Abstract
Objective:
Epidemiological evidence shows an inverse relationship between sleep duration and overweight/obesity risk. However, there are few polysomnographic studies that relate the organization of sleep stages to pediatric overweight (OW). We compared sleep organization in otherwise healthy OW and normal-weight (NW) 10-year-old children.
Subjects:
Polysomnographic assessments were performed in 37 NW and 59 OW children drawn from a longitudinal study beginning in infancy. Weight and height were used to evaluate body mass index (BMI) according to international criteria. Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep (stages N1, N2 and N3), rapid eye movement (REM) sleep (stage R) and wakefulness (stage W) were visually scored. Sleep parameters were compared in NW and OW groups for the whole sleep period time (SPT) and for each successive third of it using independent Student’s t-tests or nonparametric tests. The relationship between BMI and sleep variables was evaluated by correlation analyses controlling for relevant covariates.
Results:
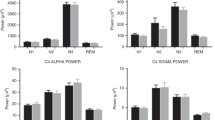
The groups were similar in timing of sleep onset and offset, and sleep period time. BMI was inversely related to total sleep time (TST) and sleep efficiency. OW children showed reduced TST, sleep efficiency and stage R amount, but higher stage W amount. In analysis by thirds of the SPT, the duration of stage N3 episodes was shorter in the first third and longer in the second third in OW children as compared with NW children.
Conclusions:
Our results show reduced sleep amount and quality in otherwise healthy OW children. The lower stage R amount and changes involving stage N3 throughout the night suggest that OW in childhood is associated with modifications not only in sleep duration, but also in the ongoing night time patterns of NREM sleep and REM sleep stages.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Han JC, Lawlor DA, Kimm SY . Childhood obesity. Lancet 2010; 375: 1737–1748.
Biro FM, Wien M . Childhood obesity and adult morbidities. Am J Clin Nutr 2010; 91: 1499S–1505S.
McAllister EJ, Dhurandhar NV, Keith SW, Aronne LJ, Barger J, Baskin M et al. Ten putative contributors to the obesity epidemic. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2009; 49: 868–913.
Trakada G, Chrousos G, Pejovic S, Vgontzas A . Sleep apnea and its association with the stress system, inflammation, insulin resistance and visceral obesity. Sleep Med Clin 2007; 2: 251–261.
Inocente CO, Lavault S, Lecendreux M, Dauvilliers Y, Reimao R, Gustin MP et al. Impact of obesity in children with narcolepsy. CNS Neurosci Ther 2013; 19: 521–528.
Van Cauter E, Knutson KL . Sleep and the epidemic of obesity in children and adults. Eur J Endocrinol 2008; 159 (Suppl 1): S59–S66.
Rajaratnam SM, Arendt J . Health in a 24-h society. Lancet 2001; 358: 999–1005.
Knutson KL, Van Cauter E, Rathouz PJ, DeLeire T, Lauderdale DS . Trends in the prevalence of short sleepers in the USA: 1975-2006. Sleep 2010; 33: 37–45.
NationalSleepFoundation. The 2006 Sleep in America Poll. 2006 [cited 2012 June 17]; Available from: http://www.sleepfoundation.org.
Chaput JP, Brunet M, Tremblay A . Relationship between short sleeping hours and childhood overweight/obesity: results from the ‘Quebec en Forme’ Project. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 1080–1085.
Chaput JP, Lambert M, Gray-Donald K, McGrath JJ, Tremblay MS, O'Loughlin J et al. Short sleep duration is independently associated with overweight and obesity in Quebec children. Can J Public Health 2011; 102: 369–374.
Chen X, Beydoun MA, Wang Y . Is sleep duration associated with childhood obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 265–274.
Patel SR, Hu FB . Short sleep duration and weight gain: a systematic review. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 643–653.
Bell JF, Zimmerman FJ . Shortened nighttime sleep duration in early life and subsequent childhood obesity. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2010; 164: 840–845.
Seegers V, Petit D, Falissard B, Vitaro F, Tremblay RE, Montplaisir J et al. Short sleep duration and body mass index: a prospective longitudinal study in preadolescence. Am J Epidemiol 2011; 173: 621–629.
Magee L, Hale L . Longitudinal associations between sleep duration and subsequent weight gain: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev 2012; 16: 231–241.
Nixon GM, Thompson JM, Han DY, Becroft DM, Clark PM, Robinson E et al. Short sleep duration in middle childhood: risk factors and consequences. Sleep 2008; 31: 71–78.
Porkka-Heiskanen T, Zitting KM, HK Wigren . Sleep, its regulation and possible mechanisms of sleep disturbances. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2013; 208: 311–328.
Peirano PD, Algarin CR, Garrido MI, Lozoff B . Iron deficiency anemia in infancy is associated with altered temporal organization of sleep states in childhood. Pediatr Res 2007; 62: 715–719.
Spruyt K, Molfese DL, Gozal D . Sleep duration, sleep regularity, body weight, and metabolic homeostasis in school-aged children. Pediatrics 2011; 127: e345–e352.
Knutson KL, Spiegel K, Penev P, Van Cauter E . The metabolic consequences of sleep deprivation. Sleep Med Rev 2007; 11: 163–178.
Resta O, Foschino Barbaro MP, Bonfitto P, Giliberti T, Depalo A, Pannacciulli N et al. Low sleep quality and daytime sleepiness in obese patients without obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. J Intern Med 2003; 253: 536–543.
Liu X, Forbes EE, Ryan ND, Rofey D, Hannon TS, Dahl RE . Rapid eye movement sleep in relation to overweight in children and adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008; 65: 924–932.
Wojnar J, Brower KJ, Dopp R, Wojnar M, Emslie G, Rintelmann J et al. Sleep and body mass index in depressed children and healthy controls. Sleep Med 2010; 11: 295–301.
Benca RM, Obermeyer WH, Thisted RA, Gillin JC . Sleep and psychiatric disorders. A meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1992; 49: 651–668 discussion 69-70.
Kalra M, Mannaa M, Fitz K, Kumar S, Chakraborty R, Sheng X et al. Effect of surgical weight loss on sleep architecture in adolescents with severe obesity. Obes Surg 2008; 18: 675–679.
Dixon JB, Schachter LM, O'Brien PE . Polysomnography before and after weight loss in obese patients with severe sleep apnea. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005; 29: 1048–1054.
Lozoff B, De Andraca I, Castillo M, Smith JB, Walter T, Pino P . Behavioral and developmental effects of preventing iron-deficiency anemia in healthy full-term infants. Pediatrics 2003; 112: 846–854.
de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J . Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ 2007; 85: 660–667.
Jasper HH . The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 1958; 10: 370–375.
Kemp B, Varri A, Rosa AC, Nielsen KD, Gade J . A simple format for exchange of digitized polygraphic recordings. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1992; 82: 391–393.
Silber MH, Ancoli-Israel S, Bonnet MH, Chokroverty S, Grigg-Damberger MM, Hirshkowitz M et al. The visual scoring of sleep in adults. J Clin Sleep Med 2007; 3: 121–131.
Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Marcus CL, Vaughn BV et alfor the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.0. Darien, IL, USA 2012.
Causa L, Held CM, Causa J, Estevez PA, Perez CA, Chamorro R et al. Automated sleep-spindle detection in healthy children polysomnograms. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2010; 57: 2135–2146.
Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Marcus CL et alfor the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.0. Darien, IL, USA, 2012.
von Kries R, Toschke AM, Wurmser H, Sauerwald T, Koletzko B . Reduced risk for overweight and obesity in 5- and 6-y-old children by duration of sleep—a cross-sectional study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 710–716.
Cappuccio FP, Taggart FM, Kandala NB, Currie A, Peile E, Stranges S et al. Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 2008; 31: 619–626.
Jarrin DC, McGrath JJ, Drake CL . Beyond sleep duration: distinct sleep dimensions are associated with obesity in children and adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013; 37: 552–558.
Gregory AM, Sadeh A . Sleep emotional and behavioral difficulties in children and adolescents. Sleep Med Rev 2012; 16: 129–136.
de Sousa G, Schluter B, Buschatz D, Menke T, Trowitzsch E, Andler W et al. A comparison of polysomnographic variables between obese adolescents with polycystic ovarian syndrome and healthy, normal-weight and obese adolescents. Sleep Breath 2010; 14: 33–38.
Tauman R, Gozal D . Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Expert Rev Respir Med 2011; 5: 425–440.
Shechter A, O'Keeffe M, Roberts AL, Zammit GK, RoyChoudhury A, St-Onge MP . Alterations in sleep architecture in response to experimental sleep curtailment are associated with signs of positive energy balance. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2012; 303: R883–R889.
Gonnissen HK, Hursel R, Rutters F, Martens EA, Westerterp-Plantenga MS . Effects of sleep fragmentation on appetite and related hormone concentrations over 24 h in healthy men. Br J Nutr 2012; 8: 1–9.
Mason 2nd TB, Teoh L, Calabro K, Traylor J, Karamessinis L, Schultz B et al. Rapid eye movement latency in children and adolescents. Pediatr Neurol 2008; 39: 162–169.
Adam K . Total and percentage REM sleep correlate with body weight in 36 middle-aged people. Sleep 1987; 10: 69–77.
Ohkawa T, Nakazawa Y . Correlations of some physical variables with REM sleep and slow wave sleep in man. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 1982; 36: 383–389.
Mavanji V, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Teske JA . Sleep and obesity: a focus on animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2012; 36: 1015–1029.
Arble DM, Ramsey KM, Bass J, Turek FW . Circadian disruption and metabolic disease: findings from animal models. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 24: 785–800.
Sonka K, Kemlink D, Buskova J, Pretl M, Srutkova Z, Maurovich Horvat E et al. Obesity accompanies narcolepsy with cataplexy but not narcolepsy without cataplexy. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2010; 31: 631–634.
Mavanji V, Teske JA, Billington CJ, Kotz CM . Elevated sleep quality and orexin receptor mRNA in obesity-resistant rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010; 34: 1576–1588.
Megirian D, Dmochowski J, Farkas GA . Mechanism controlling sleep organization of the obese Zucker rats. J Appl Physiol 1998; 84: 253–256.
Nedeltcheva AV, Kilkus JM, Imperial J, Kasza K, Schoeller DA, Penev PD . Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 89: 126–133.
Karacan I, Williams RL, Finley WW, Hursch CJ . The effects of naps on nocturnal sleep: influence on the need for stage-1 REM and stage 4 sleep. Biol Psychiatry 1970; 2: 391–399.
Magee CA, Huang XF, Iverson DC, Caputi P . Examining the pathways linking chronic sleep restriction to obesity. J Obes 2010; 2010 doi:10.1155/2010/821710.
Schmid SM, Hallschmid M, Jauch-Chara K, Wilms B, Benedict C, Lehnert H et al. Short-term sleep loss decreases physical activity under free-living conditions but does not increase food intake under time-deprived laboratory conditions in healthy men. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 90: 1476–1482.
Spiegel K, Leproult R, Van Cauter E . Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. Lancet 1999; 354: 1435–1439.
Bhanot JL, Chhina GS, Singh B, Sachdeva U, Kumar VM . REM sleep deprivation and food intake, 1989 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 33: 139–145.
Chaput JP, Despres JP, Bouchard C, Tremblay A . Longer sleep duration associates with lower adiposity gain in adult short sleepers. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012; 36: 752–756.
Chaput JP, Tremblay A . Sleeping habits predict the magnitude of fat loss in adults exposed to moderate caloric restriction. Obes Facts 2012; 5: 561–566.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the children and their parents who have made this research possible and the technicians and personnel for their valuable collaboration. This study was supported by grants from Chilean Agency for Funding in Science and Technology (CONICYT, Fondecyt 1110513 and 1120319) and the US National Institutes of Health (NIH R01 HD33487).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamorro, R., Algarín, C., Garrido, M. et al. Night time sleep macrostructure is altered in otherwise healthy 10-year-old overweight children. Int J Obes 38, 1120–1125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.238
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.238
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interventions to prevent obesity in Latinx children globally: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Systematic Reviews (2021)
-
The relationship between sleep duration, sleep quality and dietary intake in adults
Sleep and Biological Rhythms (2020)
-
Association between REM sleep and obstructive sleep apnea in obese and overweight adolescents
Sleep and Breathing (2019)
-
Does preterm period sleep development predict early childhood growth trajectories?
Journal of Perinatology (2017)
-
Nocturnal sleep-related variables from 24-h free-living waist-worn accelerometry: International Study of Childhood Obesity, Lifestyle and the Environment
International Journal of Obesity Supplements (2015)