Abstract
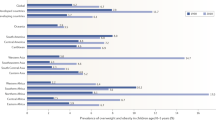
The number of overweight children is increasing rapidly, and there is an urgent need to identify the risk factors for obesity, with a view to preventing further increases in prevalence. Experimental studies in animals and preliminary observations in humans suggest that early experience may influence later risk of obesity, but we do not yet understand the extent to which early influences affect individual vulnerability to risk factors acting later in life. In the developed world, few studies have examined whether current variations in maternal diet have long-term effects on children's body composition. Rapid postnatal growth is associated with greater adiposity, but the role of variations in infant diet and the mechanisms involved are not understood, and there may be interactive effects of early diet and growth rate on body composition. Familial concordance in obesity prevalence suggests that the shared food environment is of key importance. Early life may be a time when dietary practices are established that will continue throughout childhood. Further research is needed to gain insight into the evolution of dietary habits in childhood and to determine how these practices influence obesity risk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R, for IASO International Obesity TaskForce. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obesity Rev 2004; 5 (Suppl 1): 4–85.
Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS . Childhood obesity: public health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 2002; 360: 473–482.
Nader PR, O’Brien M, Houts R, Bradley R, Belsky J, Crosnoe R et al. Identifying risk for obesity in early childhood. Pediatrics 2006; 118: e594–e601.
Lake JK, Power C, Cole TJ . Child to adult body mass index in the 1958 British birth cohort: associations with parental obesity. Arch Dis Child 1997; 77: 376–381.
SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics 2006; 118: 1510–1518.
Wardle J, Cooke L . The impact of obesity on psychological well-being. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 19: 421–440.
Williams J, Wake M, Hesketh K, Maher E, Waters E . Health-related quality of life of overweight and obese children. JAMA 2005; 293: 70–76.
Gortmaker SL, Must A, Perrin JM, Sobol AM, Dietz WH . Social and economic consequences of overweight in adolescence and young adulthood. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 1008–1012.
Sargent JD, Blanchflower DG . Obesity and stature in adolescence and earnings in young adulthood. Analysis of a British birth cohort. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1994; 148: 681–687.
Stunkard AJ, Sorensen TI, Hanis C, Teasdale TW, Chakraborty R, Schull WJ et al. An adoption study of human obesity. N Engl J Med 1986; 314: 193–198.
Koeppen-Schomerus G, Wardle J, Plomin R . A genetic analysis of weight and overweight in 4-year-old twin pairs. Int J Obes Rel Metab Disord 2001; 25: 838–844.
Davey Smith G, Steer C, Leary S, Ness A . Is there an intrauterine influence on obesity? Evidence from parent-child associations in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Arch Dis Child 2007; 92: 876–880.
Davison KK, Birch LL . Childhood overweight: a contextual model and recommendations for future research. Obesity Rev 2001; 2: 159–171.
Bowman SA, Gortmaker SL, Ebbeling CB, Pereira MA, Ludwig DS . Effects of fast-food consumption on energy intake and diet quality among children in a national household survey. Pediatrics 2004; 113: 112–118.
Harnack L, Stang J, Story M . Soft drink consumption among US children and adolescents: nutritional consequences. J Am Diet Assoc 1999; 99: 436–441.
McConahy K, Smiciklas-Wright H, Birch LL, Mitchell DC, Picciano MF . Food portions are positively related to energy intake and body weight in early childhood. J Pediatr 2002; 140: 340–347.
Fisher JO, Birch LL . Eating in the absence of hunger and overweight in girls from 5 to 7 years of age. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 76: 226–231.
Tucker LA, Seljaas GT, Hager RL . Body fat percentage of children varies according to their diet composition. J Am Diet Assoc 1997; 97: 981–986.
Jouret B, Ahluwalia N, Cristini C, Dupuy M, Negre-Pages L, Grandjean H et al. Factors associated with overweight in preschool-age children in southwestern France. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 85: 1643–1649.
Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR, Emmett PM, Ness A, Rogers I, et al., ALSPAC Study Team. Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ 2005; 330: 1357–1363.
Blair NJ, Thompson JM, Black PN, Becroft DM, Clark PM, Han DY et al. Risk factors for obesity in 7-year-old European children: the Auckland Birthweight Collaborative Study. Arch Dis Child 2007; 92: 866–871.
Baird J, Fisher D, Lucas P, Kleijnen J, Roberts H, Law CM . Being big or growing fast: a systematic review of size and growth in infancy and later obesity. BMJ 2005; 331: 929–934.
Godfrey KM, Barker DJP . Fetal programming and adult health. Public Health Nutr 2001; 4: 611–624.
Barker DJP, Forsen T, Uutela A, Osmond C, Eriksson JG . Size at birth and resilience to the effects of poor living conditions in adult life: longitudinal study. BMJ 2001; 323: 1273–1276.
Livingstone MBE . Childhood obesity in Europe: a growing concern. Public Health Nutr 2001; 4: 109–116.
Wardle J . Understanding the aetiology of childhood obesity: implications for treatment. Proc Nutr Soc 2005; 64: 73–79.
Elia M, Betts P, Jackson DM, Mulligan J . Fetal programming of body dimensions and percentage body fat measured in prepubertal children with a 4-component model of body composition, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, deuterium dilution, densitometry, and skinfold thicknesses. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 618–624.
Vickers MH, Breier BH, Cutfield WS, Hofman PL, Gluckman PD . Fetal origins of hyperphagia, obesity and hypertension and postnatal amplification by hypercaloric nutrition. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 279: E83–E87.
Bellinger L, Sculley DV, Langley-Evans SC . Exposure to undernutrition in fetal life determines fat distribution, locomotor activity and food intake in ageing rats. Int J Obes Rel Metab Disord 2006; 30: 729–738.
Bayol SA, Farrington SJ, Stickland NC . A maternal ‘junk food’ diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for ‘junk food’ and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring. Br J Nutr 2007; 98: 843–851.
Khan IY, Dekou V, Douglas G, Jensen R, Hanson MA, Poston L et al. A high-fat diet during rat pregnancy or suckling induces cardiovascular dysfunction in adult offspring. Am J Physiol 2005; 288: R127–R133.
Daenzer M, Ortmann S, Klaus S, Metges CC . Prenatal high protein exposure decreases energy expenditure and increases adiposity in young rats. J Nutr 2002; 132: 142–144.
Vickers MH, Breier BH, McCarthy D, Gluckman PD . Sedentary behaviour during postnatal life is determined by the prenatal environment and exacerbated by postnatal hypercaloric nutrition. Am J Physiol 2003; 285: R271–R273.
Bellinger L, Lilley C, Langley-Evans SC . Prenatal exposure to a maternal low-protein diet programmes a preference for high-fat foods in the young adult rat. Br J Nutr 2004; 92: 513–520.
Vickers MH, Gluckman PD, Coveny AH, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS, Gertler A et al. Neonatal leptin treatment reverses developmental programming. Endocrinology 2005; 146: 4211–4216.
Ravelli AC, van der Meulen JH, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP . Obesity at the age of 50 years in men and women exposed to famine prenatally. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 70: 811–816.
Yajnik CS, Deshpande SS, Jackson AA, Refsum H, Rao S, Fisher DJ et al. Vitamin B12 and folate concentrations during pregnancy and insulin resistance in the offspring: the Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 29–38.
Lawlor DA, Davey Smith G, O’Callaghan M, Alati R, Mamun AA, Williams GM et al. Epidemiologic evidence for the fetal overnutrition hypothesis: findings from the Mater-University study of pregnancy and its outcomes. Am J Epidemiol 2006; 165: 418–424.
Gale CR, Javaid MK, Robinson SM, Law CM, Godfrey KM, Cooper C . Maternal size in pregnancy and body composition in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 3904–3911.
Catalano PM, Ehrenberg HM . The short- and long-term implications of maternal obesity on the mother and her offspring. BJOG 2006; 113: 1126–1133.
Hillier TA, Pedula KL, Schmidt MM, Mullen JA, Charles MA, Pettitt DJ . Childhood obesity and metabolic imprinting. The ongoing effects of maternal hyperglycemia. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 2287–2292.
Scholl TO, Chen X, Khoo CS, Lenders C . The dietary glycemic index during pregnancy: influence on infant birth weight, fetal growth, and biomarkers of carbohydrate metabolism. Am J Epidemiol 2004; 159: 467–474.
Moses RG, Luebcke M, Davis WS, Coleman KJ, Tapsell LC, Petocz P et al. Effect of a low-glycemic-index diet during pregnancy on obstetric outcomes. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 84: 807–812.
Moses RG, Luebcke M, Petocz P, Brand-Miller JC . Maternal diet and infant size 2y after the completion of a low-glycemic-index diet in pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 1806.
Robinson S, Crozier SR, Borland SE, Hammond J, Barker DJP, Inskip HM . Impact of educational attainment on the quality of young women's diets. Eur J Clin Nutr 2004; 58: 1174–1180.
Khoury J, Henriksen T, Christophersen B, Tonstad S . Effect of a cholesterol-lowering diet on maternal, cord, and neonatal lipids, and pregnancy outcome: a randomised clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005; 193: 1292–1301.
Kinnunen TI, Pasanen M, Aittasalo M, Fogelholm M, Hilakivi-Clarke L, Weiderpass E et al. Preventing excessive weight gain during pregnancy—a controlled trial in primary health care. Eur J Clin Nutr 2007; 61: 884–891.
McCance RA . Food, growth and time. Lancet 1962; 2: 671–676.
Plagemann A . Perinatal programming and functional teratogenesis: impact on body weight regulation and obesity. Physiol Behav 2005; 86: 661–668.
Thompson NM, Norman AM, Donkin SS, Shankar RR, Vickers MH, Miles JL et al. Prenatal and postnatal pathways to obesity: different underlying mechanisms, different metabolic outcomes. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 2345–2354.
Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH, Davey Smith G, Gillman MW, Cook DG . The effect of breastfeeding on mean body mass index throughout life: a quantitative review of published and unpublished observational evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 1298–1307.
Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH, Davey Smith G, Cook DG . Effect of infant feeding on the risk of obesity across the life course: a quantitative review of published evidence. Pediatrics 2005; 115: 1367–1377.
Arenz S, Ruckerl R, Koletzko B, von Kries R . Breast-feeding and childhood obesity—a systematic review. Int J Obes Rel Metab Disord 2004; 28: 1247–1256.
Harder T, Bergmann R, Kallischnigg G, Plagemann A . Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 2005; 162: 397–403.
Baker JL, Michaelsen KF, Sorensen TI, Rasmussen KM . High prepregnant body mass index is associated with early termination of full and any breastfeeding in Danish women. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 404–411.
Toschke AM, Martin RM, von Kries R, Wells J, Davey Smith G, Ness AR . Infant feeding method and obesity: body mass index and dual X-ray absorptiometry measurements at 9–10 years of age from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 85: 1578–1585.
Kramer MS, Guo T, Platt RW, Vanilovich I, Sevkovskaya Z, Dzikovich I et al. Feeding effects on growth during infancy. J Pediatr 2004; 145: 600–605.
Singhal A, Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A . Early nutrition and leptin concentrations in later life. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: 993–999.
Hamosh M . Bioactive factors in human milk. Pediatr Clin North Am 2001; 48: 69–86.
Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Akrout M, Bellisle F . Influence of macronutrients on adiposity development: a follow up study of nutrition and growth from 10 months to 8 years of age. Int J Obes Rel Metab Disord 1995; 19: 573–578.
Stettler N, Zemel BS, Kumanyika S, Stallings VA . Infant weight gain and childhood overweight status in a multicenter cohort study. Pediatrics 2002; 109: 194–199.
Karaolis-Danckert N, Gunther AL, Kroke A, Hornberg C, Buyken AE . How early dietary factors modify the effect of rapid weight gain in infancy on subsequent body composition development in term children whose birth weight was appropriate for gestational age. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 1700–1708.
Noble S, Emmett P . Differences in weaning practice, food and nutrient intake between breast- and formula-fed 4-month-old infants in England. J Hum Nutr Diet 2006; 19: 303–313.
Scaglioni S, Agostoni C, De Notaris R, Radaelli G, Radice N, Valenti M et al. Early macronutrient intake and overweight at five years of age. Int J Obes Rel Metab Disord 2000; 24: 777–781.
Gunther AL, Remer T, Kroke A, Buyken AE . Early protein intake and later obesity risk: which protein sources at which time points throughout infancy and childhood are important for body mass index and body fat percentage at 7 years of age? Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 1765–1772.
Wilson AC, Forsyth JS, Greene SA, Irvine L, Hau C, Howie PW . Relation of infant diet to childhood health: seven year follow up of cohort of children in Dundee infant feeding survey. BMJ 1998; 316: 21–25.
Oliveria SA, Ellison RC, Moore LL, Gillman MW, Garrahie EJ, Singer MR . Parent-child relationships in nutrient intake: the Framingham Children's Study. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 56: 593–598.
Robinson S, Marriott L, Poole J, Crozier S, Borland S, Lawrence W, et al., SWS Study Group. Dietary patterns in infancy: the importance of maternal and family influences on feeding practice. Br J Nutr 2007; 98: 1029–1037.
Northstone K, Emmett P, ALSPAC Study Team. Multivariate analysis of diet in children at four and seven years of age and associations with socio-demographic characteristics. Eur J Clin Nutr 2005; 59: 751–760.
Foresight. Project Report. Tackling Obesities: Future Choices. Government Office for Science 2007. (http://www.foresight.gov.uk/Obesity/17.pdf).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
SM Robinson has declared no financial interests. KM Godfrey has received grant support from TANITA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, S., Godfrey, K. Feeding practices in pregnancy and infancy: relationship with the development of overweight and obesity in childhood. Int J Obes 32 (Suppl 6), S4–S10 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.201
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.201
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Early childhood body mass index trajectory and overweight/obesity risk differed by maternal weight status
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2022)
-
Developmental overnutrition and obesity and type 2 diabetes in offspring
Diabetologia (2019)
-
Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2018)
-
Catch-up growth following intra-uterine growth-restriction programmes an insulin-resistant phenotype in adipose tissue
International Journal of Obesity (2013)
-
The relationship between breastfeeding and weight status in a national sample of Australian children and adolescents
BMC Public Health (2012)