Abstract
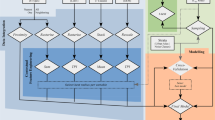
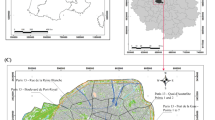
Noise prediction models and noise maps are used to estimate the exposure to road traffic noise, but their availability and the quality of the noise estimates is sometimes limited. This paper explores the application of land use regression (LUR) modelling to assess the long-term intraurban spatial variability of road traffic noise in three European cities. Short-term measurements of road traffic noise taken in Basel, Switzerland (n=60), Girona, Spain (n=40), and Grenoble, France (n=41), were used to develop two LUR models: (a) a “GIS-only” model, which considered only predictor variables derived with Geographic Information Systems; and (b) a “Best” model, which in addition considered the variables collected while visiting the measurement sites. Both noise measurements and noise estimates from LUR models were compared with noise estimates from standard noise models developed for each city by the local authorities. Model performance (adjusted R2) was 0.66–0.87 for “GIS-only” models, and 0.70–0.89 for “Best” models. Short-term noise measurements showed a high correlation (r=0.62–0.78) with noise estimates from the standard noise models. LUR noise estimates did not show any systematic differences in the spatial patterns when compared with those from standard noise models. LUR modelling with accurate GIS source data can be a promising tool for noise exposure assessment with applications in epidemiological studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Environment Agency. Transport at a crossroads TERM 2008: indicators tracking transport and environment in the European Union. EEA report. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009. Available at <http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/transport-at-a-crossroads> (last accessed 5 May 2013).
Basner M, Babisch W, Davis A, Brink M, Clark C, Janssen S et al. Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014; 383: 1325–1332.
Babisch W . Transportation noise and cardiovascular risk: updated review and synthesis of epidemiological studies indicate that the evidence has increased. Noise & Health 2006; 8: 1–29.
Floud S, Vigna-Taglianti F, Hansell A, Blangiardo M, Houthuijs D, Breugelmans O et al. Medication use in relation to noise from aircraft and road traffic in six European countries: results of the HYENA study. Occup Environ Med 2011; 68: 518–524.
Stansfeld SA, Berglund B, Clark C, Lopez-Barrio I, Fischer P, Ohrström E et al. Aircraft and road traffic noise and children’s cognition and health: a cross-national study. Lancet 2005; 365: 1942–1949.
Van Kempen E, Babisch W . The quantitative relationship between road traffic noise and hypertension: a meta-analysis. J Hypertens 2012; 30: 1075–1086.
European Commission. Directive 2002/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 June 2002 relating to the assessment and management o environmental noise. Off J Eur Commun L189, 12–25.
European Commission’s Working Group - Assessment of Exposure to Noise (WG-AEN). Position paper: Good practice guide for strategic noise mapping and the production of associated data on noise exposure. 2003. Available at http://ec.europa.eu/environment/noise/pdf/best_practice_guide.pdf (last accessed 18 March 2013).
Hoek G, Beelen R, de Hoogh K, Vienneau D, Gulliver J, Fischer P et al. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos Env 2008; 42: 7561–7578.
Jerrett M, Arain A, Kanaroglou P, Beckerman B, Potoglou D, Sahsuvaroglu T et al. A review and evaluation of intraurban air pollution exposure models. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004; 15: 185–204.
Beelen R, Hoek G, Vienneau D, Eeftens M, Dimakopoulou K, Pedeli X et al. Development of NO2 and NOx land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in Europe: The ESCAPE project. Atmos Env 2013; 72: 10–23.
de Hoogh K, Wang M, Adam M, Badaloni C, Beelen R, Birk M et al. Development of land use regression models for particle composition in twenty study areas in Europe. Environ Sci Technol 2013; 47: 5778–5786.
Eeftens M, Beelen R, de Hoogh K, Bellander T, Cesaroni G, Cirach M et al. Development of land use regression models for PM2.5, PM2.5 absorbance, PM10 and PM coarse in 20 European study areas; results of the ESCAPE project. Environ Sci Technol 2012: 46: 11195–111205.
Xie D, Liu Y, Chen J . Mapping urban environmental noise: a land use regression method. Environ Sci Technol 2011: 45: 7358–7364.
Deltell A . Elaboració del mapa acústic de trànsit de la ciutat de Girona. Degree Project Dissertation [in Catalan]. Universitat de Girona: Spain, 2005.
Aguilera I, Sunyer J, Fernández-Patier R, Hoek G, Aguirre-Alfaro A, Meliefste K et al. Estimation of outdoor NOx, NO2, and BTEX exposure in a cohort of pregnant women using land use regression modeling. Environ Sci Technol 2008; 42: 815–821.
Brauer M, Hoek G, van Vliet P, Meliefste K, Fischer P, Gehring U et al. Estimating long-term average particulate air pollution concentrations: application of traffic indicators and geographic information systems. Epidemiology 2003; 14: 228–239.
Morgenstern V, Zutavern A, Cyrys J, Brockow I, Gehring U, Koletzko S et al. Respiratory health and individual estimated exposure to traffic-related air pollutants in a cohort of young children. Occup Environ Med 2007; 64: 8–16.
Allen RW, Davies H, Cohen MA, Mallach G, Kaufman JD, Adar SD . The spatial relationship between traffic-generated air pollution and noise in 2 US cities. Environ Res 2009; 109: 334–342.
Davies HW, Vlaanderen JJ, Henderson SB, Brauer M . Correlation between co-exposures to noise and air pollution from traffic sources. Occup Environ Med 2009; 66: 347–350.
Gan WQ, McLean K, Brauer M, Chiarello SA, Davies HW . Modeling population exposure to community noise and air pollution in a large metropolitan area. Environ Res 2012; 116: 11–16.
Rivera M, Basagaña X, Aguilera I, Agis D, Bouso L, Medina-Ramón M et al. Spatial distribution of ultrafine particles in Girona, Spain: a land-use regression model. Atmos Environ 2012; 54: 657–666.
Basagaña X, Rivera M, Aguilera I, Agis D, Bouso L, Elosua R et al. Effect of the number of measurement sites on land-use regression models in estimating local air pollution. Atmos Environ 2012; 54: 634–642.
Jacquemin B, Lepeule J, Boudier A, Arnould C, Benmerad M, Chappaz C et al. Impact of geocoding methods on associations between long-term exposure to urban air pollution and lung function. Environ Health Perspect 2013; 121: 1054–1060.
Lee CSY, Fleming GG, Measurement of highway-related noise. Report No. FHWA-PD-96-046 and DOT-VNTSC-FHWA-96-5. John A. Volpe National Transportation Systems Center, Acoustics Facility, Cambridge, MA: May 1996.
Wang M, Beelen R, Eeftens M, Meliefste K, Hoek G, Brunekreef B . Systematic evaluation of land use regression models for NO2 . Environ Sci Technol 2012; 46: 4481–4489.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by ADEME (French Environment and Energy Management Agency; TRI-TABS study contract 0966C0304). Inmaculada Aguilera holds a postdoctoral fellowship awarded from the Catalan Agency for Management of University and Research Grants (BP-DGR-2011-00214). We thank Alex Ineichen (SwissTPH), Marta Cirach (CREAL), and Cécile Fontagné (Air Rhône-Alpes) for their assistance in deriving the GIS variables; n-Sphere (Zürich, Switzerland) and Acoucité Noise Observatory (Lyon, France) for providing the modelled noise estimates in Basel and Grenoble, respectively; and La Métro city council (Grenoble) for providing access to local data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilera, I., Foraster, M., Basagaña, X. et al. Application of land use regression modelling to assess the spatial distribution of road traffic noise in three European cities. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 25, 97–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2014.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2014.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Random effect generalized linear model-based predictive modelling of traffic noise
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2024)
-
Evaluating long-term and high spatiotemporal resolution of wet-bulb globe temperature through land-use based machine learning model
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2023)
-
Predicting traffic noise using land-use regression—a scalable approach
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2022)
-
Space-time characterization of community noise and sound sources in Accra, Ghana
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Satellitendaten zur Erfassung gesundheitsrelevanter Umweltbedingungen: Beispiele und interdisziplinäre Potenziale
Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Gesundheitsforschung - Gesundheitsschutz (2020)