interphase FISH. Twenty-nine specimens scored negative for inv(16) and two were positive. RT-PCR detected CBFβ/MYH11 transcripts in four of the nine CR samples analyzed, being more sensitive than interphase FISH. Eight of the 13 patients relapsed at a median time of 6.5 months (range 1–15) from the last negative FISH analysis. Of the two patients with positive FISH in CR, one relapsed soon after. At diagnosis and relapse, interphase-FISH proved to be an effective technique for detecting inv(16) appearing more sensitive than CC. Prospective studies with more frequent controls and possibly additional FISH probes are needed to assess the value of interphase FISH for minimal residual disease (MRD) and relapse prediction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Beau MM, Larson RA, Bitter MA, Vardiman JW, Golomb HM, Rowley JD . Association of an inversion of chromosome 16 with abnormal marrow eosinophils in acute myelomonocytic leukemia New Engl J Med 1983 309: 630–636
Rowley JD . Recurring chromosome abnormalities in leukemia and lymphoma Semin Hematol 1990 27: 122–136
Liu PP, Hajra A, Wijmenga C, Collins FS . Molecular pathogenesis of the chromosome 16 inversion in the M4Eo subtype of acute myeloid leukemia Blood 1995 85: 2289–2302
van der Reijden BA, Lombardo M, Dauwerse HG, Giles RH, Mühlematter D, Jotterand Bellomo M, Wessels HW, Beverstock GC, van Ommen GJB, Hagemeijer A, Breuning MH . RT-PCR diagnosis of patients with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia and inv(16)(p13q22) and identification of a new alternative splicing in CBFβ-MYH11 transcripts Blood 1995 86: 277–282
Mrozek K, Heinonen K, de la Chapelle, Bloomfield CD . Clinical significance of cytogenetics in acute myeloid leukemia Semin Oncol 1997 24: 17–31
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G, Rees J, Hann I, Stevens R, Burnett A, Goldstone A . The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 Trial Blood 1998 92: 2322–2333
Liu P, Tarlè SA, Hajra A, Claxton DF, Marlton P, Freedman M, Siciliano MJ, Collins FS . Fusion between trancription factor CBFb/PEBP2b and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia Science 1993 261: 1041–1044
Dauwerse JG, Wessels JW, Giles RH, Wiegant J, Raap AK, van der Reijden BA, Fugazza G, Jumelet EA, Smit E, Baas F, Hagemeijer A, Beverstock GC, van Ommen GJB, Breuning MH . Cloning the breakpoint cluster region of the inv(16) in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia M4 Eo Hum Mol Genet 1993 2: 1527–1534
Kuss BJ, Deeley RG, Cole SPG, Willman CL, Kopecky KJ, Wolman SR, Eyre HJ, Lane SA, Nancarrow JK, Withmore SA, Callen DF . Deletion of gene for multidrug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia with inversion in chromosome 16: prognostic implications Lancet 1994 343: 1531–1534
Martinet D, Mühlematter D, Leeman M, Parlier V, Hess U, Gmür J Jotterand M . Detection of 16p deletions by FISH in patients with inv(16) or t(16;16) and myeloid leukemia (AML) Leukemia 1997 11: 964–970
Claxton DF, Liu P, Hsu HB, Marlton P, Hester J, Collins F, Deisseroth AB, Rowley JD, Siciliano MJ . Detection of fusion transcripts generated by the inversion 16 chromosome in acute myelogenous leukemia Blood 1994 83: 1750–1756
Hebert J, Cayuela J-M, Daniel M-T, Berger R, Sigaux F . Detection of minimal residual disease in acute myelomonocytic leukemia with abnormal marrow eosinophils by nested polymerase chain reaction with allele specific amplification Blood 1994 84: 2291–2296
Sacchi N, Magnani I, Kearney L, Wijsman J, Hagemeijer A, Darfler M . Interphase cytogenetics of the t(8;21)(q22;q22) associated with acute myelogenous leukemia by two colour fluorescence in situ hybridization Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1995 79: 97–103
Mancini M, Nanni M, Cedrone M, Diverio D, Avvisati G, Riccioni R, De Cuia MR, Fenu S, Alimena G . Combined cytogenetic, FISH and molecular analysis in acute promyelocytic leukemia at diagnosis and in complete remission Br J Haematol 1995 91: 878–884
Liu P, Claxton DF, Marlton P, Hajra A, Siciliano J, Freedman M, Chandrasekharappa SC, Yanagisawa K, Stallings RL, Collins FS, Siciliano MJ . Identification of yeast artificial chromosomes containing the inversion 16 p-arm breakpoint associated with acute myelomonocytic leukemia Blood 1993 82: 716–721
Dauwerse JG, Kievits T, Beverstock GC, van der Keur D, Smit E, Wessels HW, Hagemeijer A, Pearson PL, Van Ommen G-JB, Breuning MH . Rapid detection of chromosome 16 inversion in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, subtype M4, regional localization of the breakpoint in 16p Cytogenet Cell Genet 1990 53: 126–128
ISCN. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Mitelman F (ed) S Karger: Basel, 1995
Arnoldus EPJ, Wiegant J, Noordmeer IA, Wessels JW, Beverstock GC, Grosveld GC, van der Ploeg M, Raap AK . Detection of Philadelphia chromosome in interphase nuclei Cytogenet Cell Genet 1990 54: 108–111
Chomczynsky P, Sacchi N . Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction Anal Biochem 1987 162: 156–160
Dierlamm J, Stul M, Vranckx H, Michaux L, Olde Weghuis DEM, Speleman F, Selleslag D, Kramer MHH, Noens L, Cassiman JJ, Van den Berghe H, Hagemeijer A . FISH identifies inv(16)(p13q22) masked by translocations in three cases of acute myeloid leukemia Genes Chromosom Cancer 1998 22: 87–94
Vandenberghe P, Verhoef GEG, Emonds MP, Demuynck H, Zachée P, De Wolf-Peeters C, Decorte R, Cassiman JJ, Boogaerts MA . A single course of remission reinduction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia relapsing after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is complicated by graft-versus-host disease and followed by sustained complete remission Leukemia 1997 11: 1775–1778
Dauwerse HG, Smit EME, Giles RH, Slater R, Breuning MH, Hagemeijer A, van der Reijden BA . Two-colour FISH detection of the inv(16) in interphase nuclei of patients with acute myeloid leukemia Br J Haematol 1999 106: 111–114
Nucifora G, Larson RA, Rowley JD . Persistence of the 8;21 translocation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia type M2 in long-term remission Blood 1993 82: 712–715
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Biomed Concerted Action: contract grant CT 94-1703; the Belgian programme on Interuniversity Poles of Attraction initiated by the Belgian State, Prime Minister's Office, Science Policy Programming (the scientific responsibility is assumed by the authors); the Flemish Government in the frame of the action Kom op tegen Kanker/Vlaamse Kankerliga and partially by MURST fondi 60% (GA). We gratefully acknowledge the collaboration of Dr A Bosly, P Brock, A Ferrant, D Selleslag and G Verhoef, for providing the clinical data and of Dr B Santulli for providing cytogenetic data of patient No. 23. C Mecucci is partially supported by AIRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mancini, M., Cedrone, M., Diverio, D. et al. Use of dual-color interphase FISH for the detection of inv(16) in acute myeloid leukemia at diagnosis, relapse and during follow-up: a study of 23 patients. Leukemia 14, 364–368 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401678
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401678
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Relapse assessment following allogeneic SCT in patients with MDS and AML
Annals of Hematology (2014)
-
Directional genomic hybridization for chromosomal inversion discovery and detection
Chromosome Research (2013)
-
Molecular-Based Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Role in Directing Rational Therapy
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2012)
-
Monitoring of WT1 expression in PB and CD34+ donor chimerism of BM predicts early relapse in AML and MDS patients after hematopoietic cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning
Leukemia (2011)
-
Pre-transplant prognostic factors for patients with high-risk leukemia undergoing an unrelated cord blood transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)