Abstract
Objective:
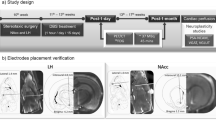
The authors proposed an intraventricular ‘floating’ electrode inserted in the third ventricle (V3) adjacent to the ventromedian hypothalamus (VMH) in a freely moving Macaca fascicularis to modulate food intake (FI), body fat (BF), body weight (BW) and body mass index (BMI), as a potential treatment of obesity.
Methods:
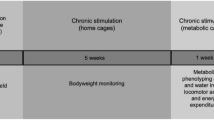
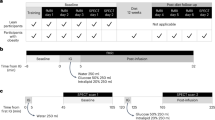
Five adult Macaca fascicularis monkeys were implanted stereotactically in the V3 contiguous to the VMH with one deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrode. The study was divided in two phases: (a) acute 24 h-fasting trials: different electrical stimulation parameters were applied to a fasting primate to determine the best combination in reducing FI; and (b) chronic 8-week stimulation trials: three cycles of intraventricular-VMH DBS lasting 8–10 weeks were performed at 130 Hz, 80 Hz (most effective frequency reducing FI) and 30 Hz, respectively. BMI, BW, BF content, skinfolds and hormones were measured during baseline and at the end of each session of stimulation.
Results:
Acute 24 h-fasting trials: there was a decrease in FI in all subjects at 80 Hz, (11–19%, mean 15%). Chronic 8-week stimulation trials: a significant decrease in BW and BMI was observed in three out of four monkeys at 80 Hz (mean 8±4.4%). Subcutaneous skinfolds were reduced in all four subjects at 80 Hz and slightly increased at 130 Hz. The sham monkey remained stable. No significant adverse effects were recorded.
Conclusion:
The stimulation of the VMH region through an intraventricular approach might acutely modulate FI and induce a sustained decrease in BW and fat mass in normal non-human primate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roe DA, Eickwort KR . Relationships between obesity and associated health factors with unemployment among low income women. J Am Med Womens Assoc 1976; 31: 193–194 198-199, 203–194.
Fontaine KR, Redden DT, Wang C, Westfall AO, Allison DB . Years of life lost due to obesity. JAMA 2003; 289: 187–193.
Pories WJ, MacDonald KG . The surgical treatment of morbid obesity. Curr Opin Gen Surg 1993; 195–205.
Korner J, Aronne LJ . The emerging science of body weight regulation and its impact on obesity treatment. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 565–570.
Brolin RE . Critical analysis of results: weight loss and quality of data. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55: 577S–581S.
Benabid AL, Benazzouz A, Hoffmann D, Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P . Long-term electrical inhibition of deep brain targets in movement disorders. Mov Disord 1998; 13 (Suppl 3): 119–125.
Levy RM . Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of intractable pain. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2003; 14: 389–399, vi.
Gabriels L, Cosyns P, Nuttin B, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J . Deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: psychopathological and neuropsychological outcome in three cases. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2003; 107: 275–282.
Cosyns P, Gabriels L, Nuttin B . Deep brain stimulation in treatment refractory obsessive compulsive disorder. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg 2003; 65: 385–399; discussion 399–400.
Benabid AL, Koudsie A, Benazzouz A, Vercueil L, Fraix V, Chabardes S et al. Deep brain stimulation of the corpus luysi (subthalamic nucleus) and other targets in Parkinson's disease. Extension to new indications such as dystonia and epilepsy 1. J.Neurol 2001; 248 (Suppl 3): III37–III47.
Benabid AL, Minotti L, Koudsie A, de Saint Martin A, Hirsch E . Antiepileptic effect of high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (corpus luysi) in a case of medically intractable epilepsy caused by focal dysplasia: a 30-month follow-up: technical case report. Neurosurgery 2002; 50: 1385–1391; discussion 1391–1382.
Chabardes S, Kahane P, Minotti L, Koudsie A, Hirsch E, Benabid AL . Deep brain stimulation in epilepsy with particular reference to the subthalamic nucleus. Epileptic Disord 2002; 4 (Suppl 3): S83–S93.
May A . Hypothalamic deep-brain stimulation: target and potential mechanism for the treatment of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2008; 28: 799–803.
Talairach J, Szikla G . Application of stereotactic concepts to the surgery of epilepsy. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1980; 30: 35–54.
Percheron G, Francois C, Yelnik J . Instruments and techniques for the stereotactic surgery based on the CA-CP ventricular system of coordinates in monkeys. J Neurosci Methods 1986; 17: 89–99.
Paxinos, Huang XF, Aw T . The Rhesus Monkey Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: New York, 1999.
Larsson B, Seidell J, Svärdsudd K, Welin L, Tibblin G, Wilhelmsen L et al. Obesity, adipose tissue distribution and health in men--the study of men born in 1913. Appetite 1989; 13: 37–44.
Pender JR, Pories WJ . Epidemiology of obesity in the United States. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2005; 34: 1–7.
Anand BK, Brobeck JR . Localization of a ‘feeding center’ in the hypothalamus of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1951; 77: 323–324.
Sani S, Jobe K, Smith A, Kordower JH, Bakay RA . Deep brain stimulation for treatment of obesity in rats. J Neurosurg 2007; 107: 809–813.
Bielajew C, Stenger J, Schindler D . Factors that contribute to the reduced weight gain following chronic ventromedial hypothalamic stimulation. Behav Brain Res 1994; 62: 143–148.
Stenger J, Fournier T, Bielajew C . The effects of chronic ventromedial hypothalamic stimulation on weight gain in rats. Physiol Behav 1991; 50: 1209–1213.
Lacan G, De Salles AA, Gorgulho AA, Krahl SE, Frighetto L, Behnke EJ et al. Modulation of food intake following deep brain stimulation of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the vervet monkey. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg 2008; 108: 336–342.
Robinson BW, Mishkin M . Alimentary responses to forebrain stimulation in monkeys. Exp Brain Res 1968; 4: 330–366.
Takaki A, Aou S, Oomura Y, Okada E, Hori T . Feeding suppression elicited by electrical and chemical stimulations of monkey hypothalamus. Am J Physiol 1992; 262: R586–R594.
Vercueil L, Pollak P, Fraix V, Caputo E, Moro E, Benazzouz A et al. Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of severe dystonia. J Neurol 2001; 248: 695–700.
Krauss JK, Loher TJ, Weigel R, Capelle HH, Weber S, Burgunder JM . Chronic stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for treatment of non-dYT1 generalized dystonia and choreoathetosis: 2-year follow up. J Neurosurg 2003; 98: 785–792.
Delgado JM, Anand BK . Increase of food intake induced by electrical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus. Am J Physiol 1953; 172: 162–168.
Beltt BM, Keesey RE . Hypothalamic map of stimulation current thresholds for inhibition of feeding in rats. Am J Physiol 1975; 229: 1124–1133.
Masuo K, Katsuya T, Kawaguchi H, Fu Y, Rakugi H, Ogihara T et al. Rebound weight gain as associated with high plasma norepinephrine levels that are mediated through polymorphisms in the beta2-adrenoceptor. Am J Hypertens 2005; 18: 1508–1516.
Hensrud DD, Weinsier RL, Darnell BE, Hunter GR . A prospective study of weight maintenance in obese subjects reduced to normal body weight without weight- loss training. Am J Clin Nutr 1994; 60: 688–694.
Teitelbaum P, Epstein AN . The lateral hypothalamic syndrome: recovery of feeding and drinking after lateral hypothalamic lesions. Psychol Rev 1962; 69: 74–90.
Narita K, Yokawa T, Nishihara M, Takahashi M . Interaction between excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus in inducing hyper-running. Brain Res 1993; 603: 243–247.
Vissing J, Wallace JL, Scheurink AJ, Galbo H, Steffens AB . Ventromedial hypothalamic regulation of hormonal and metabolic responses to exercise. Am J Physiol 1989; 256: R1019–R1026.
Fink G . The development of the releasing factor concept. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976; 5 (Suppl): 245S–260S.
Martin JB, Reichlin S . Plasma thyrotropin (TSH) response to hypothalamic electrical stimulation and to injection of synthetic thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH). Endocrinology 1972; 90: 1079–1085.
Martin J, Reichlin S . Thyrotropin secretion in rats after hypothalamic electrical stimulation or injection of synthetic TSH-releasing factor. Science 1970; 168: 1366–1368.
Szczepanska-Sadowska E, Sobocinska J, Sadowski B, Kosowski S . Inhibition of osmotic thirst by electric stimulation of the basal forebrain in dogs. Am J Physiol 1979; 236: R117–R125.
Bernardis LL, Bellinger LL . The lateral hypothalamic area revisited: ingestive behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1996; 20: 189–287.
Lustig RH . The neuroendocrinology of obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2001; 30: 765–785.
Anderson JW, Vichitbandra S, Qian W, Kryscio RJ . Long-term weight maintenance after an intensive Weight-Loss Program. J Am Coll Nutr 1999; 18: 620–627.
MacLean PS, Higgins JA, Johnson GC, Fleming-Elder BK, Peters JC, Hill JO . Metabolic adjustments with the development, treatment, and recurrence of obesity in obesity-prone rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004; 287: R288–R297.
Chaput J-P, Tremblay A . The glucostatic theory of appetite control and the risk of obesity and diabetes. Int J Obes 2009; 33: 46–53.
Minokoshi Y, Saito M, Shimazu T . Sympathetic denervation impairs responses of brown adipose tissue to VMH stimulation. Am J Physiol 1986; 251: R1005–R1008.
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med 1995; 1: 1155–1161.
Rissanen P, Mäkimattila S, Vehmas T, Taavitsainen M, Rissanen A . Effect of weight loss and regional fat distribution on plasma leptin concentration in obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23: 645–649.
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Louveau A, Henry S, de Rougemont J . Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson disease. Appl Neurophysiol 1987; 50: 344–346.
Bittar RG, Kar-Purkayastha I, Owen SL, Bear RE, Green A, Wang S et al. Deep brain stimulation for pain relief: a meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 2005; 12: 515–519.
Niizuma H, Otsuki T, Suzuki J . CT-guided stereotaxic implantation of a deep brain electrode for the stimulation of the internal capsule--a case report]. No Shinkei Geka 1986; 14: 103–106.
Mazzone P, Lozano A, Stanzione P, Galati S, Scarnati E, Peppe A et al. Implantation of human pedunculopontine nucleus: a safe and clinically relevant target in Parkinson′s disease. Neuroreport 2005; 16: 1877–1881.
Capozzo A, Florio T, Confalone G, Minchella D, Mazzone P, Scarnati E . Low frequency stimulation of the pedunculopontine nucleus modulates electrical activity of subthalamic neurons in the rat. J Neural Transm 2009; 116: 51–56.
Drewnowski A . Energy density, palatability, and satiety: implications for weight control. Nutr Rev 1998; 56: 347–353.
Epstein LH, Leddy JJ . Food reinforcement. Appetite 2006; 46: 22–25.
Elvidge H, Challis JR, Robinson JS, Roper C, Thorburn GD . Influence of handling and sedation on plasma cortisol in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J Endocrinol 1976; 70: 325–326.
Pender C, Ortmeyer HK, Hansen BC, Goldfine ID, Youngren JF . Elevated plasma cell membrane glycoprotein levels and diminished insulin receptor autophosphorylation in obese, insulin-resistant rhesus monkeys. Metabolism 2002; 51: 465–470.
Bodkin NL, Metzger BL, Hansen BC . Hepatic glucose production and insulin sensitivity preceding diabetes in monkeys. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 1989; 256: E676–E681.
Kemnitz JW, Francken GA . Characteristics of spontaneous obesity in male rhesus monkeys. Physiol Behav 1986; 38: 477–483.
Pham P, Rubeck C, David O, Benabid A . Characterization of the electric double layer influence on currents delivered during deep brain stimulation using a temporal electrokinetic model and impedance measurements. J Neural Eng 2010.
Leone M, Franzini A, Felisati G, Mea E, Curone M, Tullo V et al. Deep brain stimulation and cluster headache. Neurol Sci 2005; 26 (Suppl 2): s138–s139.
Pinsker MO, Bartsch T, Falk D, Volkmann J, Herzog J, Deuschl G et al. Failure of deep brain stimulation of the posterior inferior hypothalamus in chronic cluster headache - report of two cases and review of the literature. Zentralbl Neurochir 2008; 69: 76–79.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the following grants: INSERM: Institut National de la santé et de la recherché, médicale, Fundayacucho and Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología, Venezuela, MEDTRONIC Europe, Ministère des affaires étrangères Gouvernement Français, Private donations from Mrs Michelle Ferrier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
MEDTRONIC, the electrode manufacturer, provided a financial endowment to the laboratory INSERM, where this study was conducted, in the form of equipment and supplies, and they also provided support for attendance to conferences in the form of air tickets, accommodation and congresses fees to Dr Torres. There was not a direct implication in the study design, collection or analysis of data and decision to publish. Dr Chabardes has received support for attendance to conferences in the form of air tickets, accommodation and congresses fees from Medtronic. Dr Annaelle Devergnas has received support for attendance to conferences in the form of air tickets, accommodation and congresses fees from Medtronic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, N., Chabardes, S., Piallat, B. et al. Body fat and body weight reduction following hypothalamic deep brain stimulation in monkeys: an intraventricular approach. Int J Obes 36, 1537–1544 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.271
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.271
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Continuous deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens reduces food intake but does not affect body weight in mice fed a high-fat diet
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Brain stimulation in obesity
International Journal of Obesity (2017)
-
Response to Deep Brain Stimulation in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area in a Rat Model of Obesity: In Vivo Assessment of Brain Glucose Metabolism
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2014)