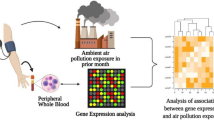
Abstract
Gene expression changes are linked to air pollutant exposures in in vitro and animal experiments. However, limited data are available on how these outcomes relate to ambient air pollutant exposures in humans. We performed an exploratory analysis testing whether gene expression levels were associated with air pollution exposures in a Los Angeles area cohort of elderly subjects with coronary artery disease. Candidate genes (35) were selected from published studies of gene expression-pollutant associations. Expression levels were measured weekly in 43 subjects (≤12 weeks) using quantitative PCR. Exposures included gaseous pollutants O3, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and CO; particulate matter (PM) pollutants elemental and black carbon (EC, BC); and size-fractionated PM mass. We measured organic compounds from PM filter extracts, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and determined the in vitro oxidative potential of particle extracts. Associations between exposures and gene expression levels were analyzed using mixed-effects regression models. We found positive associations of traffic-related pollutants (EC, BC, primary organic carbon, PM0.25-2.5 PAH and/or PM0.25 PAH, and NOx) with NFE2L2, Nrf2-mediated genes (HMOX1, NQO1, and SOD2), CYP1B1, IL1B, and SELP. Findings suggest that NFE2L2 gene expression links associations of traffic-related air pollution with phase I and II enzyme genes at the promoter transcription level.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA, 3rd, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010; 121: 2331–2378.
Delfino RJ, Staimer N, Tjoa T, Gillen DL, Polidori A, Arhami M et al. Air pollution exposures and circulating biomarkers of effect in a susceptible population: clues to potential causal component mixtures and mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect 2009; 117: 1232–1238.
Delfino RJ, Staimer N, Tjoa T, Arhami M, Polidori A, Gillen DL et al. Association of biomarkers of systemic inflammation with organic components and source tracers in quasi-ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 2010; 118: 756–762.
Gong KW, Zhao W, Li N, Barajas B, Kleinman M, Sioutas C et al. Air-pollutant chemicals and oxidized lipids exhibit genome-wide synergistic effects on endothelial cells. Genome Biol 2007; 8: R149.
Gargalovic PS, Gharavi NM, Clark MJ, Pagnon J, Yang WP, He A et al. The unfolded protein response is an important regulator of inflammatory genes in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 2490–2496.
Huang YC, Karoly ED, Dailey LA, Schmitt MT, Silbajoris R, Graff DW et al. Comparison of gene expression profiles induced by coarse, fine, and ultrafine particulate matter. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2011; 74: 296–312.
Lee R, Margaritis M, Channon KM, Antoniades C . Evaluating oxidative stress in human cardiovascular disease: methodological aspects and considerations. Curr Med Chem 2012; 19: 2504–2520.
Delfino RJ, Staimer N, Vaziri ND . Air pollution and circulating biomarkers of oxidative stress. Air Qual Atmos Health 2011; 4: 37–52.
Wu Z, Liu MC, Liang M, Fu J . Sirt1 protects against thrombomodulin down-regulation and lung coagulation after particulate matter exposure. Blood 2012; 119: 2422–2429.
Das H, Kumar A, Lin Z, Patino WD, Hwang PM, Feinberg MW et al. Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) regulates proinflammatory activation of monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 6653–6658.
Peretz A, Peck EC, Bammler TK, Beyer RP, Sullivan JH, Trenga CA et al. Diesel exhaust inhalation and assessment of peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene transcription effects: an exploratory study of healthy human volunteers. Inhal Toxicol 2007; 19: 1107–1119.
Pettit AP, Brooks A, Laumbach R, Fiedler N, Wang Q, Strickland PO et al. Alteration of peripheral blood monocyte gene expression in humans following diesel exhaust inhalation. Inhal Toxicol 2012; 24: 172–181.
Wu MT, Lee TC, Wu IC, Su HJ, Huang JL, Peng CY et al. Whole genome expression in peripheral-blood samples of workers professionally exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chem Res Toxicol 2011; 24: 1636–1643.
van Leeuwen DM, Pedersen M, Hendriksen PJ, Boorsma A, van Herwijnen MH, Gottschalk RW et al. Genomic analysis suggests higher susceptibility of children to air pollution. Carcinogenesis 2008; 29: 977–983.
van Leeuwen DM, van Herwijnen MH, Pedersen M, Knudsen LE, Kirsch-Volders M, Sram RJ et al. Genome-wide differential gene expression in children exposed to air pollution in the Czech Republic. Mutat Res 2006; 600: 12–22.
McHale CM, Zhang L, Hubbard AE, Smith MT . Toxicogenomic profiling of chemically exposed humans in risk assessment. Mutat Res 2010; 705: 172–183.
Delfino RJ, Staimer N, Tjoa T, Polidori A, Arhami M, Gillen DL et al. Circulating biomarkers of inflammation, antioxidant activity, and platelet activation are associated with primary combustion aerosols in subjects with coronary artery disease. Environ Health Perspect 2008; 116: 898–906.
Sioutas C, Delfino RJ, Singh M . Exposure assessment for atmospheric ultrafine particles (UFPs) and implications in epidemiologic research. Environ Health Perspect 2005; 113: 947–955.
von Klot S, Peters A, Aalto P, Bellander T, Berglind N, D'Ippoliti D et al. Ambient air pollution is associated with increased risk of hospital cardiac readmissions of myocardial infarction survivors in five European cities. Circulation 2005; 112: 3073–3079.
Dumeaux V, Olsen KS, Nuel G, Paulssen RH, Borresen-Dale AL, Lund E et al. Deciphering normal blood gene expression variation—The NOWAC postgenome study. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1000873.
Rainen L, Oelmueller U, Jurgensen S, Wyrich R, Ballas C, Schram J et al. Stabilization of mRNA expression in whole blood samples. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 1883–1890.
Elvidge GP, Price TS, Glenny L, Ragoussis J . Development and evaluation of real competitive PCR for high-throughput quantitative applications. Anal Biochem 2005; 339: 231–241.
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 2002; 3, RESEARCH0034.
Polidori A, Arhami M, Sioutas C, Delfino RJ, Allen R . Indoor/Outdoor relationships, trends, and carbonaceous content of fine particulate matter in retirement homes of the Los Angeles Basin. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 2007; 57: 366–379.
Singh M, Misra C, Sioutas C . Field evaluation of a personal cascade impactor sampler (PCIS). Atmos Environ 2003; 37: 4781–4793.
Arhami M, Sillanpää M, Hu S, Olson MR, Schauer JJ, Sioutas C et al. Size-segregated inorganic and organic components of PM in the communities of the Los Angeles Harbor. Aerosol Sci Technol 2009; 43: 145–160.
Arhami M, Minguillon MC, Polidori A, Schauer JJ, Delfino RJ, Sioutas C et al. Organic compound characterization and source apportionment of indoor and outdoor quasi-ultrafine particulate matter in retirement homes of the Los Angeles Basin. Indoor Air 2010; 20: 17–30.
Schauer JJ, Kleeman MJ, Cass GR, Simoneit BRT . Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 5. C1−C32 organic compounds from gasoline-powered motor vehicles. Environ Sci Technol 2002; 36: 1169–1180.
Stone EA, Snyder DC, Sheesley RJ, Sullivan AP, Weber RJ, Schauer JJ et al. Source apportionment of fine organic aerosol in Mexico City during the MILAGRO experiment 2006. Atmos Chem Phys 2008; 8: 1249–1259.
Weber RJ, Sullivan AP, Peltier RE, Russell A, Yan B, Zheng M et al. A study of secondary organic aerosol formation in the anthropogenic-influenced southeastern United States. J Geophys Res 2007; 112: D13302.
Docherty KS, Stone EA, Ulbrich IM, DeCarlo PF, Snyder DC, Schauer JJ et al. Apportionment of primary and secondary organic aerosols in Southern California during the 2005 study of organic aerosols in Riverside (SOAR-1). Environ Sci Technol 2008; 42: 7655–7662.
Sannigrahi P, Sullivan AP, Weber RJ, Ingall ED . Characterization of water-soluble organic carbon in urban atmospheric aerosols using solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 2005; 40: 666–672.
Landreman AP, Shafer MM, Hannigan MP, Schauer JJ . A macrophage-based method for the assessment of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) activity of atmospheric particulate matter (PM) and application to routine (daily-24 h) aerosol monitoring studies. Aerosol Sci Technol 2008; 42: 946–957.
Willems E, Leyns L, Vandesompele J . Standardization of real-time PCR gene expression data from independent biological replicates. Anal Biochem 2008; 379: 127–129.
Wurmbach E, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Yuen T, Ebersole BJ, Mastaitis JW, Mobbs CV et al. Validated genomic approach to study differentially expressed genes in complex tissues. Neurochem Res 2002; 27: 1027–1033.
Fan H, Hegde PS . The transcriptome in blood: challenges and solutions for robust expression profiling. Curr Mol Med 2005; 5: 3–10.
Efron B, Tibshirani R . On testing the significance of sets of genes. Ann Appl Stat 2007; 1: 107–129.
Zhu H, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Zweier JL, Li Y . Role of Nrf2 signaling in regulation of antioxidants and phase 2 enzymes in cardiac fibroblasts: protection against reactive oxygen and nitrogen species-induced cell injury. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 3029–3036.
Li N, Alam J, Venkatesan MI, Eiguren-Fernandez A, Schmitz D, Di Stefano E et al. Nrf2 is a key transcription factor that regulates antioxidant defense in macrophages and epithelial cells: protecting against the proinflammatory and oxidizing effects of diesel exhaust chemicals. J Immunol 2004; 173: 3467–3481.
Araujo JA, Barajas B, Kleinman M, Wang X, Bennett BJ, Gong KW et al. Ambient particulate pollutants in the ultrafine range promote early atherosclerosis and systemic oxidative stress. Circ Res 2008; 102: 589–596.
Shin S, Wakabayashi N, Misra V, Biswal S, Lee GH, Agoston ES et al. NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: influence on adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7188–7197.
Delfino RJ, Tjoa T, Gillen DL, Staimer N, Polidori A, Arhami M et al. Traffic-related air pollution and blood pressure in elderly subjects with coronary artery disease. Epidemiology 2010; 21: 396–404.
Delfino RJ, Gillen DL, Tjoa T, Staimer N, Polidori A, Arhami M et al. Electrocardiographic ST-segment depression and exposure to traffic-related aerosols in elderly subjects with coronary artery disease. Environ Health Perspect 2011; 119: 196–202.
Bartell S, Tjoa T, Longhurst J, Sioutas C, Delfino RJ . Particulate air pollution, ambulatory heart rate variability and arrhythmia in elderly subjects with coronary artery disease. Environ Health Perspect 2013; 121: 1135–1141.
Naeher LP, Brauer M, Lipsett M, Zelikoff JT, Simpson CD, Koenig JQ et al. Woodsmoke health effects: a review. Inhal Toxicol 2007; 19: 67–106.
Woollard KJ, Chin-Dusting J . Therapeutic targeting of p-selectin in atherosclerosis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 2007; 6: 69–74.
Galea J, Armstrong J, Gadsdon P, Holden H, Francis SE, Holt CM et al. Interleukin-1 beta in coronary arteries of patients with ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1996; 16: 1000–1006.
Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, Christensen BC, Marsit CJ, Nelson HH et al. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinformatics 2012; 13: 86.
Accomando WP, Wiencke JK, Houseman EA, Nelson HH, Kelsey KT . Quantitative reconstruction of leukocyte subsets using DNA methylation. Genome Biol 2014; 15: R50.
Bartell SM, Longhurst J, Tjoa T, Sioutas C, Delfino RJ . Particulate air pollution, ambulatory heart rate variability, and cardiac arrhythmia in retirement community residents with coronary artery disease. Environ Health Perspect 2013; 121: 1135–1141.
Hasheminassab S, Daher N, Shafer MM, Schauer JJ, Delfino RJ, Sioutas C et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of indoor and outdoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in retirement communities of the Los Angeles Basin. Sci Total Environ 2014; 490: 528–537.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences at the National Institutes of Health (NIH, R01-ES12243 and R21-ES016420), the California Air Resources Board (contracts 03-329 and 09-341), and the National Center for Research Resources at the National Institutes of Health (NIH, MO1-RR00827). SW is supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences at the National Institutes of Health (NIH, F30 ES21107) and the Stanley Behrens UCI Graduate Division Public Impact Fellowship. ND is supported by the University of Southern California Provost's PhD fellowship. The contents of this article are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies. We thank the Department of Epidemiology and General Clinical Research Center, University of California Irvine; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Southern California (USC); the Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene; the California Air Resources Board; and the South Coast Air Quality Management District.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
CS receives royalties from SKC for the air sampling device (Sioutas Personal Cascade Impactor Sampler) used in this research.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittkopp, S., Staimer, N., Tjoa, T. et al. Nrf2-related gene expression and exposure to traffic-related air pollution in elderly subjects with cardiovascular disease: An exploratory panel study. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 26, 141–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2014.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2014.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interaction of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) candidate longevity gene and particulate matter (PM2.5) on all-cause mortality: a longitudinal cohort study in China
Environmental Health (2021)
-
A multi-scale approach to study biochemical and biophysical aspects of resveratrol on diesel exhaust particle-human primary lung cell interaction
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Associations between microvascular function and short-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and particulate matter oxidative potential
Environmental Health (2016)