Abstract
Objective:
To study the association between systemic fungal infection (SFI) and the development of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and severe ROP in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants by systematic review and meta-analysis.
Study Design:
A meta-review was performed using a fixed effects model. The exposure and outcomes studied were SFI and all ROP/severe ROP, respectively in VLBW infants. Results and effect sizes analyzed with Review Manager 4.2 software are expressed as relative risk (RR), odds ratio (OR), risk difference (RD) and number needed to harm (NNH) with 95% confidence intervals.
Result:
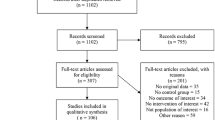
Data for severe ROP were available from eight studies and on all ROP from seven of those eight studies. Estimated gestational age ranged from 24.7±1.6 to 28.6±4 weeks and birth weight from 673 (median) (range 426 to 995) to 1108±266 g (mean±s.d.). A total of 261 of 303 babies with SFI had all ROP vs 1081 of 1648 babies without SFI (OR 3.4*, 2.34–4.95) and 118 of 330 babies with SFI had severe ROP vs 235 of 1951 babies without SFI (OR 4.06*, 3.05–5.42). The NNH was 5.56* (4.54–7.14) for all ROP and 4.54* (3.70 to 5.88) for severe ROP (*P<0.00001).
Conclusion:
SFIs are associated with the development of all degrees of ROP and severe ROP in VLBW infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2002; 110: 285–291.
Saiman L, Ludlington E, Pfaller M, Rangel-Frausto S, Wiblin RT, Dawson J et al. Risk factors for candidemia in neonatal intensive care unit patients. The National Epidemiology of Mycosis Survey Study Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2000; 19: 319–324.
Fanaroff AA, Korones SB, Wright LL, Verter J, Poland RL, Bauer CR et al. Incidence, presenting features, risk factors and significance of late onset septicemia in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1998; 17: 593–598.
Stoll BJ, Gordon T, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Bauer CR et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: a report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr 1996; 129: 63–71.
Rowen JL, Atkins JT, Levy ML, Baer SC, Baker CJ . Invasive fungal dermatitis in the ≤ 1000 gram neonate. Pediatrics 1995; 95: 682–687.
Faix RG, Kovarik SM, Shaw TR, Johnson RV . Mucocutaneous and invasive candidiasis among very low birth weight (<1500 grams) infants in intensive care nurseries: a prospective study. Pediatrics 1989; 83: 101–107.
Bendel CM, Hostetter MK . Systemic candidiasis and other fungal infections in the newborn. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis 1994; 5: 35–41.
Fraser VJ, Jones M, Dunkel J, Storfer S, Medoff G, Dunagan WC . Candidemia in a tertiary care hospital: epidemiology, risk factors, and predictors of mortality. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 15: 414–421.
Klein JJ, Watanakunakorn C . Hospital-acquired fungemia: its natural course and clinical significance. Am J Med 1979; 67: 51–58.
Wey SB, Mori M, Pfaller MA, Woolson RF, Wenzel RP . Hospital acquired candidemia: the attributable mortality and excess length of stay. Arch Intern Med 1988; 148: 2642–2645.
Kaufman D, Boyle R, Hazen KC, Patrie JT, Robinson M, Donowitz LG . Fluconazole prophylaxis against fungal colonization and infection in preterm infants. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1660–1666.
Mittal M, Dhanireddy R, Higgins RD . Candida sepsis and association with retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics 1998; 101: 654–657.
Manzoni P, Maestri A, Leonessa M, Mostert M, Farina D, Gomirato G . Fungal and bacterial sepsis and threshold ROP in preterm very low birth weight neonates. J Perinatol 2006; 26: 23–30.
Noyola DE, Bohra L, Paysse E, Fernandez M, Coats DK . Association of candidemia and retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants. Ophthalmology 2002; 109: 80–84.
Parupia H, Dhanireddy R . Association of postnatal dexamethasone use and fungal sepsis in the development of severe retinopathy of prematurity and progression to laser therapy in extremely low–birth-weight infants. J Perinatol 2001; 21: 242–247.
Tadesse M, Dhanireddy R, Mittal M, Higgins RD . Race, candida sepsis, and retinopathy of prematurity. Biol Neonate 2002; 81: 86–90.
Sanchez V, del Moral T, Claure N, Vanbuskirk S, Flynn J, Bancalari E . Sepsis as a risk factor for the development of retinopathy of prematurity in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 2002; 51: 367A.
Karlowicz GM, Giannone PJ, Pestian J, Morrow AL, Shults J . Does candidemia predict threshold retinopathy of prematurity in extremely low birth weight (⩽1000 g) neonates? Pediatrics 2000; 105: 1036–1040.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson DG, Rennie D et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in Epidemiology. JAMA 2000; 283: 2008–2012.
Friedman S, Richardson SE, Jacobs SE, O'Brien K . Systemic Candida infection in extremely low birth weight infants: short term morbidity and long term neurodevelopmental outcome. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2000; 19: 499–504.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG . Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002; 21: 1539–1558.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003; 327: 557–560.
An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics 1984; 74: 127.
Dickersin K . Systematic reviews in epidemiology: why are we so far behind? Int J Epidemiol 2002; 31: 6–12.
Bollen CW, Hoekstra MO, Arets HGM . Pooling of studies in meta-analysis of observational research leads to precise but spurious results. Pediatrics 2006; 117: 261–262.
Filler SG, Swerdloff JN, Hobbs C, Luckett PM . Penetration and damage of endothelial cells by Candida albicans. Infect Immunol 1995; 63: 976–983.
Filler SG, Ibe BO, Luckett PM, Raj JU, Edwards Jr JE . Candida albicans stimulates endothelial cell eicosanoid production. J Infect Dis 1991; 164: 928–935.
Filler SG, Pfunder AS, Spellberg BJ, Spellberg JP, Edwards Jr JE . Candida albicans stimulates cytokine production and leukocyte adhesion molecule expression by endothelial cells. Infect Immunol 1996; 64: 2609–2617.
Stone J, Chan-Ling T, Pe'er J, Itin A, Gnessin H, Keshet E . Roles of vascular endothelial growth factor and astrocyte degeneration in the genesis of retinopathy of prematurity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1996; 37: 290–292.
Pierce EA, Avery RL, Foley ED, Aiello LP, Smith LEH . Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor expression in a mouse model of retinal neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 905–909.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Intramural sources of support: none.
Extramural sources of support: none.
Conflict of interest: None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharwani, S., Dhanireddy, R. Systemic fungal infection is associated with the development of retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants: a meta-review. J Perinatol 28, 61–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211878
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211878
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
National guideline for ophthalmological screening of premature infants in Germany (S2k level, AWMF guidelines register no. 024/010, March 2020)
Die Ophthalmologie (2022)
-
Augenärztliche Screening-Untersuchung bei Frühgeborenen (S2k-Level, AWMF-Leitlinien-Register-Nr. 024/010, März 2020)
Der Ophthalmologe (2021)
-
Serum Fructosamine and Retinopathy of Prematurity
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2011)
-
Risikofaktoren und Prävention der Retinopathia praematurorum
Der Ophthalmologe (2008)