Abstract
Background:
Childhood obesity is a major health problem. An association between children's body mass index (BMI) and overeating has been established, but mechanisms leading to overeating are poorly understood. The personality characteristics impulsivity and reward responsiveness may be involved in the tendency to overeat. Impulsivity might relate to overeating through poor inhibition of food intake; reward responsiveness through the rewarding value of food.
Objective:
This study aimed to reveal the relationships between impulsivity, reward responsiveness, overeating and BMI in a sample of 346 Dutch children aged 6–13 years. The BMI distribution in the sample was representative of the BMI distribution in the Dutch pediatric population.
Methods:
Impulsivity and reward responsiveness were measured with the Dutch version of the parent-report Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire for children. Overeating was assessed with the Dutch translation of the parent-report Children's Eating Behaviour Questionnaire.
Results:
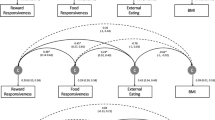
Overeating, impulsivity and reward responsiveness were significantly associated with childhood BMI. Mediation analysis revealed that impulsivity and reward responsiveness equally and significantly predicted BMI indirectly through overeating.
Conclusions:
The personality characteristics impulsivity and reward responsiveness predict childhood BMI indirectly through overeating. This suggests that these personality characteristics are risk factors for obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Banyas B, Allen K et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 802–810.
van den Hurk K, van Dommelen P, van Buuren S, Verkerk PH, Hirasing RA . Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the Netherlands in 2003 compared to 1980 and 1997. Arch Dis Child 2007; 92: 992–995.
Sleddens EFC, Kremers SPJ, Thijs C . The children's eating behaviour questionnaire: factorial validity and association with body mass index in Dutch children aged 6–7. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Activity 2008; 5: 49–57.
Braet C, Claus L, Verbeken S, Van Vlierberghe L . Impulsivity in overweight children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2007; 16: 473–483.
Davis C, Fox J . Sensitivity to reward and body mass index (BMI): evidence for a non-linear relationship. Appetite 2008; 50: 43–49.
Franken IHA, Muris P . Individual differences in reward responsiveness are related to food craving and relative body weight in healthy women. Appetite 2005; 45: 198–201.
Nederkoorn C, Braet C, Van Eijs Y, Tanghe A, Jansen A . Why obese children cannot resist food: the role of impulsivity. Eat Behav 2006; 7: 315–322.
Epstein LH, Dearing KK, Temple JL, Cavanaugh MD . Food reinforcement and impulsivity in overweight children and their parents. Eat Behav 2008; 9: 319–327.
Gray JA . The psychology of fear and stress, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987.
Carver CS, White TL . Behavioral-inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment—the Bis Bas scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 1994; 67: 319–333.
Plichta MM, Vasic N, Wolf RC, Lesch KP, Brummer D, Jacob C et al. Neural hyporesponsiveness and hyperresponsiveness during immediate and delayed reward processing in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 65: 7–14.
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR . A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 1997; 275: 1593–1599.
Spinella M . Neurobehavioral correlates of impulsivity: evidence of prefrontal involvement. Int J Neurosci 2004; 114: 95–104.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Telang F . Overlapping neuronal circuits in addiction and obesity: evidence of systems pathology. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2008; 363: 3191–3200.
Volkow ND, Wise RA . How can drug addiction help us understand obesity? Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 555–560.
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W et al. Brain dopamine and obesity. Lancet 2001; 357: 354–357.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Goldstein RZ, Alia-Klein N et al. Inverse association between BMI and prefrontal metabolic activity in healthy adults. Obesity 2009; 17: 60–65.
Nederkoorn C, Jansen E, Mulkens S, Jansen A . Impulsivity predicts treatment outcome in obese children. Behav Res Ther 2007; 45: 1071–1075.
Pauli-Pott U, Albayrak O, Hebebrand J, Pott W . Association between inhibitory control capacity and body weight in overweight and obese children and adolescents: dependence on age and inhibitory control component. Child Neuropsychol 16: 592–603.
Graziano PA, Calkins SD, Keane SP . Toddler self-regulation skills predict risk for pediatric obesity. Int J Obes 2010; 34: 633–641.
Cortese S, Angriman M, Maffeis C, Isnard P, Konofal E, Lecendreux M et al. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2008; 48: 524–537.
Holtkamp K, Konrad K, Muller B, Heussen N, Herpertz S, Herpertz-Dahlmann B et al. Overweight and obesity in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Int J Obes 2004; 28: 685–689.
Waring ME, Lapane KL . Overweight in children and adolescents in relation to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: results from a national sample. Pediatrics 2008; 122: E1–E6.
Wardle J, Guthrie CA, Sanderson S, Rapoport L . Development of the children's eating behaviour questionnaire, 2001; 42: 963–970.
Colder CR, O’Connor RM . Gray's reinforcement sensitivity model and child psychopathology: laboratory and questionnaire assessment of the BAS and BIS. J Abnorm Child Psychol 2004; 32: 435–451.
Luman M, Oosterlaan J, van Meel CS, Geurts HM . Differences in reward and punishment sensitivity in ADHD subtypes: a cross-cultural validation of the sensitivity to punishment and sensitivity to reward questionnaire for children (SPSRQ-C), 2011. (submitted).
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH . Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. Br Med J 2000; 320: 1240–1243.
Cole TJ, Flegal KM, Nicholls D, Jackson AA . Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: international survey. Br Med J 2007; 335: 194–197.
Baron RM, Kenny DA . The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 1986; 51: 1173–1182.
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF . SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 2004; 36: 717–731.
Verdejo-Garcia A, Perez-Exposito M, Schmidt-Rio-Valle J, Fernandez-Serrano MJ, Cruz F, Perez-Garcia M et al. Selective alterations within executive functions in adolescents with excess weight. Obesity 2010; 18: 1572–1578.
Dawe S, Loxton NJ . The role of impulsivity in the development of substance use and eating disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2004; 28: 343–351.
Ryden A, Sullivan M, Torgerson JS, Karlsson J, Lindroos AK, Taft C . Severe obesity and personality: a comparative controlled study of personality traits. Int J Obes 2003; 27: 1534–1540.
Mustillo S, Worthman C, Erkanli A, Keeler G, Angold A, Costello EJ . Obesity and psychiatric disorder: developmental trajectories. Pediatrics 2003; 111: 851–859.
Verte S, Geurts HM, Roeyers H, Oosterlaan J, Sergeant JA . The relationship of working memory, inhibition, and response variability in child psychopathology. J Neurosci Methods 2006; 151: 5–14.
Heard-Costa NL, Zillikens MC, Monda KL, Johansson A, Harris TB, Fu M et al. NRXN3 is a novel locus for waist circumference: a genome-wide association study from the CHARGE Consortium. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000539.
Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, Steinthorsdottir V, Sulem P, Helgadottir A et al. Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 18–24.
Willer CJ, Speliotes EK, Loos RJF, Li SX, Lindgren CM, Heid IM et al. Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 25–34.
Davis C, Strachan S, Berkson M . Sensitivity to reward: implications for overeating and overweight. Appetite 2004; 42: 131–138.
Houben K, Jansen A . Training inhibitory control. a recipe for resisting sweet temptations. Appetite 2010; 56: 345–349.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Dutch Diabetes Research Foundation, grant #2007.11.032. We thank Professor Dr Peter Heutink for his contribution to the study design. We also thank Dr Esther Sleddens for providing us with the Dutch version of the CEBQ. We are very thankful to the schools and teachers who participated in our study, as well as the children and their parents for their effort and their enthusiasm. We want to express our gratitude to Professor Dr Jeanine Houwing, Irene Draisma, Anouk Nienhuis, Marlous Irschara, Esther van Nieuwenhuize and Ms Vermeulen for statistical and practical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van den Berg, L., Pieterse, K., Malik, J. et al. Association between impulsivity, reward responsiveness and body mass index in children. Int J Obes 35, 1301–1307 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.116
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Excess BMI in early adolescence adversely impacts maturating functional circuits supporting high-level cognition and their structural correlates
International Journal of Obesity (2023)
-
Interactions of approach motivation and self-regulation in relation to obesity in children
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2021)
-
Resting and Functional Pupil Response Metrics Indicate Features of Reward Sensitivity and ASD in Children
Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders (2021)
-
Common etiological architecture underlying reward responsiveness, externally driven eating behaviors, and BMI in childhood: findings from the Gemini twin cohort
International Journal of Obesity (2020)
-
Association between impulsivity traits and body mass index at the observational and genetic epidemiology level
Scientific Reports (2019)