Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of taranabant in obese and overweight patients.
Design:
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study.
Subjects:
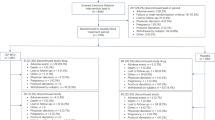
Patients were ⩾18 years old, with body mass index of 27–43 kg m–2, and 51% with metabolic syndrome (MS) randomized to placebo (N=417) or taranabant 2 mg (N=414), 4 mg (N=415) or 6 mg (N=1256) for 104 weeks.
Measurements:
Key efficacy measurements included body weight, waist circumference (WC), lipid and glycemic end points.
Results:
On the basis of risk/benefit assessments, the 6-mg dose was discontinued during year 1 (patients on 6 mg were down-dosed to 2 mg or placebo) and the 4-mg dose was discontinued during year 2 (patients on 4 mg were down-dosed to 2 mg). Changes from baseline in body weight at week 52 (all-patients-treated population, last observation carried forward analysis) were −2.6, −6.6 and −8.1 kg, respectively, for placebo and taranabant 2 and 4 mg (both doses P<0.001 vs placebo). For patients who completed year 1, changes from baseline in body weight at week 104 were −1.4, −6.4 and −7.6 kg for placebo and taranabant 2 and 4 mg, respectively (both doses P<0.001 vs placebo). The proportions of patients at weeks 52 and 104 who lost at least 5 and 10% of their baseline body weight were significantly higher and the proportions of patients who met criteria for MS were significantly lower for taranabant 2 and 4 mg vs placebo. The incidence of adverse experiences classified in the gastrointestinal, nervous, psychiatric, cutaneous and vascular organ systems were generally observed to be dose related with taranabant vs placebo.
Conclusion:
Taranabant at the 2- and 4-mg dose was effective in achieving clinically significant weight loss over 2 years and was associated with dose-related increases in adverse experiences. On the basis of these and other data, an assessment was made that the overall safety and efficacy profile of taranabant did not support its further development for the treatment of obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray GA . Medical management of obesity. In: Bray GA, Bouchard C (eds). Handbook of Obesity: Clinical Applications 3rd edn. Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, 2008. pp. 227–484.
NICE. Obesity: guidance on the prevention, identification, assessment and management of overweight and obesity in adults and children. pp. 1-84. 2006. NICE clinical guidelines 43, NHS: London, available at http://www.nice.org.uk/Guidance/CG43.
Li Z, Maglione M, Tu W, Mojica W, Arterburn D, Shugarman LR et al. Meta-analysis: pharmacologic treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142: 532–546.
Osei-Hyiaman D, Harvey-White J, Bátkai S, Kunos G . The role of the endocannabinoid system in the control of energy homeostasis. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30 (Suppl 1): S33–S38.
Gardner EL . Endocannabinoid signaling system and brain reward: emphasis on dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005; 81: 263–284.
Cota D, Marsicano G, Tschöp M, Grübler Y, Flachskamm C, Schubert M et al. The endogenous cannabinoid system affects energy balance via central orexigenic drive and peripheral lipogenesis. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 423–431.
Bensaid M, Gary-Bobo M, Esclangon A, Maffrand JP, Le Fur G, Oury-Donat F et al. The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716 increases acrp30 mRNA expression in adipose tissue of obese fa/fa rats and in cultured adipocyte cells. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 63: 908–914.
Osei-Hyiaman D, DePetrillo M, Pacher P, Liu J, Radaeva S, Bátkai S et al. Endocannabinoid activation at hepatic CB1 receptors stimulates fatty acid synthesis and contributes to diet-induced obesity. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1298–1305.
Matias I, Gonthier M, Orlando P, Martiadis V, De Petrocellis L, Cervino C et al. Regulation, function, and dysregulation of endocannabinoids in models of adipose and ß-pancreatic cells and in obesity and hyperglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 3171–3180.
Lin LS, Ha S, Ball RG, Tsou NN, Castonguay LA, Doss GA et al. Conformational analysis and receptor docking of N-[(1S,2S)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(3-cyanophenyl)-1-methylpropyl]-2-methyl-2-{[5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]oxy}propanamide (taranabant, MK-0364), a novel, acyclic cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonist. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 2108–2114.
Addy C, Wright H, Van Laere K, Gantz I, Erondu N, Musser BJ et al. The acyclic CB1R inverse agonist taranabant mediates weight loss by increasing energy expenditure and decreasing caloric intake. Cell Metab 2008; 7: 68–78.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB . The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 2001; 16: 606–613.
Addy C, Cote J, Li S, Agrawal N, Majumdar A, Li H et al. Taranabant plasma concentrations increased when co-administered with ketoconazole or diltiazem. Obes Program Abstract Suppl 2007; 15: A147.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2402–2410.
Keller SD, Bayliss MS, Ware Jr JE, Hsu MA, Damiano AM, Goss TF . Comparison of responses to SF-36 Health Survey questions with one-week and four-week recall periods. Health Serv Res 1997; 32: 367–384.
Kolotkin RL, Crosby RD, Kosloski KD, Williams GR . Development of a brief measure to assess quality of life in obesity. Obes Res 2001; 9: 102–111.
Rabin R, de Charro F . EQ-5D: a measure of health status from the EuroQol group. Ann Med Med 2001; 33: 337–343.
Wechsler D . WAIS-III Technical Manual. The Psychological Corporation, Harcourt Brace & Co: San Antonio, 1997.
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF . Manual for the Profile of Mood States (POMS). Educational and Industrial Testing Service: San Diego, CA, 1971.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW . Validation and utility of a self-report of PRIME-MD—the PHQ primary care study. JAMA 1999; 282: 1737–1744.
Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Memorandum. November 2006: Overview for December 13 Meeting of Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee (PDAC). Appendix 2: Request to Sponsors—Advice for the pharmaceutical industry in exploring their placebo-controlled clinical trials databases for suicidality and preparing data sets for analysis by FDA http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/06/briefing/2006-4272b1-01-FDA.pdf pp. 128–137.
Posner K, Oquendo MA, Gould M, Stanley B, Davies M . Columbia Classification Algorithm of Suicide Assessment (C-CASA): classification of suicidal events in the FDA's pediatric suicidal risk analysis of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry 2007; 164: 1035–1043.
Van Gaal LF, Scheen AJ, Rissanen AM, Rossner S, Hanotin C, Ziegler O . Long-term effect of CB1 blockade with rimonabant on cardiometabolic risk factors: two year results from the RIO-Europe Study. Eur Heart J 2008; 29: 1761–1771.
Van Gaal LF, Rissanen AM, Scheen AJ, Ziegler O, Rossner S . Effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker rimonabant on weight reduction and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight patients: 1-year experience from the RIO-Europe study. Lancet 2005; 365: 1389–1397.
Després JP, Golay A, Sjöström L . Rimonabant in obesity-lipids study group. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 2121–2134.
Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, Devin J, Rosenstock J . Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006; 295: 761–775.
James WP, Astrup A, Finer N, Hilsted J, Kopelman P, Rössner S et al. Effect of sibutramine on weight maintenance after weight loss: a randomised trial. STORM Study Group. Sibutramine Trial of Obesity Reduction and Maintenance. Lancet 2000; 356: 2119–2125.
McMahon FG, Fujioka K, Singh BN, Mendel CM, Rowe E, Rolston K et al. Efficacy and safety of sibutramine in obese white and African American patients with hypertension: a 1-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 2185–2191.
McMahon FG, Weinstein SP, Rowe E, Ernst KR, Johnson F, Fujioka K . Sibutramine is safe and effective for weight loss in obese patients whose hypertension is well controlled with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J Hum Hypertens 2002; 16: 5–11.
Smith IG, Goulder MA . Sibutramine Clinical Study 1047 Team. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of long-term treatment with sibutramine in mild to moderate obesity. J Fam Pract 2001; 50: 505–512.
Rucker D, Padwal R, Li SK, Curioni C, Lau DC . Long term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight: updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2007; 335: 1194–1199.
Davidson MH, Hauptman J, DiGirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999; 281: 235–242.
Klein S, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, Kelley DE, Leibel RL, Nonas C et al. Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: a consensus statement from shaping America's health: Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, the Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Obesity 2007; 15: 1061–1067.
Expert Panel on Detection Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Grundy SM, Brewer Jr HB, Cleeman JI, Smith Jr SC, Lenfant C . Definition of metabolic syndrome: report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 2004; 109: 433–438.
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J . Metabolic syndrome – a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006; 23: 469–480.
Pagotto U, Pasquali R . Fighting obesity and associated risk factors by antagonising cannabinoid type 1 receptors. Lancet 2005; 365: 1363–1364.
Scheen AJ, Finer N, Hollander P, Jensen MD, Van Gaal LF . Efficacy and tolerability of rimonabant in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled study. Lancet 2006; 368: 1660–1672.
Tonstad S . Is rimonabant a safe and effective therapy for sustained weight loss and improved cardiometabolic risk factors? Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2006; 3: 364–365.
Fong TM, Heymsfield SB . Cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonists: current understanding of mechanism of action and unanswered questions. Int J Obes (Lond) 2009; 33: 947–955.
Coutts AA, Izzo AA . The gastrointestinal pharmacology of cannabinoids: an update. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2004; 4: 572–579.
Tsou K, Brown S, Sañudo-Peña MC, Mackie K, Walker JM . Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 1998; 83: 393–411.
Pettit DA, Harrison MP, Olson JM, Spencer RF, Cabral GA . Immunohistochemical localization of the neural cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. J Neurosci Res 1998; 51: 391–402.
Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL . Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: a detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 1997; 77: 299–318.
Proietto J, Rissanen A, Harp JB, Erondu N, Yu Q, Suryawanshi S et al. A clinical trial assessing the safety and efficacy of the CB1R inverse agonist taranabant in obese and overweight patients: low-dose study. Int J Obes (in press).
Kipnes MS, Hollander P, Fujioka K, Gantz I, Seck T, Erondu N et al. A one-year study to assess the safety and efficacy of the CB1R inverse agonist taranabant in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2010, e-pub ahead of print; doi:10/1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01188.xx.
Chen RZ, Huang RR, Shen CP, MacNeil DJ, Fong TM . Synergistic effects of cannabinoid inverse agonist AM251 and opioid antagonist nalmefene on food intake in mice. Brain Res 2004; 999: 227–230.
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ . Effects of acute low-dose combined treatment with naloxone and AM 251 on food intake, feeding behaviour and weight gain in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2009; 91: 358–366.
Verty AN, McFarlane JR, McGregor IS, Mallet PE . Evidence for an interaction between CB1 cannabinoid and melanocortin MCR-4 receptors in regulating food intake. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 3224–3231.
Ständer S, Schmelz M, Metze D, Luger T, Rukwied R . Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibers and adnexal structures in human skin. J Dermatol Sci 2005; 38: 177–188.
Lee HK, Choi EB, Pak CS . The current status and future perspectives of studies of cannabinoid receptor 1 antagonists as anti-obesity agents. Curr Top Med Chem 2009; 9: 482–503.
Landsman RS, Burkey TH, Consroe P, Roeske WR, Yamamura HI . SR141716A is an inverse agonist at the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 1997; 334: R1–R2.
Gómez R, Navarro M, Ferrer B, Trigo JM, Bilbao A, Del Arco I et al. A peripheral mechanism for CB1 cannabinoid receptor-dependent modulation of feeding. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 9612–9617.
Pavón FJ, Serrano A, Pérez-Valero V, Jagerovic N, Hernández-Folgado L, Bermúdez-Silva FJ et al. Central versus peripheral antagonism of cannabinoid CB1 receptor in obesity: effects of LH-21, a peripherally acting neutral cannabinoid receptor antagonist, in Zucker rats. J Neuroendocrinol 2008; 20 (Suppl 1): 116–123.
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff and patients at the 72 clinical sites who participated in the clinical trial (see Supplementary Information). We thank Dr Barry Gumbiner and Dr Bret Musser for their contribution to the design of this study and Dr Kenneth Cheung (Biostatistics, MSPH, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA) for his independent verification of the study results database. We extend our appreciation to the Data Safety and Monitoring Committee members, Drs Julie Buring, Daniel Heijtan, Edward Horton (Chair), Robert Josse and Robert Spitzer. We thank Catherine Phillips of Merck Medical Communications Department for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The study was funded by Merck & Co. The authors IG, NE, SS, CM, SS, JN, AGM, DS, SBH, KDK and JMA are or were employees of Merck & Co., Inc. and may hold stock in that company. LA and ST are members of a Merck Diabetes and Obesity Advisory Committee.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Appendix
Appendix
Study sites
Louis J Aronne, Comprehensive Weight Control Program, New York, NY; Stephen Louis Aronoff, Research Institute of Dallas, Dallas, TX; Harold E Bays, Louisville Metabolic and Atherosclerosis Research Center, Louisville, KY; Robert J Bielski, Summit Research Network, Farmington Hills, MI; Bruce Taylor Bowling, Regional Clinical Research, Inc., Endwell, NY; George August Bray, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA; Cynthia C Brinson, Central Texas Clinical Research, Austin, TX; Mary E Bartz, Central Texas Clinical Research, Austin, TX; Richard O Butcher, Careview Medical Group, Inc., San Diego, CA; Rodney G Hood, Careview Medical Group, Inc., San Diego, CA; Robert S Call, Commonwealth Clinical Research Specialists, Richmond, VA; Antonio Caos, Central Florida Clinical Studies, Ocoee, FL; Christopher M Chappel, FPA Clinical Research, Kissimmee, FL; Harry Collins, Anderson and Collins Clinical Research, Inc., Edison, NJ; Martin J Conway, Lovelace Scientific Resources, Inc., Albuquerque, NM; Michael H Davidson, Radiant Research, Chicago, IL; Mark A Deeg, Richard L Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Indianapolis, IN; Marian Sue Kirkman, Richard L Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Indianapolis, IN; John Howard Pratt, Richard L Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Indianapolis, IN; Eleuterio P Delfin, Jr., Center for Clinical Trials, LLC; Paramount, CA; Samuel S Engel, Soundview Research Associates; Norwalk, CT; Mindy J Sotsky, Soundview Research Associates, Norwalk, CT; James Mecham Ferguson, Radiant Research; Salt Lake City, UT; Fares J Arguello, Radiant Research, Salt Lake City, UT; Harold J Fields, Village Family Practice Clinic, Houston, TX; Chester L Fisher, Jr., Health Research of Hampton Roads; Newport News, VA; Alan Duane Forker, Saint Luke's Hospital, Lipid and Diabetes Research Center, Kansas City, MO; Neil J Fraser, Troy Internal Medicine Research; Troy, MI; Ken Fujioka, Scripps Clinic and Research Foundation; San Diego, CA; Geoffrey S Gladstein, Stamford Therapeutics Consortium, Stamford, CT; David M Radin, Stamford Therapeutics Consortium; Stamford, CT; Forrest Anthony Hanke, Trover Clinic, Madisonville, KY; Lisa M Harris, Chase Wellness Center; Virginia Beach, VA; David R Hassman, Comprehensive Clinical Research, Berlin, NJ; David Keith Helton, Southeastern Clinical Research, Chattanooga, TN; Priscilla L Hollander, Baylor University Medical Center, Baylor Endocrine Center, Dallas, TX; William P Jennings, Radiant Research, San Antonio, TX; Norman J Kakos, QUEST Research Institute, Bingham Farms, MI; Adam D Karns, Lovelace Scientific Resources, Inc., Beverly Hills, CA; Alan J. Kivitz, Altoona Center for Clinical Research, Duncansville, PA; Eric J Klein, Capital Clinical Research Center, Olympia, WA; Samuel Klein, Washington University School of Medicine, Center for Human Nutrition, Saint Louis, MO; Dominic Reeds, Washington University School of Medicine, Center for Human Nutrition, Saint Louis, MO; Diane Rachel Krieger, Miami Research Associates, Inc., Miami, FL; Wayne E Larson, Radiant Research, Lakewood, WA; Frank P Maggiacomo, New England Center for Clinical Research, Cranston, RI; Dennis C McCluskey, Radiant Research, Mogadore, OH; Harris Hugh McIlwain, Tampa Medical Group, Tampa, FL; James McKenney, National Clinical Research, Inc., Richmond, VA; Alan Brad Miller, Atlanta Pharmaceutical Research Center, Inc., Dunwoody, GA; Richard E Mills, Palmetto Medical Research, Mount Pleasant, SC; Leslie Penny Moldauer, Radiant Research, Denver, CO; Arthur J Mollen, Mollen Clinic, Phoenix, AZ; David J Morin, Tri-Cities Medical Research, Bristol, TN; Bryan C Pogue, Radiant Research, Boise, ID; Terry L Poling, Heartland Research Associates, LLC, Wichita, KS; Jane L Rohlf, Premier Research, Trenton, NJ; Domenica Marie Rubino, Weight Management Program, Washington DC; Richard D Wasnich, Covance, Inc., Honolulu, HI; Jon Leslie Ruckle, Covance, Inc., Honolulu, HI; Gary E. Ruoff, Westside Family Medical Center, Kalamazoo, MI; Randall J Severance, Radiant Research, Chandler, AZ; Stephan C Sharp, Clinical Research Associates, Inc., Nashville, TN; Norman G Soler, Springfield Diabetes and Endocrine Center, Springfield, IL; Joseph Soufer, Chase Medical Research, Waterbury, CT; Mark Allen Stich, Jacksonville Center for Clinical Research, Jacksonville, FL; Phillip D Toth, Midwest Institute for Clinical Research, Indianapolis, IN; David J Turk, Madrona Medical Group, Bellingham, WA; Thomas A Wadden, University of Pennsylvania, Weight & Eating Disorder Program, Philadelphia, PA; Mervyn Upali Weerasinghe, Rochester Clinical Research, Inc., Rochester, NY; Frederick C Whittier, Clinical Research Limited, Canton, OH; Michael Paul Wiggins, Big Thompson Medical Group, PC, Loveland, CO; Troy Williams, Pivotal Research Centers, Peoria, AZ; Louise A Taber, Pivotal Research Centers, Peoria, AZ; James H Zavoral, Radiant Research, Edina, MN; Karl-Michael Derwahl, St Hedwig-Krankenhaus, Institut fur Klinische Foschung und Entwicklung GmbH, Berlin, Germany; Hans-Michael Foerster,Grafschafter Str., Baerl/Ndrhn, Germany; Andreas Hamann, Diabetes Klinik Bad Nauheim GmbH, FA fur Innere Medizin, Bad Nauheim, Germany; Alberto Allemant, Hospital Nacional ‘Hipolito Unanue’, Lima, Peru; Cesar Butron Delgado, Centro Endocrionologico, Arequipa, Peru; Luis H Zapata-Rincon, Casa De Diabetes Y Nutricion, Lima, Peru; Soren Toubro, Hvidovre Hospital, Hvidovre, Denmark; Arya Sharma, Hamilton Hospital General Division, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada; Paul F Whitsitt, Paradigm Clinical Trials, Inc., Oshawa, Ontario, Canada; Michelle Tolszczuk, Q et T Recherche Inc., Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada; Ronald Girard, Q et T Recherche Inc., Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada; Markolf Hanefeld, Gesellschaft fur Wissens-und Technologietransfer der TU Dresden GmbH, Zentrum fur Klinische Studien Forschungsbereich Endokrinologie und Stoffwechsel, Dresden, Germany; Peter Kindermann, Internistische Praxis, Riesa, Germany; Peter Marcinowski, H-Arzt Torenstr. Meersburg, Germany; Erik-Delf Schulze, Hauptstr. Berlin, Germany; Thomas Zoeller, Klinische Forschung Berlin, Berlin, Germany; Francis CC Chow, Prince of Wales Hospital, Shatin, Hong Kong; Karen Siu Ling Lam, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong; Eduardo Garcia Garcia, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Medicas y Nutricion Salvador Zubiran, Mexico City, Mexico; Jose Geraldo Gonzalez, Hospital Universitario de Monterrey, Mexico City, Nuevo Leon, Mexico; Bernhard Paulweber, St Johanns-Spital, Landesklinik fur Innere Medizin I, Salzburg, Austria; Hermann Toplak, University of Graz, Medical University Clinic, Ambulanz fur Diabetes und Stoffwechsel, Graz, Austria; Christa Firbas, Allgemeines Krankenhaus (AKH) Wien, Klinische Pharmakologie, Wien, Austria; Gerfried Hans Karl Nell, ClinPharm International GmbH & Co KG, Vienna, Austria; Rudolf Prager, Krankenhaus Lainz, Wein, Austria; Miguel Angel Rubio Herrara, Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain; Xavier Formiguera Sala, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Barcelona, Spain; Olga Gonzalez-Albarran, Hospital Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, Spain; Barbara C Biedermann, Kantonsspital Bruderholz, Bruderholz, Switzerland; Bernhard H Lauterberg, Inselspital, Bern, Switzerland; Roger Darioli, CHUV Policlinique Medicale Universitaire, Lausanne, Switzerland; Alain Golay, Hopitaux Universitaires de Geneve, Division d’Enseignement/Therapeutique pour Maladies Chroniques, Geneva, Switzerland; Jocelyne Rachelle Benatar, Green Lane Hospital, Green Lane Clinical Centre Cardiovascular Research Unit, Auckland, New Zealand; Ajith Munasinghe Dissanayake, Middlemore Hospital, Centre for Clinical Research and Effective Practice, Auckland, New Zealand; Siew Pheng Chan, University Malaya Medical Centre, Jalan University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; Chii-Min Hwu, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan; Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan; Wei-Shiung Yang, National Taiwan University, University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan; Jeff Karrasch, Peninsula Specialist Centre, Kipparing, Queensland, Australia; Robert Moses, Clinical Trials and Research Unit, Wollongong, New South Wales, Australia; Boyd Strauss, Monash Medical Centre, Body Composition Laboratory, Clayton, Victoria, Australia; Joseph Proietto, Austin & Repatriation Medical Centre, Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia; Ian Caterson, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Metabolish & Obesity Research Group, Camperdon, New South Wales, Australia; Milan Kvapil, ResTrial Outpatient Office of Diabetology, Prague, Czech Republic; Vojtech Hainer, Institute of Endocrinology, Prague, Czech Republic; Pavol Hlubik, University of Defence, Faculty of Military Health Sciences, Department of Preventive Medicine, Hradec Kralova, Czech Republic; Gerrit H de Groot, Nederlandse Obesitas Kliniek, Hilversum, Netherlands; Elisabeth M Mathuss-Vliegen, Academisch Medisch Centrum, Amsterdam, Netherlands; Manuel Ignacio Moreno, Av. Portugal, Santiago, Chile; Victor Saavedra, NovAdilap Servicios Medicos Ltda, Santiago, Chile; Verner Codoceo, FACH Hospital, Tratamiento Intermedio Medico (TIM), Santiago, Chile; Aila Marjatta Rissanen, Lihavuustutkimusyksikko, Helsinki, Finland; Markku Savolainen, Oulun Yliopisto, Sairaala Sisatautien Kilinkka, Oulu, Finland; Manuel Borrell Munoz, Centres d’Assistencia Primeria Sarria, Barcelona, Spain; Albert Ledesma-Castelltort, CAP Remei, Barcelona, Spain; Serena Tonstad, Ullevaal Hospital, Ulleval universitetssykehus HF, Oslo, Norway; Hans Olav Hoivik, Hedmark Medisinske Senter AS, Hamar, Norway; Bard Eirik Kulseng, Sankt Olavs Hospital, Trondheim, Norway.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aronne, L., Tonstad, S., Moreno, M. et al. A clinical trial assessing the safety and efficacy of taranabant, a CB1R inverse agonist, in obese and overweight patients: a high-dose study. Int J Obes 34, 919–935 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.21
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.21
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cannabinoids and their derivatives in struggle against melanoma
Pharmacological Reports (2021)
-
Limitations in anti-obesity drug development: the critical role of hunger-promoting neurons
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2012)
-
Assessing Psychiatric Adverse Effects during Clinical Drug Development
Pharmaceutical Medicine (2012)
-
Rimonabant Redux and Strategies to Improve the Future Outlook of CB1 Receptor Neutral‐Antagonist/Inverse‐Agonist Therapies
Obesity (2011)
-
Characterization of a novel, brain-penetrating CB1 receptor inverse agonist: metabolic profile in diet-induced obese models and aspects of central activity
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2011)