Abstract
Objective:
It has been proposed that the success of maintained weight loss in morbidly obese subjects following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGBP) surgery depends on inappropriately low circulating concentrations of the appetite-stimulating peptide ghrelin, being unresponsive to food intake. In this study, this hypothesis was examined.
Design:
Cross-sectional study with repeated blood samples in 40 subjects after 14 h of prolonged overnight fasting followed by a standardized mixed meal (770 kcal).
Subjects:
Twenty men and 20 women were included: 10 middle-aged morbidly obese (body mass index (BMI) 43.9±3.3 kg/m2), 10 middle-aged subjects who had undergone RYGBP at the Uppsala University Hospital (BMI 34.7±5.8 kg/m2), 10 middle-aged non-obese (BMI 23.5±2.2 kg/m2) and 10 young non-obese (BMI 22.7±1.8 kg/m2).
Measurements:
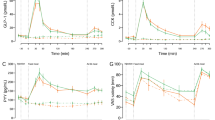
Ghrelin, glucose and insulin levels were analysed pre- and postprandially.
Results:
In the morbidly obese, ghrelin concentrations were lower in the morning than in the RYGBP group and did not change following the meal. In the RYGBP group, fasting ghrelin levels fell after meal intake and showed similar suppression as both age-matched and young non-obese controls. The RYGBP surgery resulted in an increased meal-induced insulin secretion, which was related to the degree of postprandial ghrelin suppression.
Conclusion:
The present study demonstrates low circulating concentrations of ghrelin and blunted responses to fast and feeding in morbidly obese subjects. Marked weight reduction after RYGBP at our hospital is followed by a normalization of ghrelin secretion, illustrated by increased fasting levels compared to the preoperative obese state and regain of meal-induced ghrelin suppression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K . Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999; 402: 656–660.
Arvat E, Di Vito L, Broglio F, Papotti M, Muccioli G, Dieguez C . Preliminary evidence that ghrelin, the natural GH secretagogue (GHS)-receptor ligand, strongly stimulates GH secretion in humans. J Endocrinol Invest 2000; 23: 493–495.
Takaya K, Ariyasu H, Kanamoto N, Iwakura H, Yoshimoto A, Harada M et al. Ghrelin strongly stimulates growth hormone (GH) release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 4908–4911.
Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K et al. Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes 2001; 50: 227–232.
Tschöp M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML . Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000; 407: 908–913.
Wren AM, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Brynes AE, Frost GS, Murphy KG et al. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 5992–5995.
Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni A, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML . Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 2001; 50: 707–709.
Rigamonti AE, Pincelli AI, Corrà B, Viarengo R, Bonomo SM, Galimberti D et al. Plasma ghrelin concentrations in elderly subjects: comparison with anorexic and obese patients. J Endocrinol 2002; 175: R1–R5.
Tanaka M, Naruo T, Muranaga T, Yasuhara D, Shiiya T, Nakazato M et al. Increased fasting plasma ghrelin levels in patients with bulimia nervosa. Eur J Endocrinol 2002; 146: R1–R3.
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS . A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1714–1719.
Tschöp M, Wawarta R, Riepl RL, Friedrich S, Bidlingmaier M, Landgraf R et al. Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J Endocrinol Invest 2001; 24: RC19–RC21.
English PJ, Ghatei MA, Malik IA, Bloom SR, Wilding JPH . Food fails to suppress levels in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 2984–2987.
Morpurgo PS, Resnik M, Agosti F, Cappiello V, Sartorio V, Spada A . Ghrelin secretion in severely obese subjects before and after a 3-week integrated body mass reduction program. J Endocrinol Invest 2003; 26: 723–727.
Le Roux CW, Pattersson M, Vincent RP, Hunt C, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR . Postprandial plasma ghrelin is suppressed proportional to meal calorie content in normal-weight but not obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 90: 1068–1071.
Sjöström L . Surgical intervention as a strategy for treatment of obesity. Endocrine 2000; 13: 213–230.
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, Breen PA, Ma MK, Dellinger EP et al. Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1623–1630.
Leonetti F, Silecchia G, Iacobellis G, Ribauso MC, Zappaterreno A, Tiberti C et al. Different plasma ghrelin levels after laparoscopic gastric bypass and adjustable gastric banding in morbid obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4227–4231.
Tritos N, Mun E, Bertkau A, Grayson R, Maratos-Flier E, Goldfine A . Serum ghrelin levels in response to glucose load in obese subjects post-gastric bypass surgery. Obes Res 2003; 11: 919–924.
Geloneze B, Tambascia MA, Pilla VF, Geloneze SR, Repetto EM, Pareja JC . Ghrelin: a gut–brain hormone: effect of gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg 2003; 13: 17–22.
Frühbeck G, Rotellar F, Hernàndes-Lizoain JL, Gil MJ, Ǵmez-Ambrosi J, Salvador J et al. Fasting plasma ghrelin concentrations 6 months after gastric bypass are not determined by weight loss or changes in insulinemia. Obes Surg 2004; 14: 1208–1215.
Stoeckli R, Chanda R, Langer I, Keller U . Changes of body weight and plasma ghrelin levels after gastric banding and gastric bypass. Obes Res 2004; 12: 346–350.
Holdstock C, Edén Engström B, Öhrvall M, Lind L, Sundbom M, Karlsson FA . Ghrelin and adipose tissue regulatory peptides: effect of gastric bypass surgery in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 3177–3183.
Faraj M, Havel PJ, Phélis S, Blank D, Sniderman AD, Cianflone K . Plasma acylation-stimulating protein, adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin before and after weight loss induced by gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1594–1602.
Cummings DE, Shannon MH . Ghrelin and gastric bypass: is there a hormonal contribution to surgical weight loss? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 2999–3002.
Lee HM, Wang G, Englander EW, Kojima M, Greeley GH . Ghrelin, a new gastrointestinal endocrine peptide that stimulates insulin secretion: enteric distribution, ontogeny, influence of endocrine, and dietary manipulations. Endocrinology 2002; 143: 185–190.
Maier C, Shcaller G, Buranyi B, Nowotny P, Geyer G, Wolzt M et al. The cholinergic system controls ghrelin release and ghrelin-induced growth hormone release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 4729–4733.
Le Roux CW, Neary NM, Halsey TJ, Small CJ, Martinez-Isla AM, Ghatei MA et al. Ghrelin does not stimulate food intake in patients with surgical procedures involving vagotomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 4521–4524.
Sundbom M, Gustavsson S . Randomised clinical trial of hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for the treatment of morbid obesity. Br J Surg 2004; 91: 418–423.
Janssen JA, van der Toorn FM, Hofland LJ, van Koetsveld P, Broglio F, Ghigo E et al. Systemic ghrelin levels in subjects with growth hormone deficiency are not modified by one year of growth hormone replacement therapy. Eur J Endocrinol 2001; 145: 711–716.
Morinigo R, Casamitjana R, Moize V, Lacy AM, Delgado S, Gomis R et al. Short-term effects of gastric bypass surgery on circulating ghrelin levels. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1108–1116.
Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, Conwell IM, Daud A, Restuccia NL et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 359–365.
Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE . Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2608–2615.
Saad MF, Bernaba B, Hwu CM, Jinagouda S, Fahmi S, Kogosov E et al. Insulin regulates plasma ghrelin concentration. J Clin Endcorinol Metab 2002; 87: 3997–4000.
Flanagan DE, Evans ML, Monson TP, Rife F, Heptulla RA, Tamborlane WV et al. The influence of insulin on circulating ghrelin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: 313–316.
Lucidi P, Murdolo G, Di Loreto C, De Cicco A, Parlanti N, Fanelli C et al. Ghrelin is not necessary for adequate hormonal counterregulation of insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2911–2914.
Purnell JQ, Weigle DS, Breen P, Cummings DE . Ghrelin levels correlate with insulin levels, insulin resistance, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but not with gender, menopausal status, or cortisol levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 5747–5752.
Callahan HS, Cummings DE, Pepe MS, Breen PA, Matthys CC, Weigle DS . Postprandial suppression of plasma ghrelin level is proportional to ingested caloric load but does not predict intermeal interval in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1319–1324.
Erdmann J, Töpsch R, Lippl F, Gussmann P, Schusdziarra V . Postprandial response of plasma ghrelin levels to various test meals in relation to food intake, plasma insulin, and glucose. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 3048–3054.
Acknowledgements
We thank Margareta Ericson for expert laboratory assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engström, B., Öhrvall, M., Sundbom, M. et al. Meal suppression of circulating ghrelin is normalized in obese individuals following gastric bypass surgery. Int J Obes 31, 476–480 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803440
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803440
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Efficacy of liraglutide 3.0 mg treatment on weight loss in patients with weight regain after bariatric surgery
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2022)
-
Improved acylated ghrelin suppression at 2 years in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: effects of bariatric surgery vs standard medical therapy
International Journal of Obesity (2014)
-
Gut hormones, early dumping and resting energy expenditure in patients with good and poor weight loss response after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
International Journal of Obesity (2013)
-
Weight Recidivism Post-Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review
Obesity Surgery (2013)
-
Effects of Laparoscopic Gastric Band Applications on Plasma and Fundic Acylated Ghrelin Levels in Morbidly Obese Patients
Obesity Surgery (2012)